In the previous chapters we have presented the concepts to model the business, application, and technology layers of an enterprise. However, a central issue in enterprise architecture is business-IT alignment: how can these layers be matched? In this chapter, we describe the relationships that the ArchiMate language offers to model the link between business, applications, and technology.
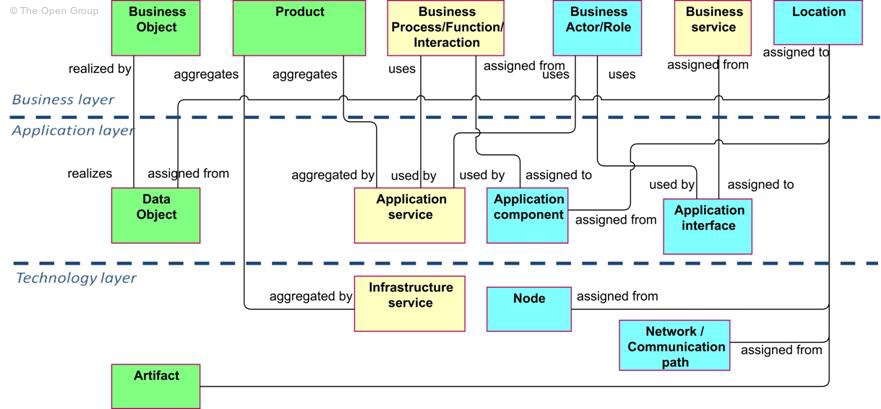
Figure 44 shows the relationships between the business layer, the application layer, and the technology layer concepts. There are three main types of relationships between these layers:
1. Used by relationships, between application service and the different types of business behavior elements, and between application interface and business role. These relationships represent the behavioral and structural aspects of the support of the business by applications.
2. A realization relationship from a data object to a business object, to indicate that the data object is a digital representation of the corresponding business object.
3. Assignment relationships, between application component and business process, function, or interaction, and between application interface and business service, to indicate that, for example, business processes or business services are completely automated. The case that a business process, function, or interaction is not completely automated but only supported by an application component is expressed with a “used by” relationship (see, e.g., the example of an Application Usage Viewpoint in Section 8.4.11).
In addition, there may be an aggregation relationship between a product and an application or infrastructure service, to indicate that the application or infrastructure service can be offered directly to a customer as part of the product. Also, a location may be assigned to all active and passive structural elements (and, indirectly, behavior elements) in the application and technology layers.

Figure 44: Relationships between Business Layer and Lower Layer Concepts
Note:����� This figure does not show all permitted relationships: there are indirect relationships that can be derived as explained in Section 7.5.
Figure 45 shows the relationships between application layer and technology layer concepts. There are two types of relationships between these layers:
1. Used by relationships, between infrastructure service and the different types of application behavior elements, and between infrastructure interface and application component. These relationships represent the behavioral and structural aspects of the use of technical infrastructure by applications.
2. A realization relationship from artifact to data object, to indicate that the data object is realized by, for example, a physical data file, and from artifact to application component, to indicate that a physical data file is an executable that realizes an application or part of an application. (Note: In this case, an artifact represents a “physical” component that is deployed on a node; this is modeled with an assignment relationship. A (logical) application component is realized by an artifact and, indirectly, by the node on which the artifact is deployed.)
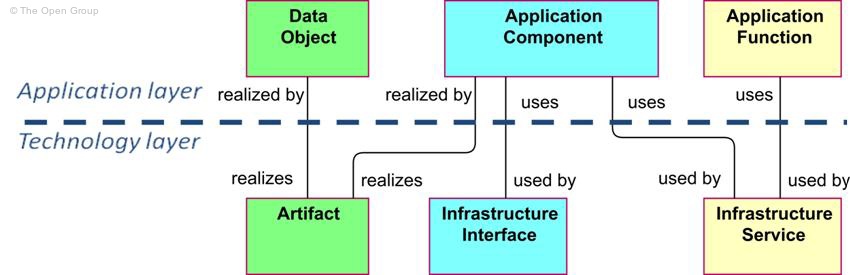
Figure 45: Relationships between Application Layer and Technology Layer Concepts
Note:����� This figure does not show all permitted relationships: there are indirect relationships that can be derived as explained in Section 7.5.
Due to the derived relationships that are explained in Section 7.5, it is also possible to draw relationships directly between the business and technology layers. For example, if a business object is realized by a data object, which in turn is realized by an artifact, this artifact indirectly realizes the business object.
Downloads of the ArchiMate documentation, are available under license from the ArchiMate information web site. The license is free to any organization wishing to use ArchiMate entirely for internal purposes (for example, to develop an information system architecture for use within that organization). A book is also available (in hardcopy and pdf) from The Open Group Bookstore as document C13L.