| You are here: | ||
| <<< Previous | Home | Next >>> |
The TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM) provides a process lifecycle to create and manage architectures within an enterprise. At each phase within the ADM, a discussion of inputs, outputs, and steps describes a number of architectural work products or artifacts, such as process and application. The content metamodel provided here defines a formal structure for these terms to ensure consistency within the ADM and also to provide guidance for organizations that wish to implement their architecture within an architecture tool.
This section provides an overview of the objectives of the content metamodel, the concepts that support the metamodel, and an overview of the metamodel itself. Subsequent sections then go on to discuss each area of the metamodel in more detail. Contents of this section are as follows:
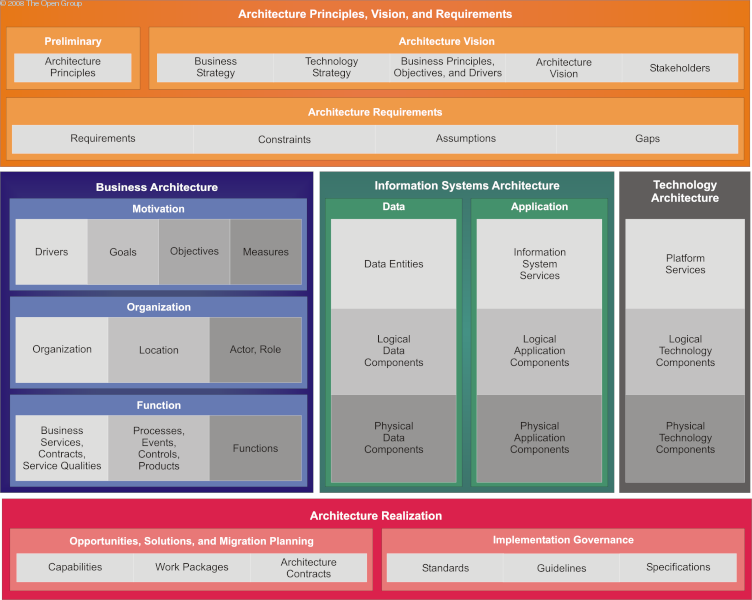
A TOGAF architecture is based on defining a number of architectural building blocks within architecture catalogs, specifying the relationships between those building blocks in architecture matrices, and then presenting communication diagrams that show in a precise and concise way what the architecture is.
This section introduces the core concepts that make up the TOGAF content metamodel, through the following subsections:
The role of TOGAF is to provide an open standard for architecture that is applicable in many scenarios and situations. In order to meet this vision, it is necessary to provide a fully featured enterprise architecture metamodel for content and also to provide the ability to avoid carrying out unnecessary activities by supporting tailoring.
The metamodel must provide a basic model with the minimum feature set and then support the inclusion of optional extensions during engagement tailoring.
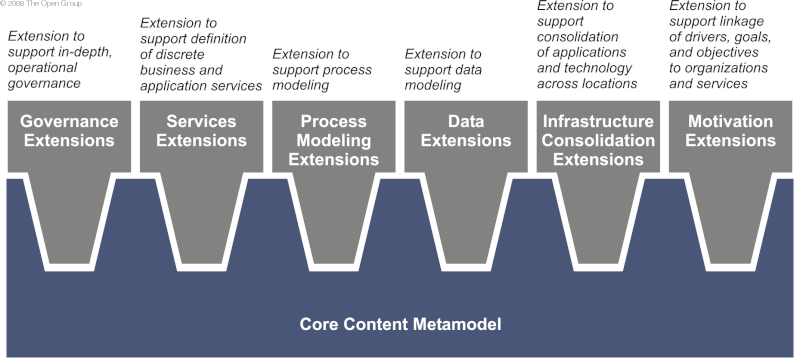
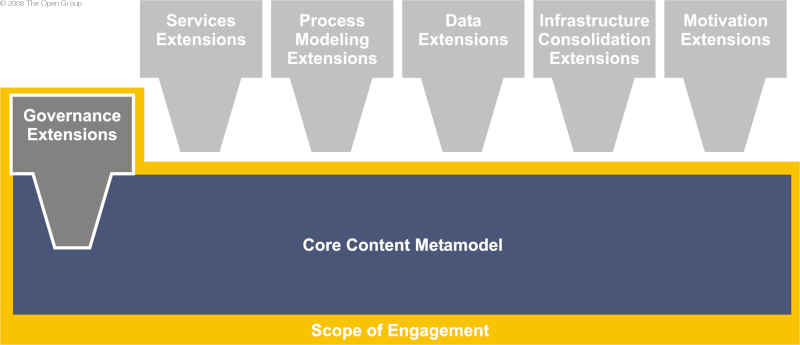
The core TOGAF content metamodel and its extensions are illustrated in TOGAF Content Metamodel and its Extensions .

The core metamodel provides a minimum set of architectural content to support traceability across artifacts. Additional metamodel concepts to support more specific or more in-depth modeling are contained within a group of extensions that logically cluster extension catalogs, matrices, and diagrams, allowing focus in areas of specific interest and focus.
All extension modules are optional and should be selected during the Preliminary phase of the architecture development to meet the needs of the organization. Additionally, the extension groupings described by the content metamodel are only a suggestion and further tailoring may be carried out to suit the specific needs at the discretion of the architects.
This core and extension concept is intended as a move towards supporting formal method extension approaches within TOGAF, such as the method plug-in concept found within the Software Process Engineering Metamodel (SPEM) developed by the Object Management Group (OMG).1
The content metamodel uses the terminology discussed within the TOGAF ADM as the basis for a formal metamodel. The following core terms are used:
A more in-depth definition of terms used within the content metamodel can be found in Part I, 3. Definitions .
Some of the key relationship concepts related to the core metamodel entities are described below:
A process is a flow of interactions between functions and services and cannot be physically deployed. All processes should describe the flow of execution for a function and therefore the deployment of a process is through the function it supports; i.e., an application implements a function that has a process, not an application implements a process.
The term "function" is used to describe a unit of business capability at all levels of granularity, encapsulating terms such as value chain, process area, capability, business function, etc. Any bounded unit of business function should be described as a function.
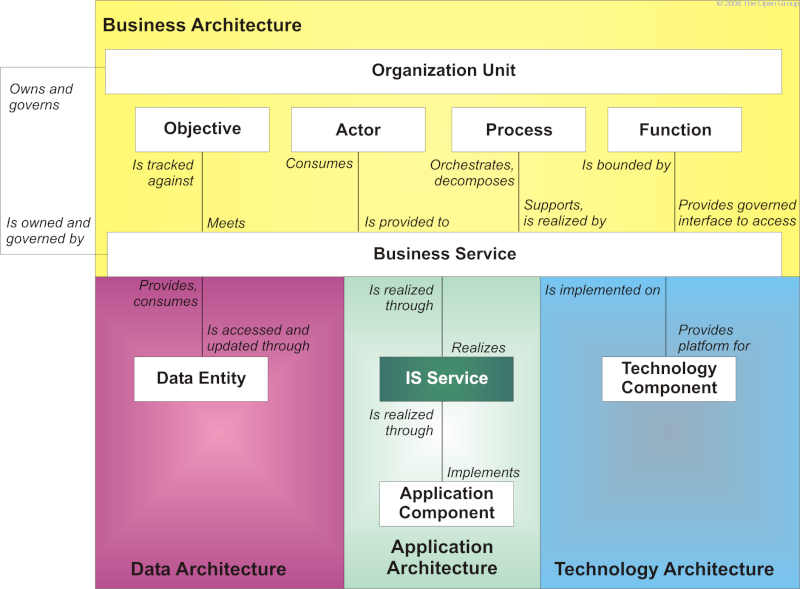
A business service operates as a boundary for one or more functions. The granularity of business services is dependent on the focus and emphasis of the business (as reflected by its drivers, goals, and objectives). A service in Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) terminology (i.e., a deployable unit of application functionality) is actually much closer to an application service, application component, or technology component, which may implement or support a business service.
Business services may be realized by business activity that does not relate to IT, or may be supported by IT. Business services that are supported by IT are deployed onto application components. Application components can be hierarchically decomposed and may support one or more business services. It is possible for a business service to be supported by multiple application components, but this is problematic from a governance standpoint and is symptomatic of business services that are too coarse-grained, or application components that are too fine-grained.
An application component is implemented by a suite of technology components. For example, an application, such as "HR System" would typically be implemented on several technology components, including hardware, application server software, and application services.
Core Entities and their Relationships illustrates the core entities and their relationships.
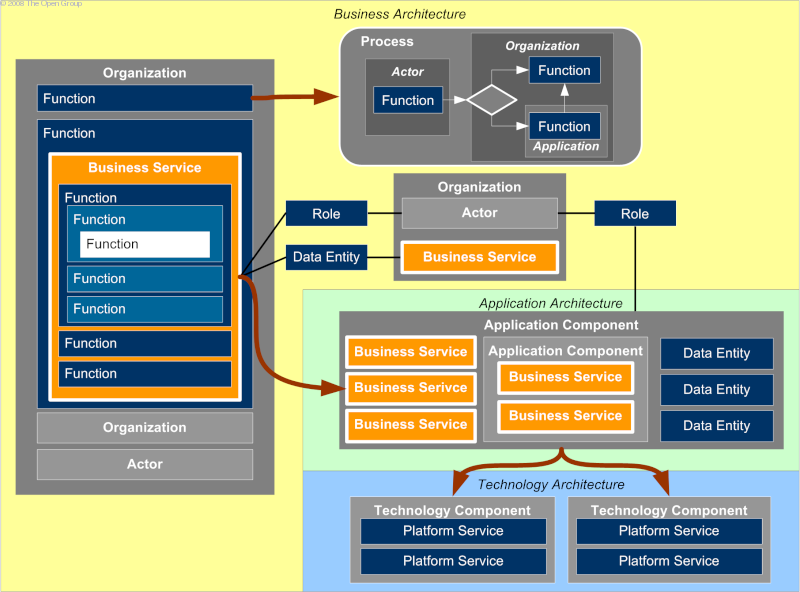
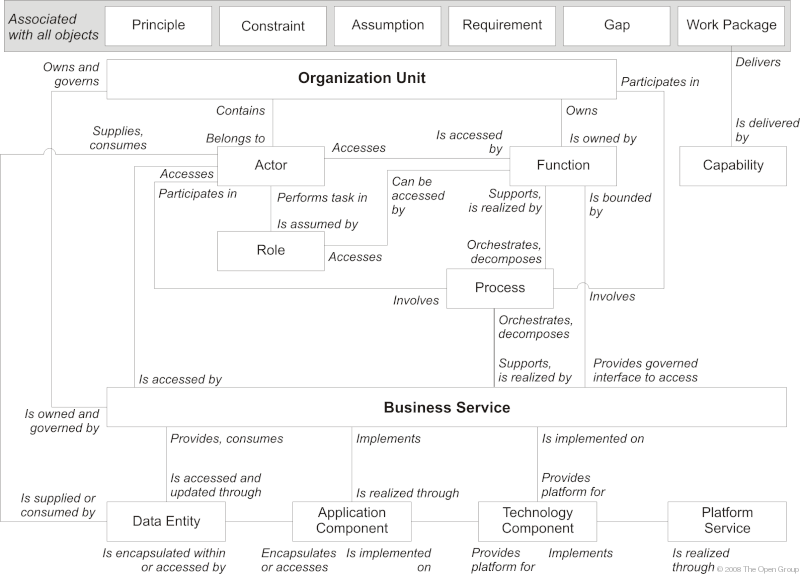
The content metamodel is used as a technique to structure architectural information in an ordered way so that it can be processed to meet the stakeholder needs. The majority of architecture stakeholders do not actually need to know what the architecture metamodel is and are only concerned with specific issues, such as "what functionality does this application support?", "which processes will be impacted by this project?", etc. In order to meet the needs of these stakeholders, the TOGAF concepts of building blocks, catalogs, matrices, and diagrams are used.
Building blocks are objects of a particular type within the metamodel (for example, a business service called "Purchase Order"). Building blocks carry metadata according to the metamodel, which supports query and analysis. For example, business services have a metadata attribute for owner, which allows a stakeholder to query all business services owned by a particular organization. Building blocks may also include dependent or contained objects as appropriate to the context of the architecture (for example, a business service called "Purchase Order" may implicitly include a number of processes, data entities, application components, etc).
Catalogs are lists of building blocks of a specific type, or of related types, that are used for governance or reference purposes (for example, an organization chart, showing locations and actors). As with building blocks, catalogs carry metadata according to the metamodel, which supports query and analysis.
Matrices are grids that show relationships between two or more model entities. Matrices are used to represent relationships that are list-based rather than graphical in their usage (for example, a CRUD matrix showing which applications Create, Read, Update, and Delete a particular type of data is difficult to represent visually).
Diagrams are renderings of architectural content in a graphical format to allow stakeholders to retrieve the required information. Diagrams can also be used as a technique for graphically populating architecture content or for checking the completeness of information that has been collected. TOGAF defines a set of architecture diagrams to be created (e.g., organization chart). Each of these diagrams may be created several times for an architecture with different style or content coverage to suit stakeholder concerns.
Building blocks, catalogs, matrices, and diagrams are all concepts that are well supported by leading enterprise architecture tools. In environments where tools are used to model the architecture, such tools typically support mechanisms to search, filter, and query the Architecture Repository.
On-demand querying of the Architecture Repository (such as the business service ownership example mentioned above) can be used to generate ad hoc catalogs, matrices, and diagrams of the architecture. As this type of query is by nature required to be flexible, it is therefore not restricted or defined within the content metamodel.
The interactions between metamodel, building blocks, diagrams, and stakeholders are shown in Interactions between Metamodel, Building Blocks, Diagrams, and Stakeholders .
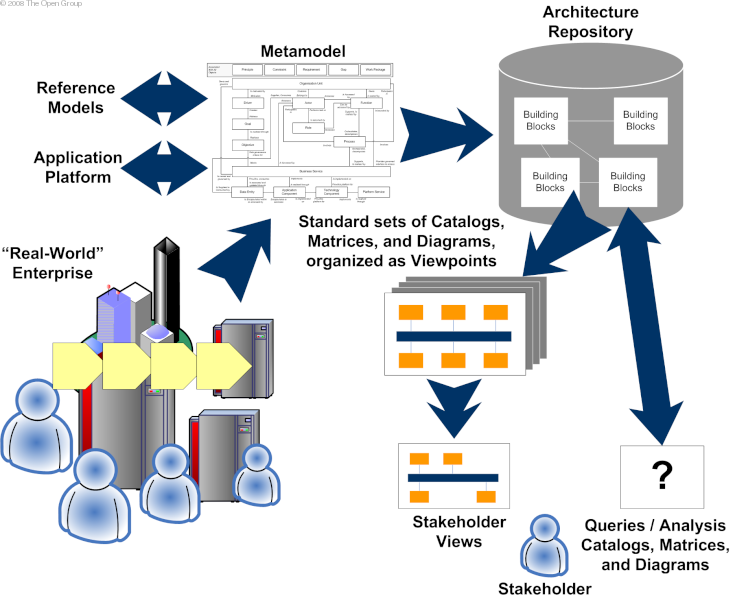
The content metamodel defines a set of entities that allow architectural concepts to be captured, stored, filtered, queried, and represented in a way that supports consistency, completeness, and traceability.
At the highest level, the content framework is divided up in line with the TOGAF ADM phases, as shown in Content Framework by ADM Phases .
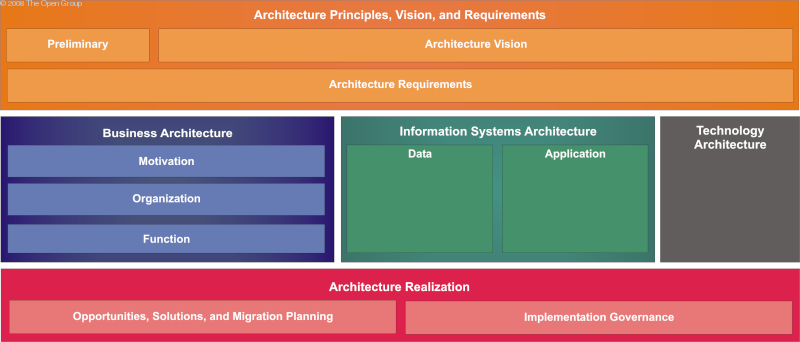
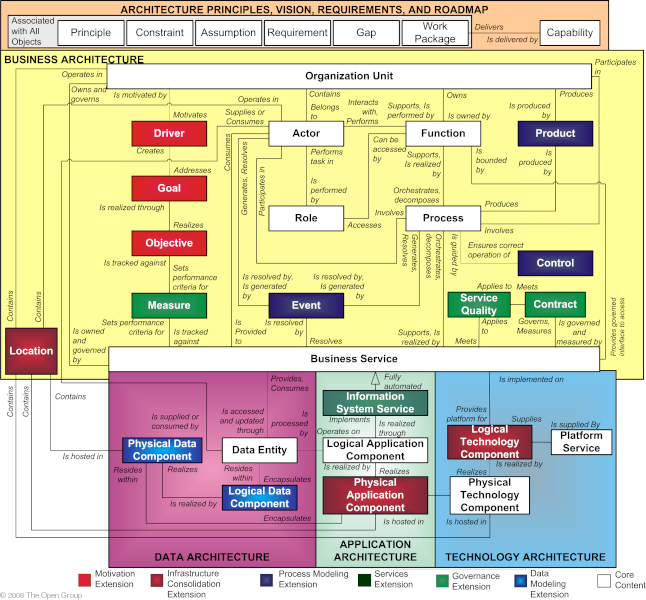
A more detailed representation of the content metamodel is shown in Detailed Representation of the Content Metamodel .
This section contains the following subsections:
Entities and Relationships Present within the Core Content Metamodel shows the metamodel entities and relationships that are present within the core content metamodel.
35. Architectural Artifacts discusses in detail the way in which the underlying content metamodel can be used to present a set of catalogs, matrices, and diagrams to address stakeholder concerns.
The following set of artifacts are intended to accompany the core content metamodel:
|
ADM Phase |
Artifacts |
|---|---|
|
Preliminary |
Principles Catalog |
|
Architecture Vision |
Stakeholder Map Matrix |
|
|
Value Chain Diagram |
|
|
Solution Concept Diagram |
|
Business Architecture |
Organization/Actor Catalog |
|
|
Role Catalog |
|
|
Business Service/Function Catalog |
|
|
Business Interaction Matrix |
|
|
Actor/Role Matrix |
|
|
Business Footprint Diagram |
|
|
Business Service/Information Diagram |
|
|
Functional Decomposition Diagram |
|
|
Product Lifecycle Diagram |
|
Information Systems |
Data Entity/Data Component Catalog |
|
(Data Architecture) |
Data Entity/Business Function Matrix |
|
|
System/Data Matrix |
|
|
Class Diagram |
|
|
Data Dissemination Diagram |
|
Information Systems |
Application Portfolio Catalog |
|
(Application Architecture) |
Interface Catalog |
|
|
System/Organization Matrix |
|
|
Role/System Matrix |
|
|
System/Function Matrix |
|
|
Application Interaction Matrix |
|
|
Application Communication Diagram |
|
|
Application and User Location Diagram |
|
|
System Use-Case Diagram |
|
Technology Architecture |
Technology Standards Catalog |
|
|
Technology Portfolio Catalog |
|
|
System/Technology Matrix |
|
|
Environments and Locations Diagram |
|
|
Platform Decomposition Diagram |
|
Opportunities and Solutions |
Project Context Diagram |
|
|
Benefits Diagram |
|
Requirements Management |
Requirements Catalog |
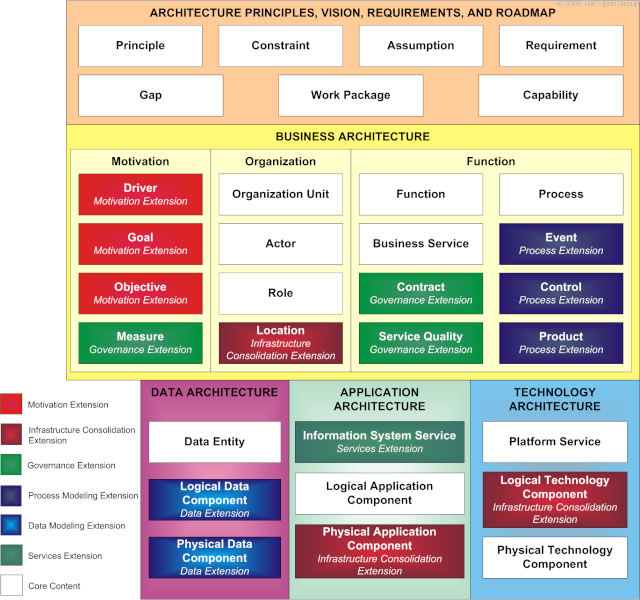
When all extensions are applied to the core content metamodel, a number of new metamodel entities are introduced. Content Metamodel with Extensions shows which entities are contained in the core content metamodel and which new entities are introduced by which extension.
The relationships between entities in the full metamodel are shown in Relationships between Entities in the Full Metamodel .
As discussed earlier, the TOGAF content metamodel supports a number of extension modules that allow more in-depth consideration for particular architecture concerns. Core Content Metamodel and Predefined Extension Modules shows the core content metamodel and predefined extension modules.

During the Architecture Vision phase of a particular engagement, the scope of the engagement will be used to make a determination on appropriate extensions to be employed in order to adequately address the architecture requirements. For example, the scope of an engagement could be defined as core content, plus the governance extensions, as shown in Core Content with Governance Extensions .
The following sections provide a more detailed description of the purpose and content of each of the extension modules.
The governance extension is intended to allow additional structured data to be held against objectives and business services, supporting operational governance of the landscape.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
In addition to the extensions described here, organizations wishing to focus on architecture governance should also consult:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Governance Extensions: Changes to Metamodel .
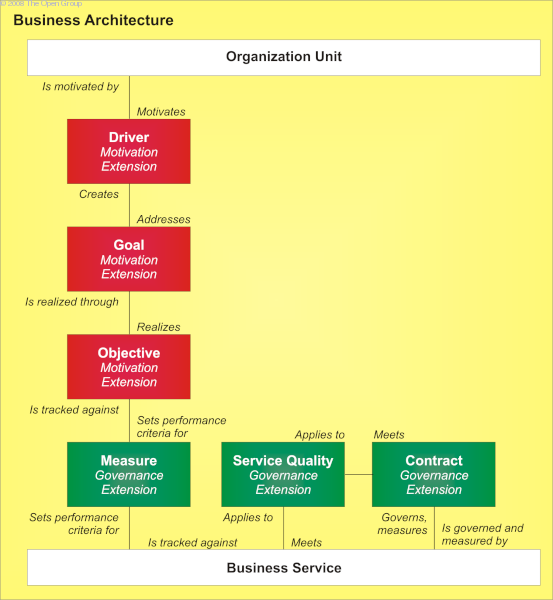
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The services extension is intended to allow more sophisticated modeling of the service portfolio by creating a concept of IS services in addition to the core concept of business services. IS services are directly supported by applications and creating the layer of abstraction relaxes the constraints on business services whilst simultaneously allowing technical stakeholders to put more formality into an IS service catalog.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
In addition to the extensions described here, organizations wishing to focus on services-centric architectures should also consult:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Services Extension: Changes to Metamodel .
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The process modeling extension is intended to allow detailed modeling of process flows by adding events, products, and controls to the metamodel. Typically, enterprise architecture does not drill into process flow, but in certain process-centric or event-centric organizations it may be necessary to elaborate process in a much more formal manner using this extension module.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
In addition to the extensions described here, organizations wishing to focus on process-centric architectures should also consult:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Process Modeling Extensions: Changes to Metamodel .
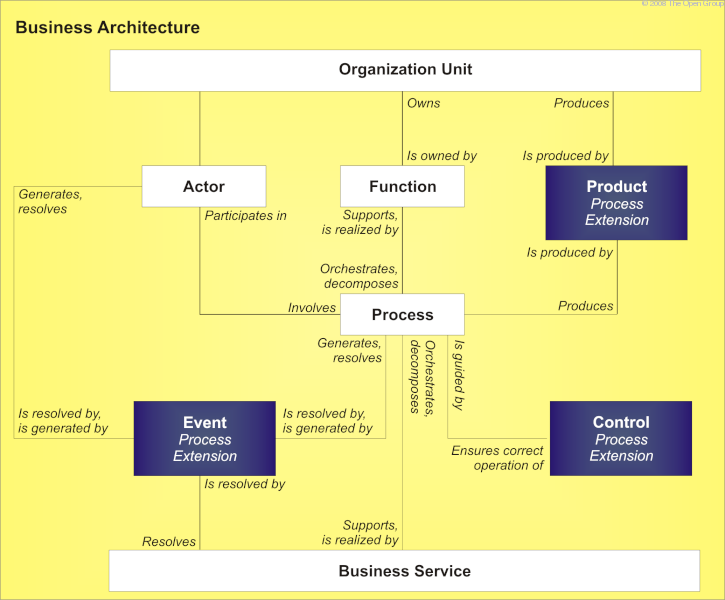
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The data extension is intended to allow more sophisticated modeling and the encapsulation of data. The core model provides a data entity concept which supports the creation of data models, which is then extended by this extension to include the concept of a data component. Data components form a logical or physical encapsulation of abstract data entities into units that can be governed and deployed into applications.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Data Extensions: Changes to Metamodel .
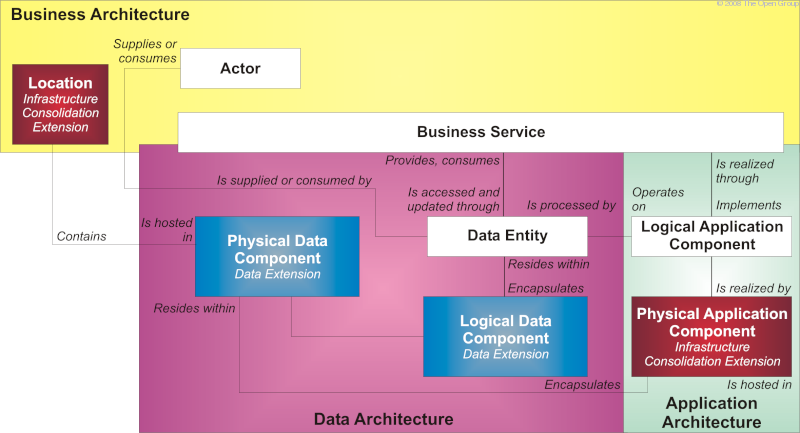
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The infrastructure consolidation extension is intended to be used in landscapes where the application and technology portfolios have become fragmented and the architecture seeks to consolidate the business as usual capability into a smaller number of locations, applications, or technology components.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
In addition to the extensions described here, organizations wishing to focus on infrastructure consolidation should also consult:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Infrastructure Consolidation Extensions: Changes to Metamodel .
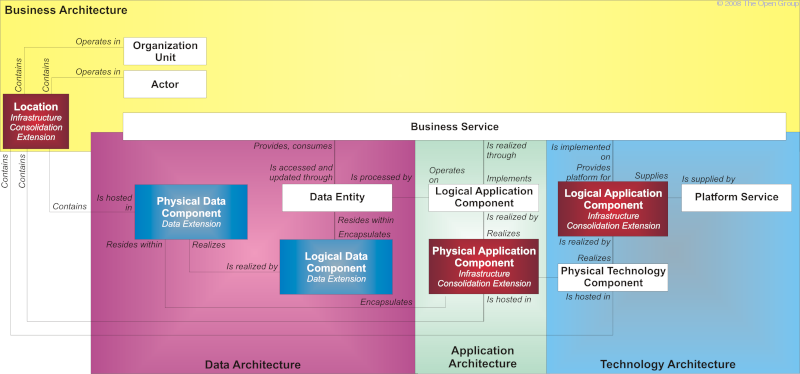
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The motivation extension is intended to allow additional structured modeling of the drivers, goals, and objectives that influence an organization to provide business services to its customers. This in turn allows more effective definition of service contracts and better measurement of business performance.
The scope of this extension is as follows:
This extension should be used in the following situations:
The benefits of using this extension are as follows:
In addition to the extensions described here, organizations wishing to focus on architecture modeling of business motivation should also consult:
Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are shown in Motivation Extensions: Changes to Metamodel .

Changes to the metamodel entities and relationships are as follows:
Changes to the metamodel attributes are as follows:
Additional diagrams to be created are as follows:
The following table lists and describes the objects within the content metamodel.
|
Metamodel Object |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Actor |
A person, organization, or system that has a role that initiates or interacts with activities; for example, a sales representative who travels to visit customers. Actors may be internal or external to an organization. In the automotive industry, an original equipment manufacturer would be considered an actor by an automotive dealership that interacts with its supply chain activities. |
|
Application Component |
An encapsulation of application functionality aligned to implementation structure. For example, a purchase request processing application. See also Logical Application Component and Physical Application Component. |
|
Assumption |
A statement of probable fact that has not been fully validated at this stage, due to external constraints. For example, it may be assumed that an existing application will support a certain set of functional requirements, although those requirements may not yet have been individually validated. |
|
Business Service |
Supports business capabilities through an explicitly defined interface and is explicitly governed by an organization. |
|
Capability |
A business-focused outcome that is delivered by the completion of one or more work packages. Using a capability-based planning approach, change activities can be sequenced and grouped in order to provide continuous and incremental business value. |
|
Constraint |
An external factor that prevents an organization from pursuing particular approaches to meet its goals. For example, customer data is not harmonized within the organization, regionally or nationally, constraining the organization's ability to offer effective customer service. |
|
Contract |
An agreement between a service consumer and a service provider that establishes functional and non-functional parameters for interaction. |
|
Control |
A decision-making step with accompanying decision logic used to determine execution approach for a process or to ensure that a process complies with governance criteria. For example, a sign-off control on the purchase request processing process that checks whether the total value of the request is within the sign-off limits of the requester, or whether it needs escalating to higher authority. |
|
Data Entity |
An encapsulation of data that is recognized by a business domain expert as a thing. Logical data entities can be tied to applications, repositories, and services and may be structured according to implementation considerations. |
|
Driver |
An external or internal condition that motivates the organization to define its goals. An example of an external driver is a change in regulation or compliance rules which, for example, require changes to the way an organization operates; i.e., Sarbanes-Oxley in the US. |
|
Event |
An organizational state change that triggers processing events; may originate from inside or outside the organization and may be resolved inside or outside the organization. |
|
Function |
Delivers business capabilities closely aligned to an organization, but not necessarily explicitly governed by the organization. Also referred to as "business function". |
|
Gap |
A statement of difference between two states. Used in the context of gap analysis, where the difference between the
Baseline and Target Architecture is identified.
|
|
Goal |
A high-level statement of intent or direction for an organization. Typically used to measure success of an organization. |
|
Information System |
The automated elements of a business service. An information system service may deliver or support part or all of one or more business services. |
|
Location |
A place where business activity takes place and can be hierarchically decomposed. |
|
Logical Application |
An encapsulation of application functionality that is independent of a particular implementation. For example, the classification of all purchase request processing applications implemented in an enterprise. |
|
Logical Data |
A boundary zone that encapsulates related data entities to form a logical location to be held; for example, external procurement information. |
|
Logical Technology |
An encapsulation of technology infrastructure that is independent of a particular product. A class of technology product; for example, supply chain management software as part of an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) suite, or a Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) purchase request processing enterprise service. |
|
Measure |
An indicator or factor that can be tracked, usually on an ongoing basis, to determine success or alignment with objectives and goals. |
|
Objective |
A time-bounded milestone for an organization used to demonstrate progress towards a goal; for example, "Increase capacity utilization by 30% by the end of 2009 to support the planned increase in market share". |
|
Organization Unit |
A self-contained unit of resources with line management responsibility, goals, objectives, and measures. Organizations may include external parties and business partner organizations. |
|
Physical Application |
An application, application module, application service, or other deployable component of functionality. For example, a configured and deployed instance of a Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) supply chain management application. |
|
Physical Data |
A boundary zone that encapsulates related data entities to form a physical location to be held. For example, a purchase order business object, comprising purchase order header and item business object nodes. |
|
Physical Technology |
A specific technology infrastructure product or technology infrastructure product instance. For example, a particular product version of a Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) solution, or a specific brand and version of server. |
|
Platform Service |
A technical capability required to provide enabling infrastructure that supports the delivery of applications. |
|
Principle |
A qualitative statement of intent that should be met by the architecture. Has at least a supporting rationale and a
measure of importance.
|
|
Process |
A process represents flow of control between or within functions and/or services (depends on the granularity of definition). Processes represent a sequence of activities that together achieve a specified outcome, can be decomposed into sub-processes, and can show operation of a function or service (at next level of detail). Processes may also be used to link or compose organizations, functions, services, and processes. |
|
Product |
Output generated by the business. The business product of the execution of a process. |
|
Requirement |
A quantitative statement of business need that must be met by a particular architecture or work package. |
|
Role |
The usual or expected function of an actor, or the part somebody or something plays in a particular action or event. An actor may have a number of roles. See also Actor. |
|
Service |
An element of behavior that provides specific functionality in response to requests from actors or other services. A service delivers or supports business capabilities, has an explicitly defined interface, and is explicitly governed. Services are defined for business, information systems, and platforms. |
|
Service Quality |
A preset configuration of non-functional attributes that may be assigned to a service or service contract. |
|
Technology Component |
An encapsulation of technology infrastructure that represents a class of technology product or specific technology product. |
|
Work Package |
A set of actions identified to achieve one or more objectives for the business. A work package can be a part of a project, a complete project, or a program. |
The following table shows typical attributes for each of the metamodel objects described previously.
|
Metamodel Object |
Metamodel Attribute |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
All Metamodel Objects |
ID |
Unique identifier for the architecture object. |
|
|
Name |
Brief name of the architecture object. |
|
|
Description |
Textual description of the architecture object. |
|
|
Category |
User-definable categorization taxonomy for each metamodel object. |
|
|
Source |
Location from where the information was collected. |
|
|
Owner |
Owner of the architecture object. |
|
Capability |
Business value |
Describes how this capability provides value to the enterprise. |
|
|
Increments |
Lists possible maturity/quality levels for the capability. |
|
Constraint |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Gap |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Location |
Category |
The following categories of Location apply: Region (applies to a grouping of countries or territory; e.g., South East Asia, UK, and Ireland), Country (applies to a single country; e.g., US), and Building (applies to a site of operation; where several offices are collected in a single city, this category may represent a city), Specific Location (applies to any specific location within a building, such as a server room). |
|
Principle |
Category |
The following categories of principle apply: Guiding Principle, Business Principle, Data Principle, Application Principle, Integration Principle, Technology Principle. |
|
|
Priority |
Priority of this principle relative to other principles. |
|
|
Statement of principle |
Statement of what the principle is. |
|
|
Rationale |
Statement of why the principle is required and the outcome to be reached. |
|
|
Implication |
Statement of what the principle means in practical terms. |
|
|
Metric |
Identifies mechanisms that will be used to measure whether the principle has been met or not. |
|
Requirement |
Statement of requirement |
Statement of what the requirement is, including a definition of whether the requirement shall be met, should be met, or may be met. |
|
|
Rationale |
Statement of why the requirement exists. |
|
|
Acceptance criteria |
Statement of what tests will be carried out to ensure that the requirement will be met. |
|
Actor |
# FTEs |
Estimated number of FTEs that operate as this Actor. |
|
|
Actor goal |
Objectives that this actor has, in general terms. |
|
|
Actor tasks |
Tasks that this actor performs, in general terms. |
|
Business Service |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Contract |
Behavior characteristics |
Functional behavior to be supported within the scope of the contract. |
|
|
Service name "caller" |
Consuming service. |
|
|
Service name "called" |
Providing service. |
|
|
Service quality characteristics |
Non-functional behavior to be supported within the scope of the contract |
|
|
Availability characteristics |
Degree to which something is available for use. |
|
|
Service times |
Hours during which the service must be available. |
|
|
Manageability characteristics |
Ability to gather information about the state of something and control it. |
|
|
Serviceability characteristics |
Ability to identify problems and take corrective action, such as to repair or upgrade a component in a running system. |
|
|
Performance characteristics |
Ability of a component to perform its tasks in an appropriate time. |
|
|
Response requirements |
Response times that the service provider must meet for particular operations. |
|
|
Reliability characteristics |
Resistance to failure. |
|
|
Quality of information required |
Contracted requirements on accuracy and completeness of information. |
|
|
Contract control requirements |
Level of governance and enforcement applied to the contractual parameters for overall service. |
|
|
Result control requirements |
Measures in place to ensure that each service request meets contracted criteria. |
|
|
Recoverability characteristics |
Ability to restore a system to a working state after an interruption. |
|
|
Locatability characteristics |
Ability of a system to be found when needed. |
|
|
Security characteristics |
Ability of a system to prevent unauthorized access to functions and data. |
|
|
Privacy characteristics |
Protection of data from unauthorized access. |
|
|
Integrity characteristics |
Ability of a system to ensure that data has not been corrupted. |
|
|
Credibility characteristics |
Ability of a system to ensure that the service request originates from an authorized source. |
|
|
Localization characteristics |
Ability of a service to support localized variants for different consumer groups. |
|
|
Internationalization characteristics |
Ability of a service to support international variations in business logic and data representation (such as character set). |
|
|
Interoperability characteristics |
Ability of the service to interoperate with different technical environments, inside and outside of the organization. |
|
|
Scalability characteristics |
Ability of the service to grow or shrink its performance or capacity appropriately to the demands of the environment in which it operates. |
|
|
Portability characteristics |
Of data, people, applications, and components. |
|
|
Extensibility characteristics |
Ability to accept new functionality. |
|
|
Capacity characteristics |
Contracted capacity of the service provider to meet requests. |
|
|
Throughput |
Required throughput capacity. |
|
|
Throughput period |
Time period needed to deliver throughput capacity. |
|
|
Growth |
Expected future growth rate of service request. |
|
|
Growth period |
Time period needed to reach the expected growth rate. |
|
|
Peak profile short term |
Short-term profile of peak service traffic. |
|
|
Peak profile long term |
Long-term profile of peak service traffic. |
|
Control |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Driver |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Event |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Function |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Goal |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Measure |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Objective |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Organization Unit |
Headcount |
Number of FTEs working within the organization. |
|
Process |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
|
Process criticality |
Criticality of this process to business operations. |
|
|
Manual or automated |
Whether this process is supported by IT or is a manual process. |
|
|
Process volumetrics |
Data on frequency of process execution. |
|
Product |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Role |
Estimated number of FTEs that operate in this Role |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Service Quality |
No additional attributes |
This metamodel object has only basic attributes. |
|
Service |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Application Component |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Information System |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Logical Application |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Physical Application |
Lifecycle status |
Proposed, In Development, Live, Phasing Out, Retired. |
|
|
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
|
Initial live date |
Date when the first release of the application was/will be released into production. |
|
|
Date of last release |
Date when the last release of the application was released into production. |
|
|
Date of next release |
Date when the next release of the application will be released into production. |
|
|
Retirement date |
Date when the application was/will be retired. |
|
|
Availability characteristics |
Degree to which something is available for use. |
|
|
Service times |
Hours during which the application must be available. |
|
|
Manageability characteristics |
Ability to gather information about the state of something and control it. |
|
|
Serviceability characteristics |
Ability to identify problems and take corrective action, such as to repair or upgrade a component in a running system. |
|
|
Performance characteristics |
Ability of a component to perform its tasks in an appropriate time. |
|
|
Reliability characteristics |
Resistance to failure. |
|
|
Recoverability characteristics |
Ability to restore a system to a working state after an interruption. |
|
|
Locatability characteristics |
Ability of a system to be found when needed. |
|
|
Security characteristics |
Ability of a system to prevent unauthorized access to functions and data. |
|
|
Privacy characteristics |
Protection of data from unauthorized access. |
|
|
Integrity characteristics |
Ability of a system to ensure that data has not been corrupted. |
|
|
Credibility characteristics |
Ability of a system to ensure that the service request originates from an authorized source. |
|
|
Localization characteristics |
Ability of a service to support localized variants for different consumer groups. |
|
|
Internationalization characteristics |
Ability of a service to support international variations in business logic and data representation (such as character set). |
|
|
Interoperability characteristics |
Ability of the service to interoperate with different technical environments, inside and outside of the organization. |
|
|
Scalability characteristics |
Ability of the service to grow or shrink its performance or capacity appropriately to the demands of the environment in which it operates. |
|
|
Portability characteristics |
Of data, people, applications, and components. |
|
|
Extensibility characteristics |
Ability to accept new functionality. |
|
|
Capacity characteristics |
Contracted capacity of the service provider to meet requests. |
|
|
Throughput |
Required throughput capacity. |
|
|
Throughput period |
Time period needed to deliver throughput capacity. |
|
|
Growth |
Expected future growth rate of service request. |
|
|
Growth period |
Time period needed to reach the expected growth rate. |
|
|
Peak profile short term |
Short-term profile of peak service traffic. |
|
|
Peak profile long term |
Long-term profile of peak service traffic. |
|
Data Entity |
Category |
The following categories of data entity apply: Message, Internally Stored Entity. |
|
|
Privacy classification |
Level of restriction placed on access to the data. |
|
|
Retention classification |
Level of retention to be placed on the data. |
|
Logical Data |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Physical Data |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
Logical Technology |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
|
Category |
Logical Technology Components are categorized according to the TOGAF TRM, which may be extended to meet the needs of an individual organization. |
|
Physical Technology |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Standard creation date |
If the product is a standard, when the standard was created. |
|
|
Last standard review date |
Last date that the standard was reviewed. |
|
|
Next standard review date |
Next date for the standard to be reviewed. |
|
|
Retire date |
Date when the standard was/will be retired. |
|
|
Category |
Physical Technology Components are categorized according to the TOGAF TRM, which may be extended to meet the needs of an individual organization. |
|
|
Product name |
Name of the product making up the technology component. |
|
|
Module name |
Module, or other sub-product, name making up the technology component. |
|
|
Vendor |
Vendor providing the technology component. |
|
|
Version |
Version of the product making up the technology component. |
|
Platform Service |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
|
Category |
Platform Services are categorized according to the TOGAF TRM, which may be extended to meet the needs of an individual organization. |
|
Technology Component |
Standards class |
Non-Standard, Proposed Standard, Provisional Standard, Standard, Phasing-Out Standard, Retired Standard. |
|
Work Package |
Category |
The following categories of work package apply: Work Package, Work Stream, Project, Program, Portfolio. |
|
|
Capability delivered |
Describes the contribution this work package makes to capability delivery. |
|
Source Object |
Target Object |
Name |
Extension Module |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Actor |
Event |
Generates |
Process |
|
Actor |
Event |
Resolves |
Process |
|
Actor |
Function |
Interacts with |
Core |
|
Actor |
Function |
Performs |
Core |
|
Actor |
Location |
Operates in |
Infrastructure |
|
Actor |
Organization Unit |
Belongs to |
Core |
|
Actor |
Process |
Participates in |
Core |
|
Actor |
Role |
Performs task in |
Core |
|
Actor |
Service |
Consumes |
Core |
|
Actor |
Actor |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Actor |
Data Entity |
Supplies/Consumes |
Core |
|
Capability |
Work Package |
Is delivered by |
Core |
|
Contract |
Service |
Governs and Measures |
Governance |
|
Contract |
Service Quality |
Meets |
Governance |
|
Control |
Process |
Ensures correct operation of |
Process |
|
Data Entity |
Logical Application |
Is processed by |
Core |
|
Data Entity |
Logical Data |
Resides within |
Data |
|
Data Entity |
Service |
Is accessed and updated through |
Core |
|
Data Entity |
Data Entity |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Data Entity |
Data Entity |
Relates to |
Core |
|
Driver |
Goal |
Creates |
Motivation |
|
Driver |
Organization Unit |
Motivates |
Motivation |
|
Driver |
Driver |
Decomposes |
Motivation |
|
Event |
Actor |
Is resolved by |
Process |
|
Event |
Actor |
Is generated by |
Process |
|
Event |
Process |
Is resolved by |
Process |
|
Event |
Process |
Is generated by |
Process |
|
Event |
Service |
Is resolved by |
Process |
|
Function |
Actor |
Supports |
Core |
|
Function |
Actor |
Is performed by |
Core |
|
Function |
Organization Unit |
Is owned by |
Core |
|
Function |
Process |
Supports |
Core |
|
Function |
Process |
Is realized by |
Core |
|
Function |
Role |
Can be accessed by |
Core |
|
Function |
Service |
Is bounded by |
Core |
|
Function |
Function |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Function |
Function |
Communicates with |
Core |
|
Goal |
Driver |
Addresses |
Motivation |
|
Goal |
Objective |
Is realized through |
Motivation |
|
Goal |
Goal |
Decomposes |
Motivation |
|
Location |
Actor |
Contains |
Infrastructure |
|
Location |
Organization Unit |
Contains |
Infrastructure |
|
Location |
Physical Application |
Contains |
Infrastructure |
|
Location |
Physical Data Component |
Contains |
Infrastructure |
|
Location |
Physical Technology |
Contains |
Infrastructure |
|
Location |
Location |
Decomposes |
Infrastructure |
|
Logical Application |
Data Entity |
Operates on |
Core |
|
Logical Application |
Physical Application |
Is extended by |
Infrastructure |
|
Logical Application |
Service |
Implements |
Core |
|
Logical Application |
Logical Application |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Logical Application |
Logical Application |
Communicates with |
Core |
|
Logical Data |
Data Entity |
Encapsulates |
Data |
|
Logical Data |
Physical Data Component |
Is extended by |
Data |
|
Logical Technology |
Physical Technology |
Is extended by |
Infrastructure |
|
Logical Technology |
Platform Service |
Supplies |
Core |
|
Logical Technology |
Service |
Provides platform for |
Core |
|
Logical Technology |
Logical Technology |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Logical Technology |
Logical Technology |
Is dependent on |
Core |
|
Measure |
Objective |
Sets performance criteria for |
Governance |
|
Measure |
Service |
Sets performance criteria for |
Governance |
|
Measure |
Measure |
Decomposes |
Governance |
|
Objective |
Goal |
Realizes |
Motivation |
|
Objective |
Measure |
Is tracked against |
Governance |
|
Objective |
Objective |
Decomposes |
Motivation |
|
Organization Unit |
Actor |
Contains |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Driver |
Is motivated by |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Function |
Owns |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Location |
Operates in |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Product |
Produces |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Service |
Owns and Governs |
Core |
|
Organization Unit |
Organization Unit |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Physical Application |
Location |
Is hosted in |
Infrastructure |
|
Physical Application |
Logical Application |
Extends |
Infrastructure |
|
Physical Application |
Physical Data |
Encapsulates |
Data Modeling |
|
Physical Application |
Physical Technology |
Is realized by |
Core |
|
Physical Application |
Physical Application |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Physical Application |
Physical Application |
Communicates with |
Core |
|
Physical Data |
Location |
Is hosted in |
Infrastructure |
|
Physical Data |
Logical Data |
Extends |
Data |
|
Physical Data |
Physical Data |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Physical Data |
Physical Application |
Encapsulates |
Data Modeling |
|
Physical Technology |
Location |
Is hosted in |
Infrastructure Consolidation |
|
Physical Technology |
Physical Application |
Realizes |
Core |
|
Physical Technology |
Logical Technology |
Extends |
Infrastructure |
|
Physical Technology |
Physical Technology |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Physical Technology |
Physical Technology |
Is dependent on |
Core |
|
Platform Service |
Logical Technology |
Is supplied by |
Core |
|
Process |
Actor |
Involves |
Core |
|
Process |
Control |
Is guided by |
Process |
|
Process |
Event |
Generates |
Process |
|
Process |
Event |
Resolves |
Process |
|
Process |
Function |
Orchestrates |
Core |
|
Process |
Function |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Process |
Product |
Produces |
Process |
|
Process |
Service |
Orchestrates |
Core |
|
Process |
Service |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Process |
Process |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Process |
Process |
Precedes/Follows |
Core |
|
Product |
Organization Unit |
Is produced by |
Process |
|
Product |
Process |
Is produced by |
Process |
|
Role |
Actor |
Is performed by |
Core |
|
Role |
Function |
Accesses |
Core |
|
Role |
Role |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Service |
Actor |
Is provided to |
Core |
|
Service |
Contract |
Is governed and measured by |
Governance |
|
Service |
Data Entity |
Provides |
Core |
|
Service |
Data Entity |
Consumes |
Core |
|
Service |
Event |
Resolves |
Process |
|
Service |
Function |
Provides governed interface to access |
Core |
|
Service |
Logical Application |
Is realized through |
Core |
|
Service |
Logical Technology |
Is implemented on |
Core |
|
Service |
Measure |
Is tracked against |
Governance |
|
Service |
Organization Unit |
Is owned and governed by |
Core |
|
Service |
Process |
Supports |
Core |
|
Service |
Process |
Is realized by |
Core |
|
Service |
Service Quality |
Meets |
Governance |
|
Service |
Service |
Consumes |
Core |
|
Service |
Service |
Decomposes |
Core |
|
Service Quality |
Contract |
Applies to |
Governance |
|
Service Quality |
Service |
Applies to |
Governance |
|
Work Package |
Capability |
Delivers |
Core |
The TOGAF document set is designed for use with frames. To navigate around the document:
Downloads of the TOGAF documentation, are available under license from the TOGAF information web site. The license is free to any organization wishing to use TOGAF entirely for internal purposes (for example, to develop an information system architecture for use within that organization). A book is also available (in hardcopy and pdf) from The Open Group Bookstore as document G091.