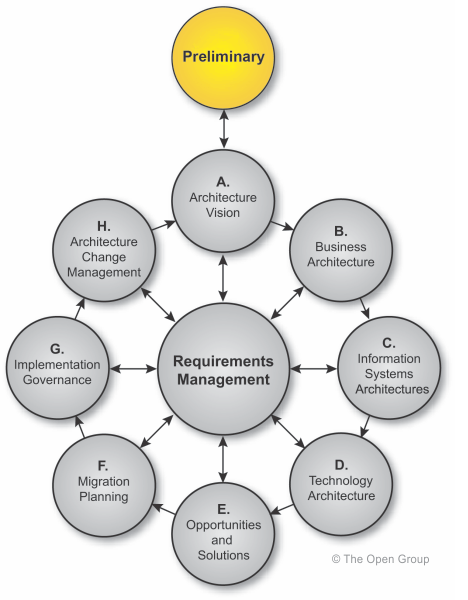
| You are here: | ||
| <<< Previous | Home | Next >>> |
This chapter describes the preparation and initiation activities required to meet the business directive for a new enterprise architecture, including the definition of an Organization-Specific Architecture framework and the definition of principles.

The objectives of the Preliminary Phase are:
This Preliminary Phase is about defining "where, what, why, who, and how we do architecture" in the enterprise concerned. The main aspects are as follows:
The enterprise architecture provides a strategic, top-down view of an organization to enable executives, planners, architects, and engineers to coherently co-ordinate, integrate, and conduct their activities. The enterprise architecture framework provides the strategic context for this team to operate within.
Therefore, developing the enterprise architecture is not a solitary activity and the enterprise architects need to recognize the interoperability between their frameworks and the rest of the business.
Strategic, interim, and tactical business objectives and aspirations need to be met. Similarly, the enterprise architecture needs to reflect this requirement and allow for operation of architecture discipline at different levels within the organization.
Depending on the scale of the enterprise and the level of budgetary commitment to enterprise architecture discipline, a number of approaches may be adopted to sub-divide or partition architecture teams, processes, and deliverables. Approaches for architecture partitioning are discussed in Part V, 40. Architecture Partitioning. The Preliminary Phase should be used to determine the desired approach to partitioning and to establish the groundwork for the selected approach to be put into practice.
The Preliminary Phase may be revisited, from the Architecture Vision phase (see Part III, 19. Applying Iteration to the ADM), in order to ensure that the organization's Architecture Capability is suitable to address a specific architecture problem.
One of the main challenges of enterprise architecture is that of enterprise scope.
The scope of the enterprise, and whether it is federated, will determine those stakeholders who will derive most benefit from the enterprise Architecture Capability. It is imperative that a sponsor is appointed at this stage to ensure that the resultant activity has resources to proceed and the clear support of the business management. The enterprise may encompass many organizations and the duties of the sponsor are to ensure that all stakeholders are included in defining, establishing, and using the Architecture Capability.
In order to make effective and informed decisions about the framework for architecture to be used within a particular enterprise, it is necessary to understand the context surrounding the architecture framework. Specific areas to consider would include:
Review of the organizational context should provide valuable requirements on how to tailor the architecture framework in terms of:
The business imperatives behind the enterprise architecture work drive the requirements and performance metrics for the architecture work. They should be sufficiently clear so that this phase may scope the business outcomes and resource requirements, and define the outline enterprise business information requirements and associated strategies of the enterprise architecture work to be done. For example, these may include:
Significant elements of these need to be articulated so that the sponsor can identify all the key decision-makers and stakeholders involved in defining and establishing an Architecture Capability.
The Preliminary Phase defines the Architecture Principles that will form part of the constraints on any architecture work undertaken in the enterprise. The issues involved in this are explained in Part III, 23. Architecture Principles.
The definition of Architecture Principles is fundamental to the development of an enterprise architecture. Architecture work is informed by business principles as well as Architecture Principles. The Architecture Principles themselves are also normally based in part on business principles. Defining business principles normally lies outside the scope of the architecture function. However, depending on how such principles are defined and promulgated within the enterprise, it may be possible for the set of Architecture Principles to also restate, or cross-refer to a set of business principles, business goals, and strategic business drivers defined elsewhere within the enterprise. Within an architecture project, the architect will normally need to ensure that the definitions of these business principles, goals, and strategic drivers are current, and to clarify any areas of ambiguity.
The issue of architecture governance is closely linked to that of Architecture Principles. The body responsible for governance will also normally be responsible for approving the Architecture Principles, and for resolving architecture issues. The issues involved in governance are explained in Part VII, 50. Architecture Governance.
The TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM) is a generic method, intended to be used by enterprises in a wide variety of industry types and geographies. It is also designed for use with a wide variety of other enterprise architecture frameworks, if required (although it can be used perfectly well in its own right, without adaptation).
TOGAF has to co-exist with and enhance the operational capabilities of other management frameworks that are present within any organization either formally or informally. In addition to these frameworks, most organizations have a method for the development of solutions, most of which have an IT component. The significance of systems is that it brings together the various domains (also known as People, Processes, and Material/Technology) to deliver a business capability.
The main frameworks suggested to be co-ordinated with TOGAF are:
As illustrated in Figure 6-2, these frameworks are not discrete and there are significant overlaps between them and the Business Capability Management. The latter includes the delivery of performance measured business value.
The overall significance is that the enterprise architect applying TOGAF cannot narrowly focus on the IT implementation, but must be aware of the impact that the architecture has on the entire enterprise.
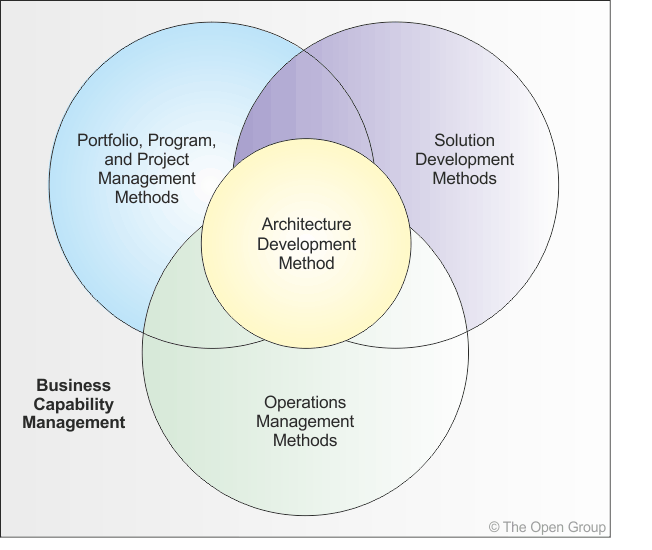
The Preliminary Phase therefore involves doing any necessary work to adapt the ADM to define an organization-specific framework, using either the TOGAF deliverables or the deliverables of another framework. The issues involved in this are discussed in 5.3 Adapting the ADM.
Figure 6-3 illustrates a more detailed set of dependencies between the various frameworks and business planning activity that incorporates the enterprise's strategic plan and direction. The enterprise architecture can be used to provide a structure for all of the corporate initiatives, the Portfolio Management Framework can be used to deliver the components of the architecture, and the Operations Management Framework supports incorporation of these new components within the corporate infrastructure.
The business planners are present throughout the process and are in a position to support and enforce the architecture by retaining approval for resources at the various stages of planning and development.
The solution development methodology is used within the Portfolio Management Framework to plan, create, and deliver the architectural components specified in the portfolio and project charters. These deliverables include, but are not exclusively, IT; for example, a new building, a new set of skills, production equipment, hiring, marketing, and so on. Enterprise architecture potentially provides the context for all enterprise activities.
The management frameworks are required to complement each other and work in close harmony for the good of the enterprise.
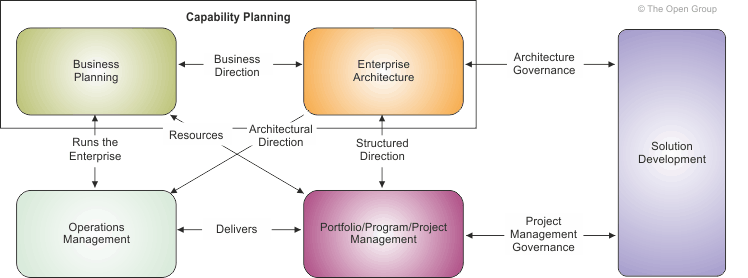
Business planning at the strategy level provides the initial direction to enterprise architecture. Updates at the annual planning level provide a finer level of ongoing guidance. Capability-based Planning is one of many popular techniques for business planning.
Enterprise architecture structures the business planning into an integrated framework that regards the enterprise as a system or system of systems. This integrated approach will validate the business plan and can provide valuable feedback to the corporate planners. In some organizations, the enterprise architects have been moved to or work very closely with the strategic direction groups. TOGAF delivers a framework for enterprise architecture.
Portfolio/project management is the delivery framework that receives the structured, detailed direction that enables them to plan and build what is required, knowing that each assigned deliverable will be in context (i.e., the piece of the puzzle that they deliver will fit into the corporate puzzle that is the enterprise architecture). Often this framework is based upon the Project Management Institute or UK Office of Government Commerce (PRINCE2) project management methodologies. Project architectures and detailed out-of-context design are often based upon systems design methodologies.
Operations management receives the deliverables and then integrates and sustains them within the corporate infrastructure. Often the IT service management services are based upon ISO 20000 or BS15000 (ITIL).
Capability Maturity Models (detailed in Part VII, 51. Architecture Maturity Models) are useful ways of assessing the ability of an enterprise to exercise different capabilities.
Capability Maturity Models typically identify selected factors that are required to exercise a capability. An organization's ability to execute specific factors provides a measure of maturity and can be used to recommend a series of sequential steps to improve a capability. It is an assessment that gives executives an insight into pragmatically improving a capability.
A good enterprise architecture maturity model covers the characteristics necessary to develop and consume enterprise architecture. Organizations can determine their own factors and derive the appropriate maturity models, but it is recommended to take an existing model and customize it as required.
Several good models exist, including NASCIO, and the US Department of Commerce Architecture Capability Maturity Model.
The use of Capability Maturity Models is detailed in Part VII, 51. Architecture Maturity Models.
Other examples include the US Federal Enterprise Architecture Maturity Model. Even though the models are originally from government, they are equally applicable to industry.
This section defines the inputs to the Preliminary Phase.
Pre-existing models for operating an enterprise Architecture Capability can be used as a baseline for the Preliminary Phase. Inputs would include:
The TOGAF ADM is a generic method, intended to be used by a wide variety of different enterprises, and in conjunction with a wide variety of other architecture frameworks, if required. The Preliminary Phase therefore involves doing any necessary work to initiate and adapt the ADM to define an organization-specific framework. The issues involved with adapting the ADM to a specific organizational context are discussed in detail in 5.3 Adapting the ADM.
The level of detail addressed in the Preliminary Phase will depend on the scope and goals of the overall architecture effort.
The order of the steps in the Preliminary Phase (see below) as well as the time at which they are formally started and completed should be adapted to the situation at hand in accordance with the established architecture governance.
The steps within the Preliminary Phase are as follows:
The architecture framework will form the keystone to the flavor (centralized or federated, light or heavy, etc.) of architecture governance organization and guidelines that need to be developed. Part of the major output of this phase is a framework for architecture governance. We need to understand how architectural material (standards, guidelines, models, compliance reports, etc.) is brought under governance; i.e., what type of governance repository characteristics are going to be required, what relationships and status recording are necessary to ascertain which governance process (dispensation, compliance, take-on, retirement, etc.) has ownership of an architectural artifact.
It is likely that the existing governance and support models of an organization will need to change to support the newly adopted architecture framework.
To manage the organizational change required to adopt the new architectural framework, the current enterprise governance and support models will need to be assessed to understand their overall shape and content. Additionally, the sponsors and stakeholders for architecture will need to be consulted on potential impacts that could occur.
Upon completion of this step, the architecture touch-points and likely impacts should be understood and agreed by relevant stakeholders.
Architecture Principles (see Part III, 23. Architecture Principles) are based on business principles and are critical in setting the foundation for architecture governance. Once the organizational context is understood, define a set of Architecture Principles that is appropriate to the enterprise.
In this step, determine what tailoring of TOGAF is required. Consider the need for:
The level of formality used to define and manage architecture content will be highly dependent on the scale, sophistication, and culture of the architecture function within the organization. With an understanding of the desired approach to architecture, it is possible to select appropriate architecture tools to underpin the architecture function.
The approach to tools may be based on relatively informal usage of standard office productivity applications, or may be based on a customized deployment of specialist architecture tools. Depending on the level of sophistication, the implementation of tools may range from a trivial task to a more involved system implementation activity.
Issues in tools standardization are discussed in Part V, 42. Tools for Architecture Development.
The outputs of the Preliminary Phase may include, but are not restricted to:
The outputs may include some or all of the following:
The TOGAF document set is designed for use with frames. To navigate around the document:
Downloads of TOGAF®, an Open Group Standard, are available under license from the TOGAF information web site. The license is free to any organization wishing to use the TOGAF standard entirely for internal purposes (for example, to develop an information system architecture for use within that organization). A book is also available (in hardcopy and pdf) from The Open Group Bookstore as document G116.