-
Preface
The Open Group
The Open Group is a global consortium that enables the achievement of business objectives through IT standards. With more than 450 member organizations, The Open Group has a diverse membership that spans all sectors of the IT community – customers, systems and solutions suppliers, tool vendors, integrators, and consultants, as well as academics and researchers – to:
• Capture, understand, and address current and emerging requirements, and establish policies and share best practices
• Facilitate interoperability, develop consensus, and evolve and integrate specifications and open source technologies
• Offer a comprehensive set of services to enhance the operational efficiency of consortia
• Operate the industry’s premier certification service
Further information on The Open Group is available at www.opengroup.org.
The Open Group publishes a wide range of technical documentation, most of which is focused on development of Open Group Standards and Guides, but which also includes white papers, technical studies, certification and testing documentation, and business titles. Full details and a catalog are available at www.opengroup.org/bookstore.
Readers should note that updates – in the form of Corrigenda – may apply to any publication. This information is published at www.opengroup.org/corrigenda.
The IT4IT™ Forum
The IT4IT Forum, a Forum of The Open Group, was created when its predecessor, the IT4IT Consortium, transferred its activities to The Open Group. The IT4IT Consortium came into being in 2011 as a practitioner-driven initiative. The Consortium was comprised of IT professionals from multiple industry segments and several IT vendors who agreed to share their experiences for the purpose of developing and publishing future-safe prescriptive guidance for implementing end-to-end an IT4IT architecture with full insight. Past and present members include Enterprise Architects and IT department leaders or industry consultants from: Accenture, Achmea, AT&T, HP IT, ING Bank, Munich RE, PwC, Royal Dutch Shell, and University of South Florida.
The Consortium formed a strategy board that spent thousands of hours sharing their insights and analyzing their experiences to develop a future-safe IT operating model. This model includes a prescriptive architecture for implementing the IT Value Chain to optimize the efficiency and effectiveness of IT. The strategy board is backed by an executive board sponsor from each member company.
“Cloud services and multi-provider outsourcing are adding new degrees of complexity to IT service management. The Consortium will use its real-life, cross-industry expertise to define a new operating model for IT.”
Dr. Dirk Heiss, Global Infrastructure Services Officer, Munich RE
This Document
The Open Group IT4IT™ Reference Architecture refers to the capability or capabilities required to manage the business of IT, covering IT end-to-end from plan, through build and operate. It assumes the principle that the business of running IT is industry-agnostic and that IT leaders share the same problems and opportunities in managing the service lifecycle effectively. At the core, these problems are rooted in IT structure, competencies, and capabilities and the missing link has been the lack of an IT operating model. The IT4IT Reference Architecture proposes that it is possible to establish an IT operating model standard mapped to the existing IT landscape yet flexible enough to support the volatility inherent in the IT industry and accommodate changing IT paradigms (composite apps, agile development, mobile technology, multi-sourcing, etc.).
The IT Value Chain and IT4IT Reference Architecture represent the IT service lifecycle XE "IT service lifecycle" in a new and powerful way, providing the missing link between industry standard best practice guides and the technology you need to select and execute those processes. The IT Value Chain and IT4IT Reference Architecture are a new foundation on which to base your IT4IT operating model and provide a welcome blueprint for the CIO to accelerate IT’s transition to becoming a service broker to the business.
This document is The Open Group IT4IT Reference Architecture, Version 2.0, an Open Group Standard. It has been developed and approved by The Open Group.
This document is structured as follows:
-
Chapter 1 (Introduction) introduces this document and the purpose of the IT4IT work.
-
Chapter 2 (Definitions) lists important definitions needed in order to read the document.
-
Chapter 3 (Overview) is an introduction for executives and others introducing the IT Value Chain and IT4IT Reference Architecture concepts.
-
Chapter 4 (IT4IT Core) defines the structure of the IT4IT standard as well as the process and document structure used by the IT4IT standard.
-
Chapter 5 (Strategy to Portfolio (S2P) Value Stream) explains the S2P Value Stream in detail.
-
Chapter 6 (Requirement to Deploy (R2D) Value Stream) explains the R2D Value Stream in detail.
-
Chapter 7 (Request to Fulfill (R2F) Value Stream) explains the R2F Value Stream in detail.
-
Chapter 8 (Detect to Correct (D2C) Value Stream) explains the D2C Value Stream in detail.
-
Appendix A (Rationale (Informative)) contains background information on the standard.
How to Use this Standard
It is recommended that the reader start by familiarizing themselves with Chapter 3 (Overview) which introduces the concepts of the IT Value Chain. This should then be followed by the IT4IT Core (Chapter 4), and the four IT Value Streams. These are:
-
Strategy to Portfolio (S2P) Value Stream (Chapter 5)
-
Requirement to Deploy (R2D) Value Stream (Chapter 6)
-
Request to Fulfill (R2F) Value Stream (Chapter 7)
-
Detect to Correct (D2C) Value Stream (Chapter 8)
Documentation Structure of the IT4IT Reference Architecture
Figure 1 is a graphical representation of the data objects associated with the IT4IT Reference Architecture. The architecture is comprised of a set of normative documents[1] and a formal model described using the ArchiMate® XE "ArchiMate language" modeling language and UML XE "UML" . These define “what” the architecture is. The normative documentation includes:
-
IT4IT Reference Architecture Overview
-
IT4IT Value Stream Overview
-
IT4IT Reference Architecture diagrams
-
IT4IT meta-model diagram
-
Glossary
The Reference Architecture diagrams, in ArchiMate notation, will be provided as a set of web pages, and also as a downloadable zip file of those pages. When available, they will be found at: https://collaboration.opengroup.org/data/IT4IT/RA_2.0.
A set of guidance documents is being developed to accompany the architecture, intended to describe “how” to apply the architecture in practice. Planned guidance documents include:
-
Multi-Supplier Management White Paper
-
Definition of IT Service White Paper
-
Service Model Management White Paper
-
Scenario White Papers (see Section 4.2.6.1)
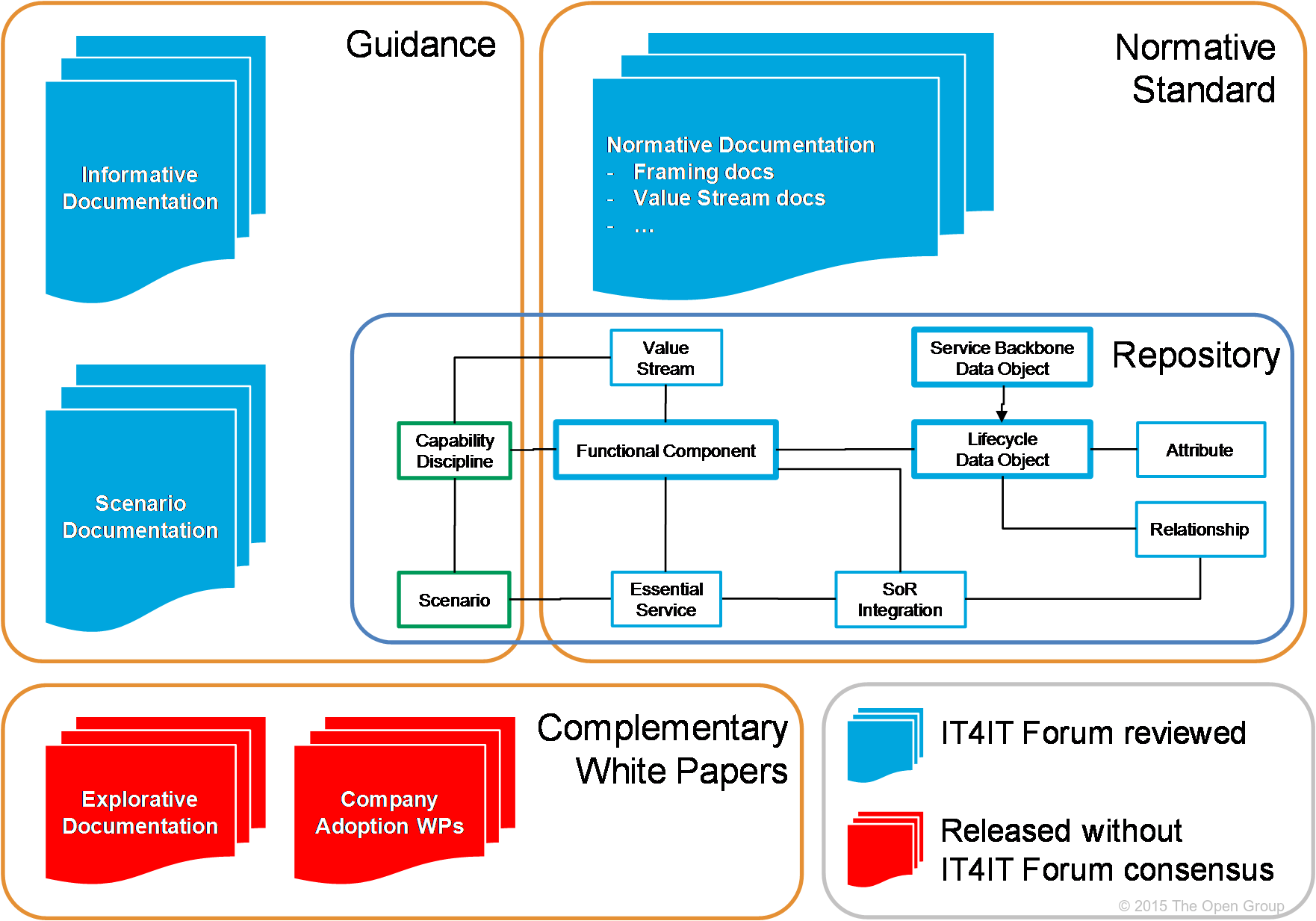
Figure 1: Documentation Structure of the IT4IT Reference Architecture
Documents/artifacts that fall into these two categories are governed by The Open Group Standards Process. In addition, The Open Group will maintain a set of White Papers that complement the architecture and elaborate on its applicability and use in various settings.
Related Industry Standards
Most IT management standards fall into one of two categories: process and/or method-focused technology and/or implementations-centric. There are no standards that prescribe both the operating model and automation guidelines for running the IT function. Therefore, the IT4IT Reference Architecture fills this gap and as such complements a number of existing standards and best practices such as:
-
ISO/IEC 19770:2012: Information Technology – Software Asset Management
-
ISO/IEC 20000:2011: Information Technology – Service Management
-
ISO/IEC 38500:2008: Corporate Governance of Information Technology
-
ISO/TC 258: Project, Program, and Portfolio Management
-
Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)
-
Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT)
-
Business Process Framework (eTOM)
-
The TOGAF® standard
-
The ArchiMate modeling language
-
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
-
The Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)
Trademarks
ArchiMate®, DirecNet®, Making Standards Work®, OpenPegasus®, The Open Group®, TOGAF®, UNIX®, and the Open Brand (“X” logo) are registered trademarks and Boundaryless Information Flow™, Build with Integrity Buy with Confidence™, Dependability Through Assuredness™, FACE™, IT4IT™, Open Platform 3.0™, Open Trusted Technology Provider™, UDEF™, and the Open “O” logo and The Open Group Certification logo are trademarks of The Open Group in the United States and other countries.
CMMI® is registered in the US Patent and Trademark Office by Carnegie Mellon University.
COBIT® is a registered trademark of the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) and the IT Governance Institute.
eTOM® is a registered trademark of the TM Forum.
ITIL® is a registered trademark of AXELOS Ltd.
OASIS™ and TOSCA™ are trademarks of OASIS.
OMG®, Unified Modeling Language®, and UML®, are registered trademarks of the Object Management Group, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
All other brands, company, and product names are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks that are the sole property of their respective owners.
Acknowledgements
This standard was prepared by The Open Group IT4IT™ Forum.
When The Open Group approved the IT4IT™ Reference Architecture, Version 2.0, an Open Group Standard, on October 5, 2015, the membership of the IT4IT™ Forum was as follows:
Chris Davis, University of South Florida, Chair
Karel van Zeeland, Shell Information Technology International BV, Vice-Chair
Martin Kirk, The Open Group, Forum Director
Andrew Josey, The Open Group, Director, Standards
Cathy Fox, The Open Group, Technical EditorContributors
The Open Group gratefully acknowledges the contribution of the following members of the IT4IT™ Forum in the development of this standard:
Richard Aarnink Jim Johnson
Rob Akershoek Linda Kavanagh
Chris Armstrong Mark Luchtmeijer
Charles Betz Sylvain Marie
Georg Bock Lakshmi Malhotra
Mark Bodman Gunnar Menzel
Paul Buckley Satya Misra
James Caruso Brian Ng
Eran Cohen Dan Rosenzweig
Sam Courtney Lars Rossen
Sukumar Daniel Vasu Sankhavaram
Dwight David Ryan Schmierer
Christopher Davis Rick Solis
Sue Desiderio Ken Street
Ulrich Feyer Mary Street
Mike Fulton Etienne Terpstra
Philippe Geneste Richard Tian
Ohad Goldfarb Kees van den Brink
Mark Gray Karel van Zeeland
Claudia Guli Gerlan Verlouw
Trey Harris Prafull Verma
Rob Hengeveld Floris Verschoor
Brian Hodgdon Ulrich Wanka
Keith Jahn Erik WitteTechnical Reviewers
Technical reviewers are those individuals who have submitted comments during the company review, or participated in the resolution process during the development of the IT4IT Reference Architecture, Version 2.0.
Sam Courtney Andrew Josey
Chris Davis Martin Kirk
Sue Desiderio Randall Ramsey
Thorbjörn Ellefsen Lars Rossen
Ohad Goldfarb Mark SmalleyIT4IT™ Forum Members
The following organizations were members of the IT4IT™ Forum at the time of approval:
Accenture Limited, USA
Achmea, The Netherlands
Action Research Foundation, India
Agency for Public Management and eGovernment (Difi), Norway
Arismore, France
Armstrong Process Group, Inc., USA
AT&T IT Architecture Solutions, USA
ATE Enterprises Ltd., UK
Biner Consulting, Sweden
BP Oil International Limited, UK
CA, Inc., USA
Capgemini S.A., The Netherlands
CC and C Solutions, USA
Conexiam Solutions, Inc., USA
Dux Diligens S.A de C.V, Mexico
EA Principals, Inc., USA
Ernst & Young, UK
ExxonMobil, USA
Fujitsu, Japan
HCL Technologies Ltd., India
Hewlett-Packard Company, USA
Huawei Technologies, Co. Ltd., China
IBM, USA
Logicalis SMC, The Netherlands
Microsoft, USA
Ministerie van Financien, The Netherlands
Munich Re Group, Germany
National Healthcare, USA
Nationwide Mutual Insurance Company, Inc., USA
Oracle Corporation, USA
Origin Energy, Australia
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, South Africa
Raytheon Company, USA
Real IRM Solutions (Pty) Ltd., South Africa
ServiceNow, Inc., USA
Shell Information Technology International B.V., The Netherlands
Shift Technologies LLC, United Arab Emirates
Stichting ASL BiSL Foundation, The Netherlands
Tata Consultancy Services Ltd., India
The Boeing Company, USA
UMBRiO, The Netherlands
University of South Florida, USA
Westbury Software, The NetherlandsReferenced Documents
(Please note that the links below are good at the time of writing but cannot be guaranteed for the future.)
Normative References
Normative references for this standard are defined in Section 1.4.
Informative References
The following documents are referenced in this standard:
-
Agile Alliance: Agile Manifesto and Principles (2001); retrieved 4/13/2011, from http://agilemanifesto.org/principles.html.
-
J. Allspaw, J. Robbins: Web Operations, Beijing China, Sebastopol CA, O'Reilly (2010).
-
ASL Foundation: Application Services Library (2005); retrieved 11/13/2005, from www.aslfoundation.org.
-
K. Behr, G. Kim et al: The Visible Ops Handbook – Implementing ITIL in Four Practical and Auditable Steps, Eugene OR, Information Technology Process Institute (2005).
-
R.J. Benson, T.L. Bugnitz et al: From Business Strategy to IT Action – Right Decisions for a Better Bottom Line, New York; Chichester, Wiley (2004).
-
C.T. Betz: Architecture and Patterns for IT: Service and Portfolio Management and Governance (Making Shoes for the Cobbler's Children), 2nd Edition, Amsterdam, Elsevier/Morgan Kaufman (2011)
-
P. Bourque, R.E. Fairley, Eds.: Guide to the Software Engineering Body of Knowledge, Version 3.0, IEEE Computer Society (2014).
-
J.A. Carbone: IT Architecture Toolkit, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall (2004).
-
J.A. Carbone: CMMI Product Team: CMMI for Acquisition, Version 1.3. Pittsburgh PA, Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute (2010).
-
CMMI Product Team: CMMI for Development, Version 1.3, Pittsburgh PA, Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute (2010).
-
CMMI Product Team: CMMI for Services, Version 1.3, Pittsburgh PA, Carnegie Mellon Software Engineering Institute (2010).
-
A. Cockburn: Writing Effective Use-Cases, Boston, Addison-Wesley (2001).
-
M.A. Cook: Building Enterprise Information Architectures – Re-Engineering Information Systems, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall (1996).
-
P.M. Duvall, S. Matyas et al: Continuous Integration – Improving Software Quality and Reducing Risk, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Addison-Wesley (2007).
-
J. Humble, D. Farley: Continuous Delivery, Boston, Addison-Wesley (2011).
-
IEEE 730-2014: IEEE Standard for Software Quality Assurance Processes.
-
ISACA: Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (COBIT 5); refer to www.isaca.org.
-
ISO/IEC 2005: Regional or National Adoption of International Standards and Other International Deliverables (Guide 21-2).
-
ISO/IEC 2008: Uncertainty of Measurement (Guide 98-3).
-
ISO/IEC 2013: ISO/IEC Directives.
-
ISO/IEC 19770:2012: Information Technology – Software Asset Management.
-
ISO/IEC 20000:2011: Information Technology – Service Management.
-
ISO/IEC 27002:2013: Information Technology – Security Techniques – Code of Practice for Information Security Controls.
-
ISO/IEC 38500:2008: Corporate Governance of Information Technology.
-
ISO/TC 258: Project, Program, and Portfolio Management.
-
J.D. Kaplan: Strategic IT Portfolio Management – Governing Enterprise Transformation, US, Pittiglio Rabin Todd & McGrath Inc. (2005).
-
H. Kern, R. Schiesser et al: IT Production Services, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall Professional Technical Reference (2004).
-
L. Klosterboer: Implementing ITIL Change and Release Management, Upper Saddle River, NJ, IBM; London: Pearson Education [distributor] (2009).
-
D. Leffingwell, A. Yakyma et al: Scaled Agile Framework, from http://scaledagileframework.com (2014).
-
T.A. Limoncelli, S.R. Chalup et al: The Practice of Cloud System Administration: Designing and Operating Large Distributed Systems, Vol. 2, Pearson Education Ltd. (2014).
-
D.C. Luckham: The Power of Events – An Introduction to Complex Event Processing in Distributed Enterprise Systems, Boston, MA; London, Addison-Wesley (2002).
-
B. Maizlish, R. Handler: IT Portfolio Management Step-By-Step: Unlocking the Business Value of Technology, Hoboken, MJ, John Wiley & Sons (2005).
-
J. Martin: Great Transition: Using the Seven Disciplines of Enterprise Engineering, ISBN: 978-0814403150, Amacom (January 1995).
-
F.W. McFarlan: Portfolio Approach to Information Systems, Harvard Business Review 59(5): 142-150 (1981).
-
OASIS: Topology and Orchestration Specification for Cloud Applications (TOSCA), Version 1.0 (2013).
-
G. O’Donnell, C. Casanova: The Configuration Management Database (CMDB) Imperative: How to Realize the Dream and Avoid the Nightmares, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall; London: Pearson Education [distributor] (2009).
-
Office of Government Commerce: Application Management, London, The Stationary Office (2002).
-
M. O’Loughlin: The Service Catalog: A Practitioner Guide, Zaltbommel, The Netherlands, Van Haren Publishing (2009).
-
M. Porter: Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance, ISBN: 978-0684841465, Free Press; 1st Edition (June 1998).
-
Project Management Institute: A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) (2013).
-
T.A. Quinlan: Chargeback and IT Cost Accounting, Santa Barbara, CA, IT Financial Management Association (2003).
-
T.A. Quinlan, S.J. Quinlan: Readings in IT Financial Management, Santa Barbara, CA, IT Financial Management Association (2003).
-
Rational Software: Rational Unified Process: Best Practices for Software Development Teams (2011).
-
D. Remenyi, A.H. Money et al: The Effective Measurement and Management of ICT Costs and Benefits, Oxford; Burlington, MA, CIMA (2007).
-
R. Schiesser: IT Systems Management, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall (2010).
-
R. Schiesser, H. Kern: Enterprise Computing Institute: IT Systems Management, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall (2002).
-
SOA Reference Architecture, Open Group Standard (C119), December 2011, published by The Open Group; refer to: www.opengroup.org/bookstore/catalog/c119.htm.
-
S.H. Spewak, S.C. Hill: Enterprise Architecture Planning – Developing a Blueprint for Data, Applications, and Technology, Boston, QED Pub. Group (1993).
-
R. Sturm, W. Morris et al: Foundations of Service-Level Management, Indianapolis, IN, SAMS (2000).
-
The Stationery Office: ITIL Continual Service Improvement, Norwich UK (2011).
-
The Stationery Office: ITIL Service Design, Norwich UK (2011).
-
The Stationery Office: ITIL Service Operation, Norwich UK (2011).
-
The Stationery Office: ITIL Service Strategy, Norwich UK (2011).
-
The Stationery Office: ITIL Service Transition, Norwich UK (2011).
-
TOGAF Version 9.1 (English version), Open Group Standard, available online at www.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-doc/arch, and also available as TOGAF Version 9.1 “The Book” (ISBN: 978 90 8753 6794, G116) at www.opengroup.org/bookstore/catalog/g116.htm.
-
W. Ulrich, N. McWhorter: Business Architecture: The Art and Practice of Business Transformation, Tampa, FL, Meghan-Kiffer (2010).
-
Unified Modeling Language (UML), Object Management Group (OMG); refer to: www.uml.org.
-
W. Van Grembergen: Strategies for Information Technology Governance, Hershey, PA; London, Idea Group Publishing (2004).
-
W. Van Grembergen, S. Haes: Enterprise Governance of Information Technology – Achieving Strategic Alignment and Value, New York, Springer (2009).
-
E.A. Van Schaik: A Management System for the Information Business – Organizational Analysis, Englewood Cliffs; London, Prentice Hall (1985).
-
P. Weill, J.W. Ross: IT Governance – How Top Performers Manage IT Decision Rights for Superior Results, Boston, MA, Harvard Business School; [London: McGraw-Hill] (2004).
Downloads
Downloads of the IT4IT Reference Architecture, Version 2.0, an Open Group Standard, are available under license from the IT4ITinformation web site. The license is free to any organization wishing to use the IT4ITstandard entirely for internal purposes (for example, to develop an information system architecture for use within that organization). A book is also available (in pdf) from The Open Group Bookstore as document C155.
-