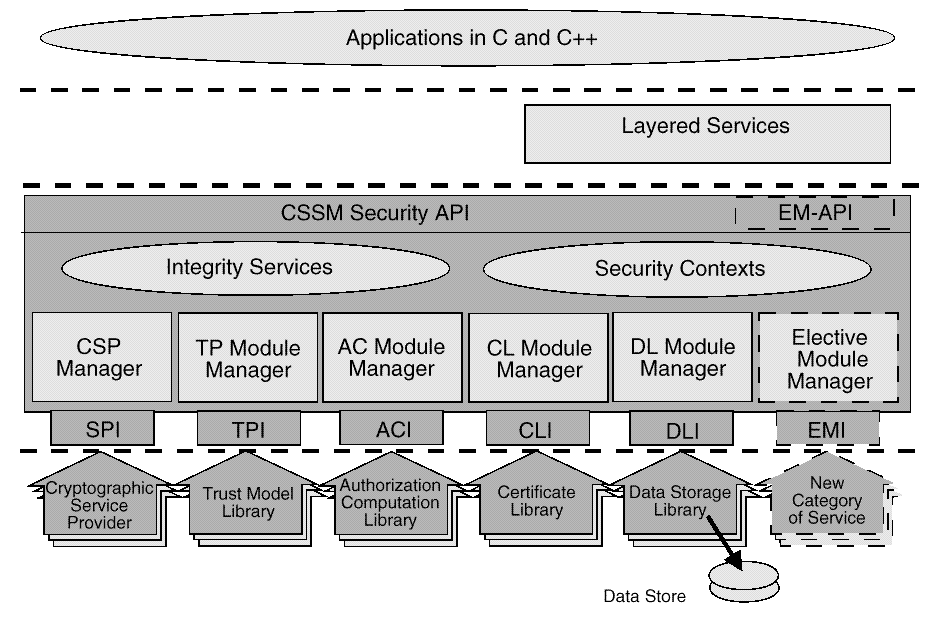
The Common Security Services Manager (CSSM) is the core of CDSA. It provides a means for applications to directly access security services through the CSSM security API, or to indirectly access security services via layered security services and tools implemented over the CSSM API. CSSM manages the add-in security modules and re-directs application calls through the CSSM API to the selected add-in modules that will service the request.
This four layer architecture defines five categories of basic add-in module security services. Basic services are required to meet the security needs of all applications. CSSM also supports the dynamic inclusion of APIs for new categories of security services, required by selected applications. These elective services are dynamically, and transparently added to a running CSSM environment when required by an application. Elective services are required by only a subset of security aware applications. When an elective service is needed a module manager for that category of service can be transparently attached to the system followed by the requested add-in service module. Once attached to the system, the elective module manager is a peer with all other CSSM module managers. Applications interact uniformly with add-in modules of all types.
The five basic categories of security services modules are:
Cryptographic Service Providers (CSPs) are add-in modules that perform cryptographic operations including encryption, decryption, digital signaturing, key pair generation, random number generation, and key exchange. Trust Policy (TP) modules implement policies defined by authorities, institutions, and applications, such as your Corporate Information Technology Group (as a certificate authority), MasterCard* (as an institution), or Secure Electronic Transfer (SET) applications. Each trust policy module embodies the semantics of a trust environment based on digital credentials. A certificate is a form of digital credential. Applications may use a digital certificate as an identity credential and/or an authorization credential. Certificate Library (CL) modules provide format-specific, syntactic manipulation of memory-resident digital certificates and certificate revocation lists. Data Storage Library (DL) modules provide persistent storage for certificates, certificate revocation lists, and other security-related objects.
Examples of elective security service categories are key recovery and audit logging.

Applications dynamically select the modules used to provide security services. These add-in modules can be provided by independent software and hardware vendors. A single add-in module can provide services in multiple categories of service. These are called multi-service modules. A standalone registry system called the Module Directory Services (MDS) provides applications with information about the service modules available for use by applications.
The majority of the CSSM APIs support service operations. Service operations are functions that perform a security operation, such as encrypting data, adding a certificate to a certificate revocation list, or verifying that a certificate is trusted and/or authorized to perform some action. Service providers can require caller authentication before providing services. Application authentication is based on signed manifest credentials associated with the application.
Service modules can leverage other service modules in the implementation of their own services. Service modules acquire attach handles to other modules by:
To prevent stealth attacks, CSSM performs secure linkage checks on function invocation.
Modules can also provide services beyond those defined by the CSSM API. Module-specific operations are enabled in the API through pass-through functions whose behavior and use is defined by the add-in module developer. (For example, a CSP implementing signaturing with a fragmented private key can make this service available as a pass-through.) The PassThrough is viewed as a proving ground for potential additions to the CSSM APIs.
CSSM core services support:
The module management functions are used by applications and by add-in modules to support runtime access to security service modules.
Security context management provides runtime caching of user-specific, cryptographic context information. Multi-step cryptographic operations, such as staged hashing, require multiple calls to a CSP.
CSSM, security services modules, and optionally applications, check the identity and integrity of components of CDSA. Checkable components include: add-in service modules, CSSM itself, and in the future applications that use CSSM.
In summary, the direct services provided by CSSM through its API calls include:
The Module Directory Services (MDS), which is a standalone service outside of CDSA, implements a database describing CDSA components available from the local platform. Applications and CDSA components can query MDS to obtain the compatibility information and numerous other attributes describing features of the CDSA components. This information can be used as the basis for selecting appropriate and compatible components at runtime.
Every CDSA component must have a unique identification GUID. Not all CDSA applications are required to have an identifying GUID, but it is highly recommended. MDS uses the GUID as the primary database key for locating information about the CDSA component. Specification of the the version numbers is optional, but believed to be of value as an augmentation to the distinguished name for an executable CDSA component.
When components are selected at runtime, applications use the MDS query functions to select components based on GUID or based on other properties of the component (such as the algorithms or features provided by the component).
If the application is selecting a CSSM at runtime, the application is
responsible for loading the selected CSSM using services provided by
the platform-specific environment. The application is also responsible
for any load-specific initialization, such as symbol resolution. Once
a CSSM has been loaded with the application, CSSM initialization
proceeds as usual with the application invoking
Applications also use MDS to identify a service module providing the
features and services required by the application. Once the service
module has been identified, the application must use the CSSM services
These APIs are implemented by the CSSM, not by security service modules.
Applications can have apriori knowledge of the service module to be used or can use the Module Directory Services (MDS) to search the CDSA Directory database for service modules that provide the features and services required by the application. When service providers are made accessible on the local platform (typically through platform-specific installation procedures), the installation procedure includes registering the service module in MDS's CDSA database.
MDS records information about each installed service module and elective module manager available on the local system. MDS supports the following services and features with respect to the CDSA database:
The database entries are queried by applications, service modules, EMMs, and CSSM.
Applications select the particular security service they will use by selectively loading and attaching service modules. These modules are provided by independent vendors. Each has an assigned, Globally Unique ID (GUID), and a set of descriptive attributes to assist applications in selecting appropriate modules for their use. A module can implement a range of services across the CSSM APIs (such as, cryptographic functions and data storage functions) or a module can restrict its services to a single CSSM category of service (such as, certificate library services only). Modules that span service categories are called Multi-Service modules.
Applications use a module's GUID to specify the module to be attached. The attach function returns a handle representing a unique pairing between the caller and the attached module. This handle must be provided as an input parameter when requesting services from the attached module. CSSM uses the handle to match the caller with the appropriate service module and service type.
The calling application
attaches to a module once for each type of service it requires.
If the service type requested by the application is not
implemented by the module, the attach fails.
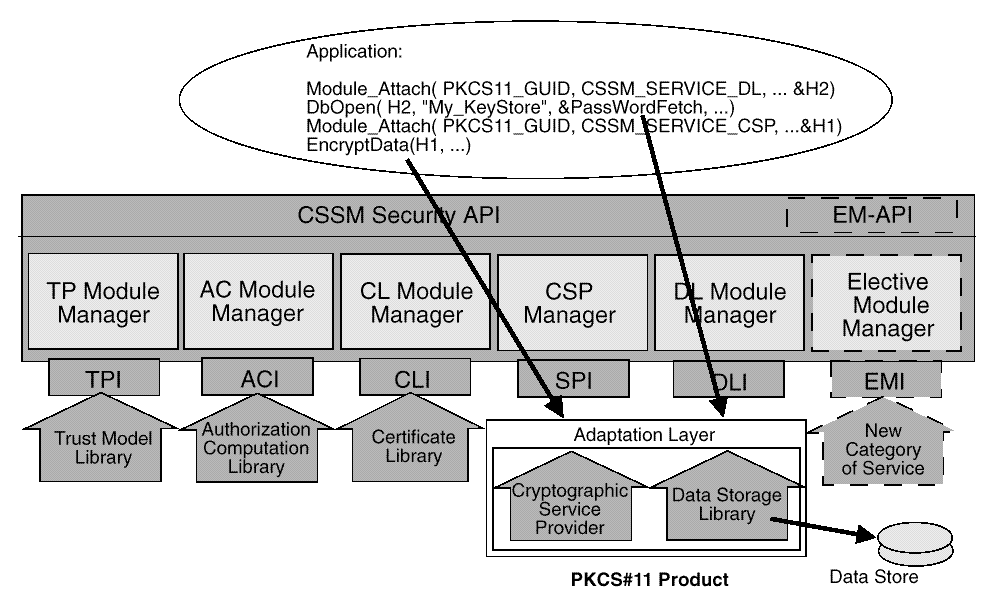
Multiple calls to attach are viewed as independent requests. Each attach request returns separate, independent handles that do not share execution state.
Before attaching a service module, an application can query the MDS CDSA database to obtain information on:
Applications use this information to select a module for use. A multi-service module has multiple capability descriptions associated with it, at least one per functional area supported by the module. The MDS CDSA database stores one record for each service category provided by a service module.
CSSM requires successful certificate-based trust verification of all
service modules when processing a
All verifications performed to enforce CSSM-defined policy are based on CSSM-selected public root keys as points of trust.
When CSSM performs a verification check on any component in the CSSM environment, the verification process has three aspects:
CDSA defines a bilateral authentication procedure by which CSSM and a component interacting with CSSM authenticate each other to achieve a mutual trust.
As part of bilateral authentication, CSSM verifies and loads a module or a module manager. If verification fails, then the module or the module manager is not linked or loaded.
Application privileges are specific to a class of applications and service providers. If used, CSSM will ensure the calling module and the target service provider are authorized to switch to the mode implied by a chosen privilege. The export privileges are a class of privileges allowing modal behavior in service providers which coincides with the export regulations over cryptography. More detail on export privileges is provided below.
Application privileges may be defined by The Open Group, and may also be vendor defined. The representation of privileges uses two 4-byte words (or an 8-byte word if the platform supports 64-bit words) The number space is divided in half between standard privileges and vendor defined privileges. The lower 32-bits are reserved for standard privileges and the upper 32-bits allocated to vendor specific privileges. The application privileges are granted to modules in signed manifests using the tag CDSA_PRIV. The CDSA_PRIV tag is added to the signer_info section of the module manifest. The associated value is a string of 4 byte base-64 encoded numbers, in big-endian order. Encoded 4-byte words are separated by colons. These numbers are the same numbers defined for the high-order word of CSSM_PRIVILEGE.
All of the CDSA logical components may be subject to export controls. Exemptions to the export policy of public record are modeled using an artifact called USEE tags. Any time an exemption to export policy is granted, a USEE tag may be defined. The semantics of the USEE tag is interpreted in the context of the Exemption Rules. A standards body should control USEE namespace and provide interpretations of the meaning of USEE tags for developers. Specific requirements for USEE tags:
Exemptions are defined for financial, medical, insurance, key recovery, key exchange and authentication. SSL is also cited as a special case exemption in that SSL ciphersuites makes accommodation for export. As such, the USEE tag for SSL signifies to CSSM that the SSL library will carry the enforcement responsibilities. The tag for domestic use is provided for compatibility reasons. Any module not exported may carry the domestic privilege. The CSSM manifest does not require USEE tags to enforce their semantics. It is anticipated that other tags will be added as export policies change.
Additionally, CSSM and EMM components may use USEE tags to configure starting state. For example, the key recovery tag could instruct CSSM to set an internal switch that prevents use of attach handles that have not been sanitized through the key recovery module. Likewise, the domestic tag could indicate that the CSSM will not enforce export exemptions when deployed in the U.S.
A service module can also check the application manifest directly by retrieving its manifest from the MDS and verifying the signature.
Service providers should record the exemptions they grant by listing them in an appropriate MDS relation. Currently, Cryptographic Service Providers (CSPs) advertise their exemptions by listing them in the UseeTag attribute of the MDS CSP Primary relation. This is for information only. The verifiable authorization to grant the exemption must be recorded in the service module's signed manifest credentials. If a module grants exemptions, then the module's signed manifest must include a manifest attribute attesting to this authority. The manifest attribute for currently defined exemptions is a name-value pair with name CDSA_USEE. The associated value is a string of 4-byte base-64 encoded numbers in big-endian order. Encoded 4-byte words are separated by colons. These numbers are the same numbers defined for the lower order word of CSSM_PRIVILEGE. An example of CDSA_USEE tag in the manifest (which corresponds to the base64 encoding of the CSSM_USEE_TAG) is:
-
-
CDSA_USEE: AAAAAg==:AAAABQ==:AAAAAw==
Applications can query MDS to retrieve the USEE Tags associated with any CSP.
Privileges which have numbers from the high order word of the CSSM_PRIVILEGE will use the manifest tag CDSA_PRIV, as opposed to the tag CDSA_USEE. Other than that exception, they are used exactly like the tags listed as CDSA_USEE*.
The CSSM_Init function needs to be called before calling any other CSSM
interfaces. At the time of the first CSSM_Init call, a CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE
and CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY can be passed in. Based on the platform-specific
implementation of CSSM,
There are two ways for an Application to request a privilege:
The appropriate USEE tags that validates the requested exemption may be in either the signed manifest of the Application (stored in the MDS Object Directory relation), and/or in the signed manifest of the CSSM. Either the Application or the CSSM (or both) must have a signed manifest with the appropriate USEE tag.
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_BOOL
#define CSSM_FALSE (0)
#define CSSM_TRUE (!CSSM_FALSE)
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_RETURN;
#define CSSM_OK (0)
-
-
#define CSSM_MODULE_STRING_SIZE (64)
typedef char CSSM_STRING [CSSM_MODULE_STRING_SIZE + 4];
-
-
typedef struct cssm_data{
uint32 Length; /* in bytes */
uint8 *Data;
} CSSM_DATA, *CSSM_DATA_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_guid{
uint32 Data1;
uint16 Data2;
uint16 Data3;
uint8 Data4[8];
} CSSM_GUID, *CSSM_GUID_PTR;
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_BITMASK;
typedef CSSM_BITMASK CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY;
#define CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY_NONE (0)
#define CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY_INTEG (1)
#define CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY_EXPORT (2)
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 | PVC validation is not performed |
| 1 | PVC validation is performed on application modules |
| 2 | PVC validation is performed on service provider modules |
| 3 | Both types of PVC validations are performed |
-
-
typedef CSSM_BITMASK CSSM_PVC_MODE;
#define CSSM_PVC_NONE (0)
#define CSSM_PVC_APP (1)
#define CSSM_PVC_SP (2)
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE;
#define CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_NONE (0)
#define CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_PROCESS (1)
#define CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_THREAD (2)
-
-
typedef struct cssm_version {
uint32 Major;
uint32 Minor;
} CSSM_VERSION, *CSSM_VERSION_PTR;
The minor number uses two digits to represent minor releases and revisions. The revision number is represented in the least significant digit. The remaining more significant digits represent minor numbers. The first release has the value of zero. There can be 9 subsequent releases then the minor number must be incremented. For example, the minor number for the very first release of a product would be represented as "00". Subsequent releases would be "01", "02", "03" etc., to "09". If version number changes at each release then the minor numbers would increment from "00", "10", "20" etc., to "90". A minor version of 10 release 1 would be "100".
-
-
typedef struct cssm_subservice_uid {
CSSM_GUID Guid;
CSSM_VERSION Version;
uint32 SubserviceId;
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE SubserviceType;
} CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID, *CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID_PTR;
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_HANDLE, *CSSM_HANDLE_PTR;
-
-
#if defined (WIN32)
typedef unsigned __int64 uint64; /* MSVC++ 5 declaration */
#else
typedef unsigned long long uint64; /* gcc 2.7.2 declaration */
#endif
typedef uint64 CSSM_LONG_HANDLE, *CSSM_LONG_HANDLE_PTR;
-
-
typedef CSSM_HANDLE CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE, *CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE_PTR;
-
-
typedef enum cssm_module_event {
CSSM_NOTIFY_INSERT = 1,
CSSM_NOTIFY_REMOVE = 2,
CSSM_NOTIFY_FAULT = 3,
} CSSM_MODULE_EVENT, *CSSM_MODULE_EVENT_PTR;
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_SERVICE_MASK;
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CSSM (0x1)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CSP (0x2)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_DL (0x4)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CL (0x8)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_TP (0x10)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_AC (0x20)
#define CSSM_SERVICE_KR (0x40)
-
-
typedef CSSM_SERVICE_MASK CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE;
The event handler defined by the CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler structure must be executed outside the thread context that registered the handler. The handler can queue the event results and schedule a reader thread to service the queue. Applications should use AppNotifyCallbackCtx to track thread-id, the head of the queue, and other state information necessary to service the queue and process the events. The event handler must not issue calls through the CSSM API. These circular calls can result in deadlock in numerous situations, hence the event handler must be implemented without using CSSM services.
The CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler can be invoked multiple times in response to a single event (such as the insertion of a smartcard). The handler and the calling application must track receipt of event notifications and ignore duplicates. Other events (such as the removal of a smartcard) can result in a single event notification.
-
-
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler)
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
void* AppNotifyCallbackCtx,
uint32 SubserviceId,
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE ServiceType,
CSSM_MODULE_EVENT EventType);
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_ATTACH_FLAGS;
#define CSSM_ATTACH_READ_ONLY (0x00000001)
The representation of privileges uses two 4-byte words (or an 8 byte word if the platform supports 64-bit words). The high-order 4-byte word is reserved for non-export related privileges and vendor-specific privileges. Of the low-order 4-byte word, the lower byte is used to represent United States export policy, also known as USEE tags. The remaining number space (3 bytes) is reserved for future expansion.
| Byte 3 | Byte 2 | Byte 1 | Byte 0 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reserved | Reserved | Reserved | USEE Tag |
typedef uint32 CSSM_USEE_TAG;
There are U.S. export exemptions for strong encryption financial, medical, insurance, key recovery, key exchange and authentication applications. SSL is cited as a special case exemption in that SSL ciphersuites make accommodation for U.S. export rules. As such, the USEE tag for SSL signifies to CSSM that the SSL library will carry the enforcement responsibilities. The tag for domestic use is provided for compatibility reasons. Any U.S. module not exported may carry the domestic privilege. The CSSM manifest does not require USEE tags to enforce their semantics. It is anticipated that other tags will be added as U.S. export policies change and other types of exemptions are identified.
The high-order 4 bytes of privilege vector allow for vendor specific privilege values. The high order bit (31) is set (1). The lower 31 bits are reserved for vendor-specific privileges. When unset (0), the lower 31 bits (0-30) are interpreted as CDSA privileges not related to export. No CDSA non-export privileges are defined at the time of publishing this Technical Standard.
| Byte 7 | Byte 6 | Byte 5 | Byte 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Other | Other | Other | Other |
| Privilege | Privilege | Privilege | Privilege |
Non-export privilege range: (0x00000000 - 0x7FFFFFFF)
Vendor specific range: (0x80000000 - 0xFFFFFFFF)
-
-
typedef uint64 CSSM_PRIVILEGE;
#define CSSM_USEE_LAST (0xFF)
#define CSSM_USEE_NONE (0)
#define CSSM_USEE_DOMESTIC (1)
#define CSSM_USEE_FINANCIAL (2)
#define CSSM_USEE_KRLE (3)
#define CSSM_USEE_KRENT (4)
#define CSSM_USEE_SSL (5)
#define CSSM_USEE_AUTHENTICATION (6)
#define CSSM_USEE_KEYEXCH (7)
#define CSSM_USEE_MEDICAL (8)
#define CSSM_USEE_INSURANCE (9)
#define CSSM_USEE_WEAK (10)
The CSSM_USEE_TAG values represent exemptions to blanket export policy. Values map to sections in a countries export regulations that permits use of stronger cryptography if the application and constituant parts abide by the stipulations. Applications and their components can be authorized to receive privileges entitling them to stronger cryptographic services.
At the time of publication, the only country known to provide commodity class exemptions to export regulations is the United States of America. The USEE tags defined herein apply to United States export policy. Subsequent export exemptions may be added to the specification, the country to which the tag applies should be included in the documentation.
Application components, CDSA service providers and CSSM may be entrusted to cooperate in the enforcement of a set of policies. The signed manifest will contain a list of privileges the component implements/enforces. The manifest attribute for currently defined exemptions is a name-value pair with name CDSA_USEE. The associated value is a string of base-64 encoded numbers separated by colons.
-
-
typedef enum cssm_net_address_type {
CSSM_ADDR_NONE = 0,
CSSM_ADDR_CUSTOM = 1,
CSSM_ADDR_URL = 2, /* char* */
CSSM_ADDR_SOCKADDR = 3,
CSSM_ADDR_NAME = 4 /* char* - qualified by access method */
} CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_TYPE;
typedef struct cssm_net_address {
CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_TYPE AddressType;
CSSM_DATA Address;
} CSSM_NET_ADDRESS, *CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_PTR;
typedef uint32 CSSM_NET_PROTOCOL;
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_NONE (0) /* local */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_CUSTOM (1) /* proprietary implementation */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_UNSPECIFIED (2) /* implementation default */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAP (3) /* light weight directory access */
/* protocol */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAPS (4) /* ldap/ssl where SSL initiates */
/* the connection */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAPNS (5) /* ldap where ldap negotiates */
/* an SSL session */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_X500DAP (6) /* X.500 Directory access protocol */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_FTP (7) /* ftp for cert/crl fetch */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_FTPS (8) /* ftp/ssl/tls where SSL/TLS */
/* initiates the connection */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_OCSP (9) /* online certificate status */
/* protocol */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_CMP (10) /* the cert request protocol */
/* in PKIX3 */
#define CSSM_NET_PROTO_CMPS (11) /* The ssl/tls derivative of CMP */
-
-
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CSSM_CALLBACK)
(CSSM_DATA_PTR OutData, void *CallerCtx);
-
-
typedef struct cssm_crypto_data {
CSSM_DATA Param;
CSSM_CALLBACK Callback;
void *CallerCtx;
} CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA, *CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA_PTR;
-
-
typedef sint32 CSSM_WORDID_TYPE;
#define CSSM_WORDID__UNK_ (-1) /* not in dictionary */
#define CSSM_WORDID__NLU_ (0) /* not yet looked up */
#define CSSM_WORDID__STAR_ (1)
#define CSSM_WORDID_A (2)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ACL (3)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ALPHA (4)
#define CSSM_WORDID_B (5)
#define CSSM_WORDID_BER (6)
#define CSSM_WORDID_BINARY (7)
#define CSSM_WORDID_BIOMETRIC (8)
#define CSSM_WORDID_C (9)
#define CSSM_WORDID_CANCELED (10)
#define CSSM_WORDID_CERT (11)
#define CSSM_WORDID_COMMENT (12)
#define CSSM_WORDID_CRL (13)
#define CSSM_WORDID_CUSTOM (14)
#define CSSM_WORDID_D (15)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DATE (16)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DB_DELETE (17)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DB_EXEC_STORED_QUERY (18)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DB_INSERT (19)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DB_MODIFY (20)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DB_READ (21)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DBS_CREATE (22)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DBS_DELETE (23)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DECRYPT (24)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DELETE (25)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DELTA_CRL (26)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DER (27)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DERIVE (28)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DISPLAY (29)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DO (30)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DSA (31)
#define CSSM_WORDID_DSA_SHA1 (32)
#define CSSM_WORDID_E (33)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ELGAMAL (34)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ENCRYPT (35)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ENTRY (36)
#define CSSM_WORDID_EXPORT_CLEAR (37)
#define CSSM_WORDID_EXPORT_WRAPPED (38)
#define CSSM_WORDID_G (39)
#define CSSM_WORDID_GE (40)
#define CSSM_WORDID_GENKEY (41)
#define CSSM_WORDID_HASH (42)
#define CSSM_WORDID_HAVAL (43)
#define CSSM_WORDID_IBCHASH (44)
#define CSSM_WORDID_IMPORT_CLEAR (45)
#define CSSM_WORDID_IMPORT_WRAPPED (46)
#define CSSM_WORDID_INTEL (47)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ISSUER (48)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ISSUER_INFO (49)
#define CSSM_WORDID_K_OF_N (50)
#define CSSM_WORDID_KEA (51)
#define CSSM_WORDID_KEYHOLDER (52)
#define CSSM_WORDID_L (53)
#define CSSM_WORDID_LE (54)
#define CSSM_WORDID_LOGIN (55)
#define CSSM_WORDID_LOGIN_NAME (56)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MAC (57)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MD2 (58)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MD2WITHRSA (59)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MD4 (60)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MD5 (61)
#define CSSM_WORDID_MD5WITHRSA (62)
#define CSSM_WORDID_N (63)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NAME (64)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NDR (65)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NHASH (66)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NOT_AFTER (67)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NOT_BEFORE (68)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NULL (69)
#define CSSM_WORDID_NUMERIC (70)
#define CSSM_WORDID_OBJECT_HASH (71)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ONE_TIME (72)
#define CSSM_WORDID_ONLINE (73)
#define CSSM_WORDID_OWNER (74)
#define CSSM_WORDID_P (75)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PAM_NAME (76)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PASSWORD (77)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PGP (78)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PREFIX (79)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PRIVATE_KEY (80)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PROMPTED_PASSWORD (81)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PROPAGATE (82)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC (83)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_PASSWORD (84)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_PIN (85)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PUBLIC_KEY (86)
#define CSSM_WORDID_PUBLIC_KEY_FROM_CERT (87)
#define CSSM_WORDID_Q (88)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RANGE (89)
#define CSSM_WORDID_REVAL (90)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RIPEMAC (91)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RIPEMD (92)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RIPEMD160 (93)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA (94)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_ISO9796 (95)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS (96)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS_MD5 (97)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS_SHA1 (98)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS1 (99)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS1_MD5 (100)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS1_SHA1 (101)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_PKCS1_SIG (102)
#define CSSM_WORDID_RSA_RAW (103)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SDSIV1 (104)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SEQUENCE (105)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SET (106)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SEXPR (107)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SHA1 (108)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SHA1WITHDSA (109)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SHA1WITHECDSA (110)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SHA1WITHRSA (111)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SIGN (112)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SIGNATURE (113)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SIGNED_NONCE (114)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SIGNED_SECRET (115)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SPKI (116)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SUBJECT (117)
#define CSSM_WORDID_SUBJECT_INFO (118)
#define CSSM_WORDID_TAG (119)
#define CSSM_WORDID_THRESHOLD (120)
#define CSSM_WORDID_TIME (121)
#define CSSM_WORDID_URI (122)
#define CSSM_WORDID_VERSION (123)
#define CSSM_WORDID_X509_ATTRIBUTE (124)
#define CSSM_WORDID_X509V1 (125)
#define CSSM_WORDID_X509V2 (126)
#define CSSM_WORDID_X509V3 (127)
#define CSSM_WORDID_X9_ATTRIBUTE (128)
#define CSSM_WORDID_VENDOR_START (0x00010000)
#define CSSM_WORDID_VENDOR_END (0xFFFF0000)
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_TYPE, *CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_DATUM (0x00)
#define CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_SUBLIST (0x01)
#define CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_WORDID (0x02)
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_LIST_TYPE, * CSSM_LIST_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_LIST_TYPE_UNKNOWN (0)
#define CSSM_LIST_TYPE_CUSTOM (1)
#define CSSM_LIST_TYPE_SEXPR (2)
-
-
typedef struct cssm_list_element *CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_PTR;
typedef struct cssm_list {
CSSM_LIST_TYPE ListType; /* type of this list */
CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_PTR Head; /* head of the list */
CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_PTR Tail; /* tail of the list */
} CSSM_LIST, *CSSM_LIST_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_list_element {
struct cssm_list_element *NextElement; /* next list element */
CSSM_WORDID_TYPE WordID; /* integer identifier associated */
/* with a Word value */
CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_TYPE ElementType;
union {
CSSM_LIST Sublist; /* sublist */
CSSM_DATA Word; /* a byte-string */
} Element;
} CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT;
| Element Type | Meaning of WordID |
|---|---|
| CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_DATUM | WordID is associated with the value in Word. If the pre-defined dictionary does not contain a mapping from the value of Word to a WordID, then WordID is zero. |
| CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_SUBLIST | WordID is associated with the Word that begins the Sublist. If the pre-defined dictionary does not contain a mapping from the value of Word to a WordID, then WordID is zero. |
| CSSM_LIST_ELEMENT_WORDID | WordID is the value of the list element. Word and Sublist are empty. |
-
-
typedef struct { /* 5-tuple definition */
CSSM_LIST Issuer; /* issuer, or empty if ACL */
CSSM_LIST Subject; /* subject */
CSSM_BOOL Delegate; /* permission to delegate */
CSSM_LIST AuthorizationTag; /* authorization field */
CSSM_LIST ValidityPeriod; /* validity information (dates) */
} CSSM_TUPLE, *CSSM_TUPLE_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_tuplegroup {
uint32 NumberOfTuples;
CSSM_TUPLE_PTR Tuples;
} CSSM_TUPLEGROUP, *CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR;
-
-
typedef CSSM_WORDID_TYPE CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE;
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PROMPTED_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE CSSM_WORDID_SIGNED_NONCE
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET CSSM_WORDID_SIGNED_SECRET
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC CSSM_WORDID_BIOMETRIC
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC
#define CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_THRESHOLD CSSM_WORDID_THRESHOLD
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE | General Description |
|---|---|
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD | The sample is a password or passphrase value. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_HASHED_PASSWORD | The sample is a password or passphrase value. The service provider receiving this value computes its hash and uses the hash value as the gathered sample. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD | The sample is a password or passphrase with an associated prompt value that can be present to an application when requesting this sample. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD | The sample is a password or passphrase gathered indirectly from a service provider operating a protected data acquisition path to acquire and verify this sample value. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE | A service provider presents a nonce to an application. The application signs the nonce with its private key. The resulting signed nonce is the sample value. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET | The application and the service provider have a shared secret. The application signs the shared secret with its private key. The signed secret is the sample value. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC | The sample is a biometric data sample provided by the caller and passed through the API. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_BIOMETRIC | The sample is a biometric data sample with an associated prompt value that can be present to an application when requesting this sample. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC | The sample is a biometric data sample, gathered indirectly from a service provider operating a protected data acquisition path to acquire and verify this sample value. |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_THRESHOLD | The sample is a choice of k-of-n samples. Each option is one of the defined sample types. |
When using this structure as an input parameter to a CDSA function, the structure can:
When using this structure as a response to a Challenge callback from a service provider, the structure must contain the sample type and sample value as immediate data values.
-
-
typedef struct cssm_sample {
CSSM_LIST TypedSample;
const CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID *Verifier;
} CSSM_SAMPLE, *CSSM_SAMPLE_PTR;
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length | No |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD | No |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length | No |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_HASHED_ PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_HASHED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length | No |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROMPTED_ PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length | No |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROTECTED_ PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Immediate Type and Protected Path Acquisition Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD | Optional |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_SIGNED_ NONCE | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE | Yes |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < signed nonce > value of specified length | Yes |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_SIGNED_ SECRET | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < signed secret > value of specified length | Yes |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET | Yes |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < signed secret > value of specified length | Yes |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template > value of specified length | Yes |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC | Yes |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template > value of specified length | Yes |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROMPTED_ BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Response to a Challenge callback | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template > value of specified length | Yes |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROTECTED_ BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents | Verifier Required? |
| Immediate Type and Protected Path Acquisition Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC | Yes |
-
-
typedef struct cssm_samplegroup {
uint32 NumberOfSamples;
const CSSM_SAMPLE *Samples;
} CSSM_SAMPLEGROUP, *CSSM_SAMPLEGROUP_PTR;
-
-
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI * CSSM_CHALLENGE_CALLBACK)
(const CSSM_LIST *Challenge,
CSSM_SAMPLEGROUP_PTR Response,
void *CallerCtx,
const CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS *MemFuncs);
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
|---|---|
| Challenge form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_HASHED_ PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_HASHED_PASSWORD |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_HASHED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| T& | |
| cb cb | |
| l l. | |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROMPTED_ PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <prompt string> value of specified length |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_SIGNED_ NONCE | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a <nonce to be signed> value of specified length |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_NONCE Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < signed nonce > value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_SIGNED_ SECRET | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_SIGNED_SECRET Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < signed secret > value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template > value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_PROMPTED_ BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <prompt string> value of specified length |
| Response form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_PROMPTED_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template > value of specified length |
| CSSM_SAMPLE_ TYPE_THRESHOLD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Challenge form | An (n+3)-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_SAMPLE_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = <k value> Third element: WordID = <n value> Fourth element: Sublist = (typed_challenge_list-1) Fifth element: Sublist = (typed_challenge_list-2) . . . n+3rd element: Sublist = (typed_challenge_list-n) |
| Response form | A k-entry array of sample responses, each responding to one of the typed challenges in the threshold list |
typedef enum cssm_cert_type {
CSSM_CERT_UNKNOWN = 0x00,
CSSM_CERT_X_509v1 = 0x01,
CSSM_CERT_X_509v2 = 0x02,
CSSM_CERT_X_509v3 = 0x03,
CSSM_CERT_PGP = 0x04,
CSSM_CERT_SPKI = 0x05,
CSSM_CERT_SDSIv1 = 0x06,
CSSM_CERT_Intel = 0x08,
CSSM_CERT_X_509_ATTRIBUTE = 0x09, /* X.509 attribute cert */
CSSM_CERT_X9_ATTRIBUTE = 0x0A, /* X9 attribute cert */
CSSM_CERT_TUPLE = 0x0B,
CSSM_CERT_ACL_ENTRY = 0x0C,
CSSM_CERT_MULTIPLE = 0x7FFE,
CSSM_CERT_LAST = 0x7FFF
} CSSM_CERT_TYPE, *CSSM_CERT_TYPE_PTR;
/* Applications wishing to define their own custom certificate
* type should define and publicly document a uint32 value greater
* than the CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_TYPE */
#define CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_TYPE 0x08000
typedef enum cssm_cert_encoding { CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_UNKNOWN = 0x00, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_CUSTOM = 0x01, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_BER = 0x02, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_DER = 0x03, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_NDR = 0x04, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_SEXPR = 0x05, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_PGP = 0x06, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_MULTIPLE = 0x7FFE, CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_LAST = 0x7FFF } CSSM_CERT_ENCODING, *CSSM_CERT_ENCODING_PTR;
/* Applications wishing to define their own custom certificate * encoding should create a uint32 value greater than the * CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_ENCODING */ #define CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_ENCODING 0x8000
typedef struct cssm_encoded_cert {
CSSM_CERT_TYPE CertType ; /* type of certificate */
CSSM_CERT_ENCODING CertEncoding ; /* encoding for this packed cert */
CSSM_DATA CertBlob ; /* packed cert */
} CSSM_ENCODED_CERT, *CSSM_ENCODED_CERT_PTR ;
typedef uint32 CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT, *CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_PTR;
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_NONE (0x00)
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_CUSTOM (0x01) /* void* */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_SEXPR (0x02) /* CSSM_LIST */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_COMPLEX (0x03) /* void* */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_OID_NAMED (0x04) /* CSSM_FIELDGROUP */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_TUPLE (0x05) /* CSSM_TUPLE */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_MULTIPLE (0x7FFE)
/* multiple forms, each cert carries a parse format indicator */
#define CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT_LAST (0x7FFF)
/* Applications wishing to define their own custom parse
format should create a * uint32 value greater than the
CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT */
#define CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT (0x8000)
typedef struct cssm_parsed_cert {
CSSM_CERT_TYPE CertType ; /* certificate type */
CSSM_CERT_PARSE_FORMAT ParsedCertFormat ;
/* struct of ParsedCert */
void *ParsedCert ; /* parsed cert (to be typecast) */
} CSSM_PARSED_CERT, *CSSM_PARSED_CERT_PTR ;
The representation used for each form (such as type, encoding, and format) is included in the applicable substructure. At least one of the two representations must be present at any given time. The omitted representation is indicated by a NULL pointer value. When the omitted alternate representation is generated, it can be added to this structure at any time. When both representations are included, those representations must be equivalent forms of a single certificate. This structure is provided for performance and convenience reasons. For security purposes, however, only a signed certificate (necessarily encoded) can have its signature checked.
typedef struct cssm_cert_pair {
CSSM_ENCODED_CERT EncodedCert; /* an encoded certificate blob */
CSSM_PARSED_CERT ParsedCert; /* equivalent parsed certificate */
} CSSM_CERT_PAIR, *CSSM_CERT_PAIR_PTR;
The certificate can have an equivalent parsed representation. If the parsed representation is provided it is contained in ParsedCert.
The certificate can have an equivalent packed representation. If the packed representation is provided it is contained in EncodedCert.
typedef uint32 CSSM_CERTGROUP_TYPE, *CSSM_CERTGROUP_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_CERTGROUP_DATA (0x00)
#define CSSM_CERTGROUP_ENCODED_CERT (0x01)
#define CSSM_CERTGROUP_PARSED_CERT (0x02)
#define CSSM_CERTGROUP_CERT_PAIR (0x03)
Each certificate in the mixed group can be represented in one or two forms:
When using encoded and parsed representations, the specific format used for each certificate and each representation must be included in the applicable substructure. At least one of the two representations must be present in each list entry. When a single entry includes both representations, those representations are assumed but not guaranteed to be equivalent representations of a single certificate.
The number of certificates in the group is contained in the structure.
typedef struct cssm_certgroup {
CSSM_CERT_TYPE CertType;
CSSM_CERT_ENCODING CertEncoding;
uint32 NumCerts ; /* # of certificates in this list */
union {
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertList; /* legacy list of single type
certificate blobs */
CSSM_ENCODED_CERT_PTR EncodedCertList ;
/* list of multi-type
certificate blobs */
CSSM_PARSED_CERT_PTR ParsedCertList;
/* list of multi-type parsed certs */
CSSM_CERT_PAIR_PTR PairCertList;
/* list of single or multi-type certs
with two representations:
blob and parsed */
} GroupList;
CSSM_CERTGROUP_TYPE CertGroupType;
/* type of structure in the GroupList */
void *Reserved ; /* reserved for implementation
dependent use */
} CSSM_CERTGROUP, *CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR;
| CertGroupType Value | Field Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CSSM_CERTGROUP_DATA | CertList | (Legacy) A pointer to an array of CSSM_DATA structures. Each CertList array entry references a single certificate structure and indicates the length of the structure. A single type and encoding apply to all certificates in this group. The type and encoding are indicated in CertType and CertEncoding respectively. |
| CSSM_CERTGROUP_
ENCODED_CERT | EncodedCertList | A pointer to an array of CSSM_ENCODED_CERT structures. Each EncodedCertList array entry references a certificate in an opaque, single byte-array representation, and describes the format of the certificate data contained in the byte-array. Each certificate encoding and type can be distinct, as indicated in each array element. |
| CSSM_CERTGROUP_
PARSED_CERT | ParsedCertList | A pointer to an array of CSSM_PARSED_CERT structures. Each ParsedCertList array entry references a certificate in a parsed representation, and indicates the certificate type and parse format of that certificate. |
| CSSM_CERTGROUP_
CERT_PAIR | PairCertList | A pointer to an array of
CSSM_CERT_PAIR structures.
Each PairCertList array entry aggregates two certificate representations: an opaque encoded certificate blob, and a parsed certificate representation. At least one of the two representations must be present in each array entry. If both are present, they are assumed but not guaranteed to correspond to one another. If the parsed form is being used in a security sensitive operation, then it must have been verified against the packed, encoded form, whose signature must have been verified |
-
-
typedef struct cssm_base_certs {
CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle;
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
CSSM_CERTGROUP Certs;
} CSSM_BASE_CERTS, *CSSM_BASE_CERTS_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_access_credentials {
CSSM_STRING EntryTag;
CSSM_BASE_CERTS BaseCerts;
CSSM_SAMPLEGROUP Samples;
CSSM_CHALLENGE_CALLBACK Callback;
void *CallerCtx;
} CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS, *CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR;
-
-
typedef sint32 CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_ANY CSSM_WORDID__STAR_
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD CSSM_WORDID_THRESHOLD
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD CSSM_WORDID_PROMPTED_PASSWORD
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY CSSM_WORDID_PUBLIC_KEY
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_HASHED_SUBJECT CSSM_WORDID_HASHED_SUBJECT
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC CSSM_WORDID_BIOMETRIC
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC CSSM_WORDID_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME CSSM_WORDID_LOGIN_NAME
#define CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME CSSM_WORDID_PAM_NAME
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_* | General Description |
|---|---|
| ANY | The subject matches everyone. The AuthorizationTag associated with this subject represents operations that can be performed by anyone. |
| THRESHOLD | The subject specifies a nested "k-of-n" subject. Each of the options is another defined ACL subject type. |
| PASSWORD | The subject value is a password or passphrase value. |
| PROTECTED_PASSWORD | The subject value is dynamically acquired and matched by a service that manages a protected data acquisition path to gather and verify a password or passphrase value. |
| PROMPTED_PASSWORD | The subject value is a password or passphrase value with an associated prompt value. The prompt value can be presented to an application. |
| PUBLIC_KEY | The subject value is a public key of some specified format. |
| HASHED_SUBJECT | The subject value is the hash value of any ACL Subject of valid type. For example, the hash of a password. |
| BIOMETRIC | The subject value is an enrolled biometric template value. |
| PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC | The subject value is acquired and matched by a service that manages a protected data acquisition path to gather and verify a biometric sample from a Biometric Sensor |
| LOGIN_NAME | The subject value is a login name. The name space of login names is defined and managed by the service provider. |
| EXT_PAM_NAME | The subject value is a user name. The name space for user names is defined and managed by the Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM), an external service. PAM is a specification standard of The Open Group. |
The operations named by these constants correspond to functions defined in the CDSA and CSSM APIs. Service providers can define names for additional controlled operations. Service providers are encouraged to identify two types of operations:
Vendors defining new constants must manage the integer name space
to avoid definitions that conflict with other vendors.
-
-
/* Authorization tag type */
typedef sint32 CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_TAG;
/* All vendor specific constants must be in the number range
starting at CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_TAG_VENDOR_DEFINED_START
*/
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_TAG_VENDOR_DEFINED_START (0x00010000)
/* No restrictions. Permission to perform all operations on
the resource or available to an ACL owner.
*/
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ANY CSSM_WORDID__STAR_
/* Defined authorization tag values for CSPs */
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_LOGIN CSSM_WORDID_LOGIN
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_GENKEY CSSM_WORDID_GENKEY
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DELETE CSSM_WORDID_DELETE
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_WRAPPED CSSM_WORDID_EXPORT_WRAPPED
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_CLEAR CSSM_WORDID_EXPORT_CLEAR
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_IMPORT_WRAPPED CSSM_WORDID_IMPORT_WRAPPED
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_IMPORT_CLEAR CSSM_WORDID_IMPORT_CLEAR
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_SIGN CSSM_WORDID_SIGN
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ENCRYPT CSSM_WORDID_ENCRYPT
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DECRYPT CSSM_WORDID_DECRYPT
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_MAC CSSM_WORDID_MAC
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DERIVE CSSM_WORDID_DERIVE
/* Defined authorization tag values for DLs */
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DBS_CREATE CSSM_WORDID_DBS_CREATE
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DBS_DELETE CSSM_WORDID_DBS_DELETE
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_READ CSSM_WORDID_DB_READ
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_INSERT CSSM_WORDID_DB_INSERT
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_MODIFY CSSM_WORDID_DB_MODIFY
#define CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_DELETE CSSM_WORDID_DB_DELETE
The meaning of each authorization tag is listed in the following table.
The tag may have slightly different meanings depending on the ACL type.
| Authorization Tag
CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_* | Meaning
The subject of the ACL is authorized to |
|---|---|
| ANY | No restrictions. Permission to perform all operations on the resource. |
| LOGIN | login to the subservice. |
| GENKEY | generate a new key resource managed by the subservice. |
| DELETE | delete resources managed by the subservice. |
| EXPORT_WRAPPED | export the key in a wrapped form. |
| EXPORT_CLEAR | export the key as cleartext. |
| IMPORT_WRAPPED | import a new key resource to be managed by the subservice. The new resource is wrapped. |
| IMPORT_CLEAR | import a new key resource to be managed by the subservice. The new resource is cleartext. |
| SIGN | perform signature operations using the key. |
| ENCRYPT | perform encryption operations using the key. |
| DECRYPT | perform decryption operations using the key. |
| MAC | perform Message Authentication Code (MAC) operation using the key. |
| DERIVE | perform key derivation operations using the key as the basis. |
| DBS_CREATE | create new databases managed by the subservice. |
| DBS_DELETE | delete existing databases managed by the subservice. |
| DB_READ | read the contents of record in a database. |
| DB_INSERT | insert new records into a database. |
| DB_MODIFY | change the value of meta-data or the data value of records in a database. |
| DB_DELETE | delete existing records in a database. |
Each type of ACL has a set of authorization tags that are valid.
The following table lists each defined ACL type and the valid attribute
values for those ACLs.
| ACL Type | Valid Authorization Tags |
|---|---|
| CSP Login | CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ANY CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_LOGIN CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_GENKEY CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DELETE CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_IMPORT_WRAPPED CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_IMPORT_CLEAR |
| CSP Secret Key | CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ANY CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DELETE CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_WRAPPED CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_CLEAR CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ENCRYPT CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DECRYPT CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_MAC CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DERIVE |
| CSP Private Key | CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ANY CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DELETE CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_WRAPPED CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_EXPORT_CLEAR CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_SIGN CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DECRYPT CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DERIVE |
| DL Database | CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_ANY CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DBS_CREATE CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DBS_DELETE CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_READ CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_INSERT CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_DB_MODIFY |
-
-
typedef struct cssm_authorizationgroup {
uint32 NumberOfAuthTags;
CSSM_ACL_AUTHORIZATION_TAG *AuthTags;
} CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP, *CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_validity_period {
CSSM_DATA StartDate;
CSSM_DATA EndDate;
} CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD, *CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD_PTR;
When an application uses this structure to provide initial values for an ACL entry, the structure is passed as an input parameter to a CDSA security service function. The structure must contain all fields as immediate data values, except the TypedSubject field. An application can provide the value of the TypedSubject field by:
An ACL entry prototype is considered to be a duplicate of an existing ACL entry if the entries have equal values for all fields except EntryTag.
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_entry_prototype {
CSSM_LIST TypedSubject;
CSSM_BOOL Delegate;
CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP Authorization;
CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD TimeRange;
CSSM_STRING EntryTag;
} CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_PROTOTYPE, *CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_PROTOTYPE_PTR;
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
ANY | CSSM_LIST Contents |
|---|---|
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_ANY |
| Query-response Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_ANY |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
THRESHOLD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | An (n+3)-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = <k value> Third element: WordID = <n value> Fourth element: Sublist = (typed_subject_list-1) Fifth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-2) . . . n+3rd element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-n) |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A 3-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = <k value> Third element: WordID = <n value> |
| Query-response Form | An (n+3)-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = <k value> Third element: WordID = <n value> Fourth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-1) Fifth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-2) . . . n+3rd element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-n) |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD |
| Query-response Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROMPTED_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A three-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <prompt string> value of specified length Third element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD |
| Query-response Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <prompt string> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROTECTED_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Protected Path Acquisition Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure identifying a <service provider subservice uid> in memory (by starting address and length). |
| Query-response Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PUBLIC_KEY | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A three-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY Second element: Word is a CSSM_KEYBLOB_RAW_FORMAT value Third element: Word is the keyblob |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY |
| Query-response Form | A three-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY Second element: Word is a CSSM_KEYBLOB_RAW_FORMAT value Third element: Word is the keyblob |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a < biometric template> value of specified length |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC |
| Query-response Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Protected Path Acquisition Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure identifying a <service provider subservice uid> in memory (by starting address and length). |
| Query-response Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
LOGIN_NAME | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < login name> value of specified length |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME |
| Query-response Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < login name> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
EXT_PAM_NAME | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| Immediate Type and Value Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < PAM-user name> value of specified length |
| Immediate Type and Request for Callback Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME |
| Query-response Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < PAM_user name> value of specified length |
After creation, the Owner may retrieve the Owner definition in the form of a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE, and replace it with a new Owner definition.
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_owner_prototype {
CSSM_LIST TypedSubject;
CSSM_BOOL Delegate;
} CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE, *CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE_PTR;
See CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_PROTOTYPE for a definition of TypedSubject and Delegate.
-
-
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI * CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_CALLBACK)
(const CSSM_LIST *SubjectRequest,
CSSM_LIST_PTR SubjectResponse,
void *CallerContext,
const CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS *MemFuncs);
If the service provider supports more than one subject type, then the first list element indicates the type CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD with a k-value of one and an n-value equal to the number of supported subject types. The following n list elements describe each supported subject type. A table defining the CSSM_LIST contents for each possible SubjectRequest and SubjectResponse pair is defined in a table below.
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
ANY | CSSM_LIST Contents |
|---|---|
| SubjectRequest Form | Not used. |
| SubjectResponse Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_ANY |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
THRESHOLD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | An (n+3)-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = 1 Third element: WordID = <n value> Fourth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-1) Fifth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-2) . . . n+3rd element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-n) |
| SubjectResponse Form | An (n+3)-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_THRESHOLD Second element: WordID = <k value> Third element: WordID = <n value> Fourth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-1) Fifth element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-2) . . . n+3rd element: Sublist = (typed_ subject _list-n) |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD SubjectResponse Form!A two-element list First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROMPTED_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD SubjectResponse Form!A three-element list First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROMPTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <prompt string> value of specified length Third element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated <password string> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROTECTED_PASSWORD | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD SubjectResponse Form!A two-element list First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_PASSWORD Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure identifying a <service provider subservice uid> in memory (by starting address and length). |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PUBLIC_KEY | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY |
| SubjectResponse Form | A three-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PUBLIC_KEY Second element: Word is a CSSM_KEYBLOB_RAW_FORMAT value Third element: Word is the keyblob |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC |
| SubjectResponse Form | A three-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure identifying a <service provider subservice uid> in memory (by starting address and length). Third element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a <biometric template> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC |
| SubjectResponse Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_PROTECTED_BIOMETRIC Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure identifying a <service provider subservice uid> in memory (by starting address and length). |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
LOGIN_NAME | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME |
| SubjectResponse Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_LOGIN_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < login name> value of specified length |
| CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_
EXT_PAM_NAME | CSSM_LIST Contents |
| SubjectRequest Form | A one-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME |
| SubjectResponse Form | A two-element list
First element: WordID = CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_TYPE_EXT_PAM_NAME Second element: Word is a CSSM_DATA structure referencing a non-terminated < PAM_user name> value of specified length |
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_entry_input {
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_PROTOTYPE Prototype;
CSSM_ACL_SUBJECT_CALLBACK Callback;
void *CallerContext;
} CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INPUT, *CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INPUT_PTR;
-
-
typedef struct cssm_resource_control_context {
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR AccessCred;
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INPUT InitialAclEntry;
} CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT, *CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT_PTR;
-
-
typedef CSSM_HANDLE CSSM_ACL_HANDLE;
The ACL information structure does not indicate the resource for which access control is being defined. A caller requests ACL information for a specific resource. The returned ACL entries are associated with the target resource.
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_entry_info {
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_PROTOTYPE EntryPublicInfo;
CSSM_ACL_HANDLE EntryHandle;
} CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO, *CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO_PTR;
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE;
#define CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_ADD (1)
#define CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_DELETE (2)
#define CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_REPLACE (3)
-
-
typedef struct cssm_acl_edit {
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE EditMode;
CSSM_ACL_HANDLE OldEntryHandle;
const CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INPUT *NewEntry;
} CSSM_ACL_EDIT, *CSSM_ACL_EDIT_PTR;
-
-
#if defined(WIN32)
typedef FARPROC CSSM_PROC_ADDR;
#else
typedef void (CSSMAPI *CSSM_PROC_ADDR) ();
#endif
typedef CSSM_PROC_ADDR *CSSM_PROC_ADDR_PTR;
-
-
typedef uint32 CSSM_KR_POLICY_TYPE;
#define CSSM_KR_INDIV_POLICY (0x00000001)
#define CSSM_KR_ENT_POLICY (0x00000002)
#define CSSM_KR_LE_MAN_POLICY (0x00000003)
#define CSSM_KR_LE_USE_POLICY (0x00000004)
-
-
typedef struct cssm_func_name_addr {
CSSM_STRING Name;
CSSM_PROC_ADDR Address;
}CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR, *CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR_PTR;
-
-
typedef void * (CSSMAPI *CSSM_MALLOC)
( uint32 size,
void * allocref)
typedef void (CSSMAPI *CSSM_FREE)
(void * memblock,
void * allocref)
typedef void * (CSSMAPI *CSSM_REALLOC)
(void * memblock,
uint32 size,
void * allocref)
typedef void * (CSSMAPI *CSSM_CALLOC)
(uint32 num,
uint32 size,
void * allocref)
typedef struct cssm_memory_funcs {
CSSM_MALLOC malloc_func;
CSSM_FREE free_func;
CSSM_REALLOC realloc_func;
CSSM_CALLOC calloc_func;
void *AllocRef;
} CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS, *CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR;
typedef CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS;
typedef CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS *CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR;
See
The Error Values that can be returned by CSSM functions can be
either derived from the Common Error
Codes defined in
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INTERNAL_ERROR \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INTERNAL_ERROR)#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MDS_ERROR \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_INPUT_POINTER \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_INPUT_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_FUNCTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_FUNCTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_SELF_CHECK_FAILED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_SELF_CHECK_FAILED)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_OS_ACCESS_DENIED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_OS_ACCESS_DENIED)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_FUNCTION_FAILED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_FUNCTION_FAILED)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_MANIFEST_VERIFY_FAILED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_MODULE_MANIFEST_VERIFY_FAILED)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_GUID)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_ INCOMPATIBLE_VERSION \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INCOMPATIBLE_VERSION)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_PRIVILEGE_NOT_GRANTED \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_PRIVILEGE_NOT_GRANTED)
#define CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR \ (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRORCODE_COMMON_EXTENT+0x10)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+1)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_PVC_ALREADY_CONFIGURED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+2)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_PVC (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+3)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_LOAD_FAILED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+4)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_UNLOAD_FAILED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+5)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_LOAD_FAILED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+6)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+7)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_UNLOAD_FAILED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+8)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_LIB_REF_NOT_FOUND (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+9)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ADDIN_FUNCTION_TABLE \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+10)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+11)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+12)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SERVICE_MASK \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+13)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_NOT_LOADED (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+14)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SUBSERVICEID (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+15)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+16)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE (CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+17)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_NOT_IN_CONTEXT \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+18)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_MANAGER_INITIALIZE_FAIL \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+19)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_MANAGER_NOT_FOUND \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+20)
#define CSSMERR_CSSM_EVENT_NOTIFICATION_CALLBACK_NOT_FOUND \
(CSSM_CSSM_BASE_CSSM_ERROR+21)
CSSM_Init
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_Init( const CSSM_VERSION *Version, CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE Scope, const CSSM_GUID * CallerGuid, CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy, CSSM_PVC_MODE *PvcPolicy, const void *Reserved)
This function initializes CSSM and verifies that the version of CSSM expected by the application is compatible with the version of CSSM on the system. This function should be called at least once by the application. It is an error to call any function of the CSSM API other thanCSSM_Init() before a call toCSSM_Init() has returned successfully (that is, with CSSM_OK).Implementations of CSSM may have platform specific characteristics associated with the implementation of
CSSM_SetPrivilege() API. The privilege value may have thread specific scope or process specific scope. The application can specify the anticipated scope atCSSM_Init() . If the anticipated scope is not appropriate for the implementation, an error is returned. The scope can be configured only once. Subsequent attempts to configure scope are ignored.The CSSM integrity model includes the ability to make and check assertions about trusted dynamically loaded libraries. Checking assertions happens while the program executes. It is known as Pointer Validation Checking (PVC). Pointer validation checking may be applied every time execution flow crosses the CSSM API or SPI interfaces.
Performing pointer validation checks has two purposes:
- It allows exportation of CSSM
- It aids in detering unanticipated run-time modification of the program
The CSSM can be configured to bypass pointer validation under some circumstances. Pointer validation cannot be bypassed when privileged operations are being performed.
The prerequisites for performing PVC on another module, be it service provider, CSSM, or other library, are:
- The module must have been signed and have an accompanying Signed Manifest
- The module must be loaded into process address space
- An entry-point into the module must be available
Typically, the entry-points are discovered when a module's functions are called by another module. The CSSM will perform pointer validation checks based on the configured checking policy. Checking policies are established by the manufacturers of CSSM and other libraries. The checking policy to be applied during execution is configured using the
CSSM_Init() call. The policy can be configured once during the life of the process and occurs the first timeCSSM_Init() is called.PVC Policy Configuration Options
Pointer validation checking can be applied at the CSSM API interface, the CSSM SPI interface or both. The CSSM vendor can configure a default policy through instructions contained in the CSSM signed manifest. Manifest attributes pertaining to pointer validation checking are defined as follows:
Module Tag Value Description CSSM CDSA_PVC_API unspecified CSSM will perform PVC checks at the API boundary CSSM CDSA_PVC_API OFF CSSM will not perform PVC checks at the API boundary CSSM CDSA_PVC_SPI unspecified CSSM will perform PVC checks at the SPI boundary CSSM CDSA_PVC_SPI OFF CSSM will not perform PVC checks at the SPI boundary App CDSA_PVC_API EXEMPT The calling module is allowed to override the CSSM policy for the API boundary App CDSA_PVC_API unspecified The calling module cannot weaken the CSSM API policy App CDSA_PVC_SPI EXEMPT The calling module is allowed to override the CSSM policy for the SPI boundary App CDSA_PVC_SPI unspecified The calling module cannot weaken the CSSM SPI policy The PvcPolicy parameter to
CSSM_Init() configures the run-time policy for the process. The PvcPolicy parameter is a bitmask allowing both API and SPI policies to be specified simultaneously. Unspecified policies default to the most conservative operational mode. The CSSM performs pointer validation checks unless explicitly disabled. Application modules may not override CSSM policy unless exemptions are explicitly granted. The following table shows the what policies may be configured for various manifest attribute values:
CSSM Manifest Calling Module Manifest Acceptable PvcPolicy Values CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> CDSA_PVC_API=EXEMPT API checks: off (0) or on (1) CDSA_PVC_API=OFF CDSA_PVC_API=EXEMPT API checks: off (0) or on (1) CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> API checks: on (1) CDSA_PVC_API=OFF CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> API checks: off (0) or on (1) The following table shows the PvcPolicy configuations available for the SPI:
SSM Manifest Calling Module Manifest Acceptable PvcPolicy Values CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> CDSA_PVC_SPI=EXEMPT SPI checks: off (0) or on (2) CDSA_PVC_SPI =OFF CDSA_PVC_SPI=EXEMPT SPI checks: off (0) or on (2) CDSA_PVC_SPI =<n/a> CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> SPI checks: on (2) CDSA_PVC_SPI =OFF CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> SPI checks: off (0) or on (2) If an application module does not have a manifest and CSSM requires the application module be subject to pointer validation checks, then pointer validation checks fail and CSSM will not operate with the anonymous module. All service provider modules are expected to have signed maniefests.
- Version (input)
The major and minor version number of the CSSM release the application is compatible with.
- Scope (input)
The scope of the global privilege value. The scope may either process scope wide (CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_PROCESS) or thread wide (CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_THREAD). This parameter is ignored after the first call toCSSM_Init() .
- CallerGuid (input)
The GUID associated with the caller. This GUID is used to locate the caller's credentials when evaluating the request for privileges.
- KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY flag directing CSSM what embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
- PvcPolicy (input/output)
Configures the way in which pointer validation checks will be performed. If not the first call toCSSM_Init() , the previously configured policy is returned in the PvcPolicy bitmask and theCSSM_Init() call continues processing. If successfully completed, the error code CSSMERR_CSSM_PVC_ALREADY_CONFIGURED is returned.
Value Description 0 PVC validation is not performed 1 PVC validation is performed on application modules 2 PVC validation is performed on service provider modules 3 Both types of PVC validations are performed
- Reserved (input)
A reserved input.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
CSSMERR_CSSM_PVC_ALREADY_CONFIGURED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_PVC
CSSM_Terminate
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_Terminate ( )
This function terminates the caller's use of CSSM. CSSM can cleanup all internal state associated with the calling application. This function must be called once by each application.
CSSM_Terminate() must be called one time for each timeCSSM_Init() was previously called. CSSM services remain available to the program until the final call toCSSM_Terminate() completes. After that final call, all information introduced by the caller (including privileges, handles, contexts, introduced libraries, etc.) is lost, and it is an error to subsequently call any CSSM API function other thanCSSM_Init() .
None
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values.
CSSM_Init() .
CSSM_ModuleLoad
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleLoad (const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid, CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy, CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler AppNotifyCallback, void* AppNotifyCallbackCtx)
This function initializes the security service service module. Initialization includes registering the application's module-event handler and enabling events with the security service service module. The application can choose to provide an event handler function to receive notification of insert, remove and fault events. The specified event handler is the single callback points for all attached sessions with the specified service module.The function
CSSM_Init() must be invoked prior to callingCSSM_ModuleLoad() . The functionCSSM_ModuleAttach() can be invoked multiple times per call toCSSM_ModuleLoad() .
- ModuleGuid (input)
The GUID of the module selected for loading.
- KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY flag directing CSSM what embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
- AppNotifyCallback (input/optional)
The event notification function provided by the caller. This defines the callback for event notifications from the loaded (and later attached) service module.
- AppNotifyCallbackCtx (input/optional)
When the selected service module raises an event, this context is passed as an input to the event handler specified by AppNotifyCallback. CSSM does not interpret or modify the value of AppNotifyCallbackCtx.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_LOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_LOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
CSSM_ModuleUnload
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleUnload (const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid, CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler AppNotifyCallback, void* AppNotifyCallbackCtx)
The function deregisters event notification callbacks for the caller identified by ModuleGuid.CSSM_ModuleLoad() is the analog call toCSSM_ModuleLoad() . If all registered callbacks registered with CSSM are removed, then CSSM unloads the service module that was loaded by calls toCSSM_ModuleLoad() . Calls toCSSM_ModuleUnload() that are not matched with a previous call toCSSM_ModuleLoad() result in an error.The CSSM uses the three input parameters ModuleGuid, AppNotifyCallback, and AppNotifyCallbackCtx to uniquely identify registered callbacks.
This function should be invoked after all necessary calls to
CSSM_ModuleDetach() have been performed.
- ModuleGuid (input)
The GUID of the module selected for unloading.
- AppNotifyCallback (input/optional)
The event notification function to be de-registered. The function must have been provided by the caller inCSSM_ModuleLoad() .
- AppNotifyCallbackCtx (input/optional)
The event notification context that was provided in the corresponding call toCSSM_ModuleLoad() .
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_UNLOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_UNLOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EVENT_NOTIFICATION_CALLBACK_NOT_FOUND
CSSM_Introduce
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_Introduce (const CSSM_GUID *ModuleID, CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy)
TheCSSM_Introduce() function identifies a dynamically loadable executable module (e.g. DLL) to the CSSM framework. CSSM uses the ModuleID information to locate the signed manifest and library on the host platform. The Module Directory Service (MDS) should be used to obtain the information. CSSM performs an integrity crosscheck on the module identified by ModuleID and caches the result in an internal structure. Integrity crosscheck uses the KeyHierarchy information to determine which classes of embedded public keys must serve as anchors when doing certificate path validation. If the export key hierarchy is specified, the set of export privileges contained in the manifest are retrieved from the manifest and saved with the integrity state information in the cache. Privileges granted to a module are accepted only if the manifest sections containing the privilege set have been signed by a principal in the export key hierarchy class and that hash of the module binary is part of the hash of the privilege attributes.
CSSM_Introduce() may be called at any time afterCSSM_Init() , by any module, on behalf of any module. Once a module is introduced into CSSM the load location of the module must not change. If the load location changes then the module must be re-introduced. Once introduced, the module load location, integrity and privilege information is held untilCSSM_Terminate() is called or the process terminates. Initialization of internal data structures maintaining the table of introductions is performed whenCSSM_Init() is called.If
CSSM_Introduce() is called on behalf of another module, then the caller needs to make sure that the other module is loaded into the process address space. If the library is already loaded into process address space, but a reference to the library cannot be obtained, a different error is returned (CSSMERR_CSSM_LIB_REF_NOT_FOUND).
- ModuleID (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the calling library or other library that may call CDSA interfaces. The GUID is used to locate the signed manifest credentials of the named module to calculate module integrity information.
- KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY flag directing CSSM what embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
CSSMERR_CSSM_LIB_REF_NOT_FOUND
CSSM_Unintroduce
CSSM_RETURN CSSM_Unintroduce
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleID)
The
CSSM_Unintroduce()
function removes the module referenced by
ModuleID
from the list of module information maintained by the CSSM framework.
A caller may
un-introduce
modules other than itself if the caller has been previously introduced.
- ModuleID (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the calling library or other library that may call
CDSA interfaces. The GUID is used to locate the module integrity
and privilege information. If the
ModuleID
is NULL then the caller will be "un-introduced".
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSM_ModuleAttach
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleAttach
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
const CSSM_VERSION *Version,
const CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS *MemoryFuncs,
uint32 SubserviceID,
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE SubServiceType,
CSSM_ATTACH_FLAGS AttachFlags,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR *FunctionTable,
uint32 NumFunctionTable,
const void *Reserved,
CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE_PTR NewModuleHandle)
This function attaches the service provider module and verifies that
the version of the module expected by the application is compatible
with the version on the system. The module can implement sub-services
(as described in the service provider's documentation). The caller can
specify a specific sub-service provided by the module.
If the sub-service is supported as part of the CSSM framework as well
as by an EMM,
ModuleAttach
attaches the Service Provider to the CSSM framework. If the sub-service
is only supported by an EMM,
ModuleAttach
loads the appropriate EMM. The Service Provider is given an indication
of whether it is being attached to the CSSM framework or an EMM.
The caller may provide a function table containing
function-names for the desired services. On output each function name
is matched with an API function pointer. The caller can use the pointers
to invoke service module operations through CSSM.
- ModuleGuid (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_GUID structure containing the global unique
identifier for the CSP module.
- Version (input)
The major and minor version number of CDSA that
the application is compatible with.
- MemoryFuncs (input)
A structure containing pointers to the memory routines.
- SubserviceID (input)
A
SubServiceID
identifying a particular subservice within the module.
Subservice IDs can be obtained from MDS or gleaned from insertion events
reported through the
callback
function installed through
CSSM_ModuleLoad() .
Modules that provide only one service may use zero as
their Subservice ID.
- SubServiceType (input)
A service mask describing the type of service the caller is requesting
of the service provider module.
- AttachFlags (input)
A mask representing the caller's request for session-specific services.
- KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY flag directing CSSM what embedded key to use
when verifying integrity of the named module.
- FunctionTable (input/output/optional)
A table of function-name and API function-pointer pairs. The caller
provides the name of the functions as input. The corresponding API
function pointers are returned on output. The function table allows
dynamic linking of CDSA interfaces, including interfaces to Elective Module
Managers, which are transparently loaded by CSSM during
CSSM_ModuleAttach() .
- NumFunctionTable (input)
The number of entries in the
FunctionTable
parameter. If no
FunctionTable
is provided this value must be zero.
- Reserved (input)
This field is reserved for future use. It should always be set to zero
- NewModuleHandle (output)
A new module handle that can be used to interact with the requested
service provider. The value will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the
function fails.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ADDIN_FUNCTION_TABLE
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SERVICE_MASK
CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_NOT_LOADED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SUBSERVICEID
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSM_ModuleDetach()
CSSM_ModuleDetach
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleDetach (CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle)
This function detaches the application from the service provider module.
- ModuleHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider module.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values.
CSSM_ModuleAttach()
CSSM_SetPrivilege
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SetPrivilege (CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
TheCSSM_SetPrivilege() function accepts as input a privilege value and stores it internal to the CSSM framework. The integrity credentials of the module callingCSSM_SetPrivilege() must be verified by CSSM before the privilege value is updated. Integrity credentials are established usingCSSM_Introduce() . CSSM will perform pointer validation check to ensure the caller has been previously introduced.CSSM_SetPrivilege() will fail if no integrity information can be found for the caller.After pointer validation checks, CSSM verifies the requested privilege is authorized. This is done by comparing Privilege with the set of privileges contained in the caller manifest. If Privilege is not a member, the
CSSM_SetPrivilege() call fails.Subsequent calls to the framework that require privileges inherit the privilege value previously established by
CSSM_SetPrivilege() . The CSSM will perform pointer validation checks on the API caller before servicing the API call. If OK, then the Privilege value is supplied to the SPI function.Internally, CSSM builds and maintains privilege information based on the chosen scope of the implementation. The scope may be dictated by the capabilities of the platform hosting the CSSM. If threading is available, the privilege value may be associated with the thread ID of the currently executing thread. In this scenario, CSSM may manage a table of tuples consisting of threadID and privilege value. If threading is not available, the privilege value may be global to the process.
Since the selected privilege value is shared, the application programmer should take precautions to reset the privilege value whenever program flow leaves the caller's module and again when control flow returns. In general, anytime there is a possibility for
CSSM_SetPrivilege() to be called while within the context of the security critical section,CSSM_SetPrivilege() should be called again. Otherwise, the module receiving execution control could have calledCSSM_SetPrivilege() resulting in the privilege value being reset.Data structures used to maintain the global privilege value should be initialized in
CSSM_Init() . This includes lock initialization and preliminary resource allocation.CSSM_Init() is assumed to be idempotent with respect to shared structure initialization. This meansCSSM_Init() will ensure a single thread initializes the shared structure and subsequent calls toCSSM_Init() will not re-initialize it. A reference count of calls toCSSM_Init() is needed to ensure matching calls toCSSM_Terminate() are handled.Resource cleanup is performed at
CSSM_Terminate() , after the reference count falls to zero. The last call toCSSM_Terminate() results in shared resources being freed and lock structures being released.
- Privilege (input)
The CSSM_PRIVILEGE value to be applied to subsequent calls to CSSM interfaces.
See the general error codes and common error codes and values section.
CSSM_GetPrivilege
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetPrivilege (CSSM_PRIVILEGE *Privilege);
TheCSSM_GetPrivilege() function returns the CSSM_PRIVILEGE value currently established in the framework.
- Privilege (output)
The CSSM_PRIVILEGE value currently set.
See General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values sections.
CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle (CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle, CSSM_GUID_PTR ModuleGUID)
Returns the GUID of the attached module identified by the specified handle.
- ModuleHandle (input)
Handle of the module for which the GUID should be returned.
- ModuleGUID (output)
GUID of the module associated with ModuleHandle.n.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values sections.
CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle()
CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle (CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle, CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID_PTR SubserviceUID)
This function completes a structure containing the persistent unique identifier of the attached module subservice, as identified by the input handle.
- ModuleHandle (input)
Handle of the module subservice for which the subservice unique identifier should be returned.
- SubserviceUID (output)
Subservice UID value associated with ModuleHandle. The caller has to allocate the buffer.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values sections.
CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle()
CSSM_ListAttachedModuleManagers
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ListAttachedModuleManagers (uint32 *NumberOfModuleManagers, CSSM_GUID_PTR ModuleManagerGuids)
This function returns a list of GUIDs for the currently attached/active module managers in the CSSM environment.
- NumberOfModuleManagers (input/output)
The number of GUIDs in the array. If the array is not large enough, then the actual number needed is returned and the error CSSMERR_CSSM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL is returned. The caller should then allocate an appropriately-sized list and call the function again. If the supplied list is larger than needed, the number of module managers found is returned and no error is set.
- ModuleManagerGuids (input/output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_GUID structures, one per active module manager. The caller allocates this array.
CSSMERR_CSSM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSM_GetAPIMemoryFunctions
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetAPIMemoryFunctions (CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE AddInHandle, CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR AppMemoryFuncs)
This function retrieves the memory function table associated with the security service service module identified by the input handle.
- AddInHandle (input)
The handle to the security service service module that is associated with the requested memory function table.
- AppMemoryFuncs (output)
Pointer to an empty memory functions table. Upon function return, the table is filled with the memory function pointers associated with the specified attach handle. Caller has to allocate the buffer.
CSSM_OK if the function was successful.
See General Error Codes and Common Error Codes and Values sections.
None.
| Contents | Next section | Index |