Previous section.
Common Security: CDSA and CSSM, Version 2 (with corrigenda)
Copyright © 2000 The Open Group
Trust Policy Services API
Overview
Digital Certificate
A digital certificate is the binding of some identification to a public
key in a particular domain. When a certificate is issued (created and
signed) by the owner and authority of a domain, the binding between key
and identity is validated by the digital signature on the certificate.
The issuing authority also associates a level of trust with the
certificate. The actions of the user, whose identity is bound to the
certificate, are constrained by the trust policy governing the
certificate's usage domain. A digital
certificate is intended to be an unforgeable credential in cyberspace.
The use of digital certificates is the foundation on which the CDSA is
designed. The CDSA assumes the concept of digital certificates in its
broadest sense. Applications use the credential for:
-
Identification
-
Authentication
-
Authorization
The applications interpret and manipulate the contents of certificates
to achieve these ends, based on the real-world trust model they chose
as their model for trust and security. The primary purpose of a Trust
Policy (TP) module is to answer the question,
"Is this certificate trusted for this action?" The CSSM Trust Policy
API determines the generic operations that should be defined for
certificate-based trust in every application domain. The specific
semantics of each operation is defined by the:
-
Application domain
-
Trust model
-
Policy statement for a domain
-
Certificate type
-
Real-world operation the user is trying to perform within the
application domain
-
The sources of trust (called anchors) and the sources of distrust in
revocation lists
Trust Model
The trust model is expressed as an executable policy that is used by
all applications that subscribe to that policy and the trust model it
represents. As an infrastructure, CSSM is policy-neutral with respect
to application-domain policies; it does not incorporate any single
policy. For example, the verification procedure for a credit card
certificate should be defined and implemented by the credit company
issuing the certificate. Employee access to a lab housing a critical
project should be defined by the company whose intellectual property is
at risk. Rather than defining policies, CSSM provides the
infrastructure for installing and managing policy- specific modules.
This ensures complete extensibility of certificate-based trust on every
platform hosting CSSM.
The general CSSM trust model defines a set of basic trust objects that
most (if not all) trust policies use to model their trust domain and
the policies over that domain. These basic trust objects include:
-
Policies
-
Certificates
-
Defined sources of trust (called anchors)
-
Certificate revocation lists
-
Application-specific actions
-
A set of data objects targeted by those actions
-
Evidence of the results of the trust evaluation
Policies define the credentials required for authorization to
perform an action on another object. Certificates are the basic
credentials representing a trust relationship among a set of two
or more parties. When an organization issues certificates it
defines its issuing procedure in a Certification Practice
Statement (CPS). The statement identifies existing policies with
which it is consistent. The statement can also be the source of
new policy definitions if the action and target object domains
are not covered by an existing, published policy. An application
domain can recognize multiple policies. A given policy can be
recognized by multiple application domains.
Evaluation of trust depends on relationships among certificates.
Certificate chains represent
hierarchical
trust, where a root authority
is the source of trust. Entities attain a level of trust based
on their relationship to the root authority. Certificate graphs represent an
introducer
model of trust, where the number and strength of endorsers
(represented by immediate links in the trust graph) increases the level
of trust attained by an entity. In both models, the trust domain can
define accepted sources of trust, called
anchors. Anchors can be mandated by fiat or can be computed by
some other means. In contrast to the sources of trust,
certificate revocation lists represent sources of distrust. Trust
policies may consult these lists during the verification process.
Trust evaluation can be performed with respect to a specific action the
bearer wishes to perform, or with respect to a policy, or with respect
to the application domain in general. In the latter case, the action is
understood to be either one specific action, or any and all actions in
the domain.
When verifying trust, a Trust Policy Module (TPM) processes a group of
certificates. The first certificate in the group is the target of the
verification process. The other certificates in the group are used in
the verification process to connect the target certificate with one or
more anchors of trust. Supporting certificates can also be provided
from a data store accessed by the TPM. It is also possible to provide a
data store of anchor certificates. This case is less common. Typically
the points of trust are few in number and are embedded in the caller or
in the TPM during software manufacturing or at runtime.
The result of verification is a list of evidence, which forms an audit
trail of the process. The evidence may be a list of verified attribute
values that were contained in the certificates, or the entire set of
verified certificates, or some other information that serves as
evidence of the verification.
In the final analysis, the trust and authorizations that are
asserted are based on the authority implied by a set of assumed or
otherwise-specified public keys.
Trust Services
Different trust policies define different actions that an application
may request. Some of these actions are common to every trust policy,
and are operations on objects all trust models use. The objects
believed to be common to all trust models are certificates and
certificate revocation records. The basic operations on these objects
are sign, verify, and revoke.
The CDSA Trust Policy modules include interfaces for two categories of
trust services:
-
Evaluating trust based on the policies of a specific application domain
In this case, applications are viewed as executing solely within a
trust domain. For
example, executing an installation program at the office takes place
within the corporate information technology trust domain. Executing an
installation program on a system at home takes place within the user's
personal system trust domain. The trust policy that allows or blocks
the installation action is different for the two domains. The corporate
domain may require extensive credentials and accept only credentials
signed by selected parties. The personal system domain may require
only a credential that establishes the bearer as a known user on the
local system.
-
Providing access to the services of other authoritative agents that
support the life cycle of certificates and certificate revocation
lists, upon which trust is based.
In this case, the Trust Policy interfaces
provide access to authorities providing services that support
the complete life cycles of certificates and certificate life cycles.
The certificate life cycle is presented in
Certificate Life Cycle States and Actions.
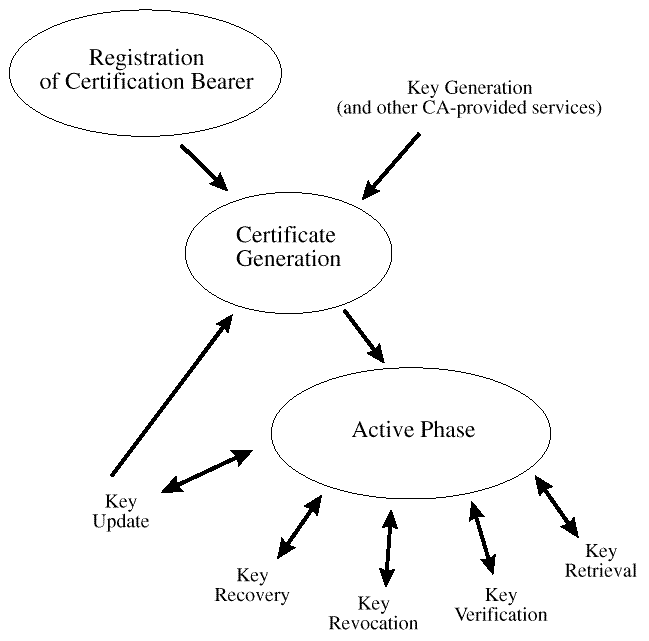
Figure: Certificate Life Cycle States and Actions
It begins with the registration process. During registration, the
authenticity of a user's identity is verified. This can be a two-part
process, beginning with manual procedures requiring physical presence,
followed by back-office procedures to entire status and results for use
by the automated system. The level of verification associated with the
identity of the individual will depend on the Security Policy and
Certificate Management Practice Statements that apply to the individual
who will receive a certificate, and the domain in which that
certificate will be used.
After registration, keying material is generated and certificates are
created. Once the private key material and public key certificate are
issued to a user and backed up if appropriate, the active phase of the
certificate management life cycle begins.
The active phase includes:
-
Retrieval-retrieving a certificate from a remote repository such
as an X.500 directory
-
Verification-verifying the validity dates, signatures on a
certificate and revocation status
-
Revocation-asserting that a previously-legitimate certificate is no
longer a valid certificate
-
Recovery-when an end-user has forgotten the passphrase required to
use the private key associated with some certificate for
signing or for decryption
-
Update-issuing a new public/private key pair when a legitimate
pair has or will expire soon.
These services can be provided by a local authority or a
remote authority. Requesters must be authorized to request a
service and to receive the results of that service.
Ultimately access is controlled by the authority's policy.
Policy enforcement can be distributed. By distributed enforcement we
mean a local client system may enforce portions of the CA's policy
prior to submitting request to the remote authority. The local
policy statement can be the empty set (if appropriate). The
remote authority enforces policy and performs the service.
If the requester is authorized and the service succeeds,
then results are returned to the requester. To support asynchronous
completion of services, submitting a request and retrieving a result
are performed using separate interfaces. The function pairs are:
-
Authenticated Submit and Authenticated Retrieve
One function to request a controlled service and one to retrieve
the result of that controlled request. The caller is authenticated
by the local service provider before any service is performed.
-
Authenticated Confirm and Receive
One function to acknowledge successful retrieval of results and one
to receive the confirmation.
-
Non-Authenticated Submit and Non-Authenticated Retrieve
One function to request a public service and one to retrieve the result
of that public service request.
The request service may not complete for several days. Applications
can submit requests and retrieve results in separate executions
of the application.
CDSA TP Features
Based on this analysis, CSSM defines two categories of API calls that
should be implemented by TP modules. The first category allows the TP
module to validate operations relevant within an application domain
(such as requesting authorization to make a $200 charge on a credit
card certificate, and requesting access to the locked project lab). The
second category supports all of the currently provided operations
supporting the life cycle of certificates and certificate revocation lists.
Application developers and trust domain authorities benefit from the
ability to define and implement policy-based modules. Application
developers are freed from the burden of implementing a policy
description and certifying that their implementation conforms.
Instead, the application needs only to build in a list of the
authorities and certificate
issuers it uses.
Domain authorities also benefit from an infrastructure that supports
add-in Trust Policy modules. Authorities are ensured that applications
using their module(s) adhere to the policies of the domain. Also,
dynamic download of trust modules (possibly from remote systems)
ensures timely and accurate propagation of policy changes. Individual
functions within the module may combine local and remote processing.
This flexibility allows the module developer to implement policies
based on the ability to communicate with a remote authority system.
This also allows the policy implementation to be decomposed in any
convenient distributed manner.
Implementing a Trust Policy module may or may not be tightly coupled
with one or more Certificate Library modules or one or more Data
Storage Library modules. The trust policy embodies the semantics of the
domain. The certificate library and the data storage library embody the
syntax of a certificate format and operations on that format. A trust
policy can be completely independent of certificate format, or it may
be defined to operate with one or a small number of certificate
formats. A trust policy implementation may invoke a certificate library
module or data storage library modules to facilitate making policy
based manipulations.
The MDS records that describe the TP service
provider should include a list of the authorities and life cycle
services the TP module can access on behalf of a caller. If the
authority is remote, the protocol used to communication with the
remote authority is encapsulated in the local Trust Policy Service
Provider. The TP service provider can record the implemented protocols
in it's associated MDS records. Applications can query MDS records
to determine what services are provided by a TP module.
SPI TP
Add-In Module
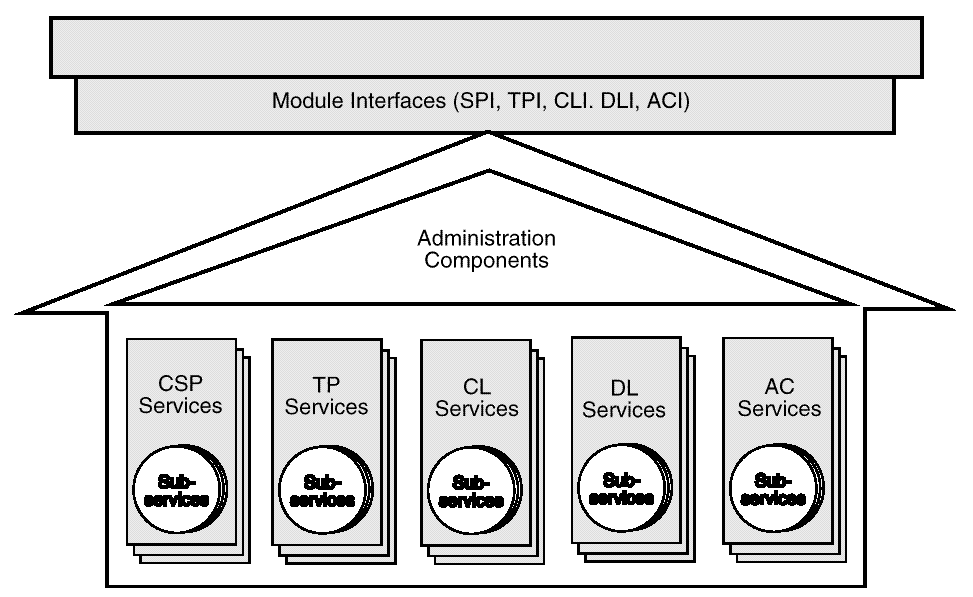
Figure: CDSA Add-In Module Structure
A CDSA add-in module is a dynamically-linkable library, composed of
functions that implement some or all of the CSSM Module Interfaces.
Add-in module functionality is partitioned into two areas:
-
The provision of security services to applications
-
Module administration.
Add-in modules provide one or more categories of security services
to applications. In this case it provides Trust Policy (TP) services.
Each module, regardless of the security services it offers, has the
same set of administrative responsibilities. Every module must expose
functions that allow CSSM to indicate events such as module
attach
and
detach.
In addition, as part of the
attach
operation, every module
must be able to verify its own integrity, verify the integrity of CSSM,
and register with CSSM. Detailed information about add-in module
structure, administration, and interfaces can be found in
Part 14
of this Technical Standard.
Operations
The CSSM Trust Policy API defines the generic operations that each TP
module supports. Each module may choose to implement the required
subset of these operations for the policy it serves.
The CSSM API defines a
pass-through
function, which allows each module
to provide additional functions, along with those defined by the CSSM
Trust Policy API. When a TP function determines the trustworthiness of
performing an action, it may invoke Certificate Library functions and
Data storage Library functions to carry out the mechanics of the
approved action. TP modules must be installed and registered with the
CSSM Trust Policy services manager. Applications may query the
services manager to retrieve properties of
the TP module, as defined during installation.
An application determines the availability of a Trust Policy module by
querying the CSSM Registry. When a new TP is installed on a system, it
must be registered with CSSM. When a client requests that CSSM attach
to a TP, CSSM returns a TP handle to the application which uniquely
identifies the pairing of the application thread to the TP module
instance. The application uses this handle to identify the TP
in future function calls.
CSSM manages function tables provided by the TP module and the
application. A function upcall table is used to register application
memory allocation and de-allocation functions with CSSM. The Trust
Policy module will have access to the upcall table. The Trust Policy
module registers its function table with CSSM at library load time
using the function
CSSM_RegisterServices()).
See
Part 14
(CSSM Add-in Module Structure and Administration Specification) for details of module installation and registration.
Many applications are hard-coded to select a specific Trust Policy.
The Module Directory Services (MDS) system provides
query mechanisms so applications can access TP
module descriptions. This information is provided by the TP module
during installation and can assist the application in selecting the
appropriate TP module for a given application domain.
Data Structures
CSSM_TP_HANDLE
This data structure represents the trust policy module handle. The
handle value is a unique pairing between a trust policy module and an
application that has attached that module. TP handles can be returned
to an application as a result of the CSSM_ModuleAttach
function.
typedef CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE CSSM_TP_HANDLE; /* Trust Policy Handle */
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID
This data structure identifies an Authority who provides security-related
services. It is used as input to functions requesting authority services.
typedef struct cssm_tp_authority_id {
CSSM_DATA *AuthorityCert;
CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_PTR AuthorityLocation;
} CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID, *CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID_PTR;
Definitions
- AuthorityCert
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the desired
Authority's certificate. If the
AuthorityCert
is NULL, a service provider module can provide a certificate
identifying a default authority.
- AuthorityLocation
A pointer to a network address directly or indirectly identifying
the location of the authority process. If the input is NULL,
a service provider module can determine an authority process and
its location based on the
AuthorityCert
input parameter or can assume a default authority location.
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE
This extensible list defines the type of a request to an Authority
providing certificate-related services.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE,
*CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTISSUE (0x01)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTREVOKE (0x02)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTSUSPEND (0x03)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTRESUME (0x04)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTVERIFY (0x05)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTNOTARIZE (0x06)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CERTUSERECOVER (0x07)
#define CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_CRLISSUE (0x100)
CSSM_TP_VERIFICATION_RESULTS_CALLBACK
This type defines the form of the callback function a service provider
module must use to incrementally return verified certificates to
a caller whose credentials are being verified.
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI * CSSM_TP_VERIFICATION_RESULTS_CALLBACK)
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle,
void *CallerCtx,
CSSM_DATA_PTR VerifiedCert);
Definitions
- ModuleHandle
The CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE for the attach session under which the
verification process is being performed and incrementally reported
to the caller.
- CallerCtx
A generic pointer to context information that was provided by
the original requester and is being returned to its originator.
- VerifiedCert
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure containing the most recently
verified certificate in an incremental certificate verification process.
CSSM_TP_POLICYINFO
This data structure contains a set of one or more policy identifiers
and application-domain-specific information used to control evaluation
of the named policies.
typedef struct cssm_tp_policyinfo {
uint32 NumberOfPolicyIds;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR PolicyIds;
void *PolicyControl;
} CSSM_TP_POLICYINFO, *CSSM_TP_POLICYINFO_PTR;
Definitions
- NumberOfPolicyIds
The number of policy identifiers provided in the
PolicyIds
parameter.
- PolicyIds
The policy identifier is a OID-value pair. The CSSM_OID structure
contains the name of the policy and the value is an optional,
caller-specified input value for use when applying the policy.
The name space for policy identifiers is defined externally by the
application domains served by the certification authority module.
- PolicyControl
A pointer to provider-specific data to be used when evaluating
the policies specified by
PolicyIds.
CSSM_TP_SERVICES
This bit mask defines the additional back-office services that a
Certification Authority (CA) can offer. Such services include
(but are not limited to) archiving a certificate and keypair,
publishing a certificate to one or more certificate directory services,
and sending automatic, out-of-band notifications of the need to
renew a certificate. A CA may offer any subset of these services.
Additional services may be defined over time.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_SERVICES;
/* bit masks for additional Authority services available through TP */
#define CSSM_TP_KEY_ARCHIVE (0x0001) /* archive cert & keys */
#define CSSM_TP_CERT_PUBLISH (0x0002) /* register cert in
directory */
#define CSSM_TP_CERT_NOTIFY_RENEW (0x0004) /* notify at renewal time */
#define CSSM_TP_CERT_DIR_UPDATE (0x0008) /* update cert registry
entry */
#define CSSM_TP_CRL_DISTRIBUTE (0x0010) /* push CRL to everyone */
CSSM_TP_ACTION
This data structure represents a descriptive value defined by the
trust policy module. A trust policy can define application-specific
actions for the application domains over which the trust policy applies.
Given a set of credentials, the trust policy module verifies authorizations
to perform these actions.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_ACTION;
#define CSSM_TP_ACTION_DEFAULT (0)
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON
This enumerated list defines the conditions controlling termination of
the verification process by the trust policy module when a set of
policies/conditions must be tested.
typedef enum cssm_tp_stop_on {
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON_POLICY = 0, /* use the pre-defined stopping
criteria */
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON_NONE = 1, /* evaluate all condition whether
TRUE or FALSE */
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON_FIRST_PASS = 2, /* stop evaluation at first TRUE */
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON_FIRST_FAIL = 3 /* stop evaluation at first FALSE */
} CSSM_TP_STOP_ON;
CSSM_TIMESTRING
Values must be expressed in Greenwich Mean Time (Zulu) and must
include seconds, even when the value of seconds is "00". Values must
not include fractional seconds.
This string contains a date and time in the format "YYYYMMDDhhmmss",
defined by:
- YYYY
- - four characters representing the year
- MM
- - two characters representing the month within a year
- DD
- - two characters representing the day within a month
- hh
- - two characters representing the hours within a day ["00" through "23"]
- mm
- - two characters representing the minutes within a hour ["00" through "59"]
- ss
- - two characters representing the seconds within a minute ["00" through "59"]
typedef char *CSSM_TIMESTRING;
CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT
This data structure contains the basic parameters required to
authenticate the caller who is requesting a certificate-related
service from a certificate authority.
typedef struct cssm_tp_callerauth_context {
CSSM_TP_POLICYINFO Policy;
CSSM_TIMESTRING VerifyTime;
CSSM_TP_STOP_ON VerificationAbortOn;
CSSM_TP_VERIFICATION_RESULTS_CALLBACK CallbackWithVerifiedCert;
uint32 NumberOfAnchorCerts;
CSSM_DATA_PTR AnchorCerts;
CSSM_DL_DB_LIST_PTR DBList;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR CallerCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT, *CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_PTR;
Definitions
- Policy
A structure identifying one or more policies and associated control
information. The authentication should be performed under one or
more of the specified policies.
- VerifyTime
A CSSM_TIMESTRING specifying the point-in-time for which the
caller's credentials should be authenticated for validity.
- VerificationAbortOn
When multiple conditions or multiple policies are supported, the
service provider module can allow the caller to specify when to
abort the verification process. If supported, the selected option can
affect the verification evidence returned to the caller. The default
stopping condition is to stop evaluation according to the implicit
policy defined by the service provider. The specify-able stopping
conditions and their meaning are defined as follows:
| CSSM_TP_STOP_ON
| Definition
|
|---|
| CSSM_STOP_ON_POLICY
| Stop verification whenever the policy dictates it
|
| CSSM_STOP_ON_NONE
| Stop verification only after all conditions have been tested (ignoring the pass-
fail status of each condition)
|
| CSSM_STOP_ON_FIRST_PASS
| Stop verification on the first condition that passes
|
| CSSM_STOP_ON_FIRST_FAIL
| Stop verification on the first condition that fails
|
The service provider module can ignore the caller's specified
stopping condition and revert to the implicit, default stopping policy.
- CallbackWithVerifiedCert
A caller defined function to be invoked by the service provider module
once for each certificate examined in the verification process.
The verified certificate is passed back to the caller via this
function. The reported certificate is represented as an encoded
certificate in a CSSM_DATA structure allocated by the service provider.
The caller implementing the callback function must free the
CSSM_DATA structure and its contents. If the verification process completes
in a single verification step, then no callbacks are made from the
service provider module to the caller. If the callback function pointer
is NULL, no callbacks are performed.
- NumberOfAnchorCerts
The number of anchor certificates provided in the
AnchorCerts
parameter.
- AnchorCerts
A pointer to an array of the CSSM_DATA structures containing one or
more certificates to be used in the process of authenticating
a caller of this function.
These certificates are in addition to the caller-owned credentials.
- DBList
A list of databases containing credentials that can be used in the
process of authenticating a caller of this function. The list contains
a Data Library Module handle and an open data base handle. The
Data Library interfaces must be used to access these data bases.
Each data base can contains multiple credential types appropriate to
supporting the authentication process, such as certificates and
certificate revocation lists.
- CallerCredentials
A pointer to the CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS structure containing one
or more credentials the caller requires to authenticate to the service
provider. The information is input to certification authority functions
that require caller authentication before being serviced. The credentials
structure can contain an immediate value for the credential, such as
a passphrase or the caller can specify a callback function the CSP can
use to carry out a credential acquisition protocol with the caller
to obtain one or more credentials. The supported protocols are recorded
in the MDS entry for the service provider module.
CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT
This extensible list defines the parse formats for a CRL.
typedef uint32 CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT, * CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_PTR;
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_NONE (0x00)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_CUSTOM (0x01)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_SEXPR (0x02)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_COMPLEX (0x03)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_OID_NAMED (0x04)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_TUPLE (0x05)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_MULTIPLE (0x7FFE)
#define CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_LAST (0x7FFF)
/* Applications wishing to define their own custom parse
* format should create a uint32 value greater than the
* CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT */
#define CSSM_CL_CUSTOM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT (0x8000)
CSSM_PARSED_CRL
This structure holds a parsed representation of a CRL. The CRL type
and representation format are included in the structure.
typedef struct cssm_parsed_crl {
CSSM_CRL_TYPE CrlType; /* CRL type */
CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT ParsedCrlFormat; /* struct of ParsedCrl */
void *ParsedCrl; /* parsed CRL (to be typecast) */
} CSSM_PARSED_CRL, *CSSM_PARSED_CRL_PTR ;
Definitions
- CrlType
Indicates the type of CRL that had been parsed to yield ParsedCrl.
- ParsedCrlFormat
Indicates the structure and format representation of the parsed CRL.
If the parsed representation is not available, then this value
is CSSM_CRL_PARSE_FORMAT_NONE.
- ParsedCrl
A pointer to a parsed CRL represented in the structure and format
indicated by
ParsedCrlFormat.
CSSM_CRL_PAIR
This structure holds a parsed representation and an encoded representation
of a CRL. The two elements should be different representations of
a single CRL.
typedef struct cssm_crl_pair {
CSSM_ENCODED_CRL EncodedCrl; /* an encoded CRL blob */
CSSM_PARSED_CRL ParsedCrl; /* equivalent parsed CRL */
} CSSM_CRL_PAIR, *CSSM_CRL_PAIR_PTR;
Definitions
- EncodedCrl
A CSSM_ENCODED_CRL structure containing:
-
A reference to an opaque, single byte-array representation of the CRL
-
A CRL type descriptor
-
A CRL encoding descriptor.
The CRL can have an equivalent parsed representation. If the parsed
representation is provided it is contained in
ParsedCrl.
- ParsedCrl
A CSSM_PARSED_CRL structure containing:
-
A CRL type
-
A reference to a parsed representation of the CRL
-
A parse format descriptor
The CRL can have an equivalent encoded representation. If the encoded
representation is provided it is contained in
EncodedCrl.
CSSM_CRLGROUP_TYPE
This extensible list defines the type of a CRL group. A group can contain
a single type of CRL or multiple types of CRLs. Each CRL in the group
can be represented in an encoded representation or a parsed representation.
typedef uint32 CSSM_CRLGROUP_TYPE, * CSSM_CRLGROUP_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_CRLGROUP_DATA (0x00)
#define CSSM_CRLGROUP_ENCODED_CRL (0x01)
#define CSSM_CRLGROUP_PARSED_CRL (0x02)
#define CSSM_CRLGROUP_CRL_PAIR (0x03)
CSSM_CRLGROUP
This data structure aggregates a group of one or more memory-resident
CRLs. The CRLs can be of one type or of mixed types and encodings.
typedef struct cssm_crlgroup {
CSSM_CRL_TYPE CrlType;
CSSM_CRL_ENCODING CrlEncoding;
uint32 NumberOfCrls;
union {
CSSM_DATA_PTR CrlList ; /* CRL blob */
CSSM_ENCODED_CRL_PTR EncodedCrlList ; /* CRL blob
w/ separate type */
CSSM_PARSED_CRL_PTR ParsedCrlList; /* bushy, parsed CRL */
CSSM_CRL_PAIR_PTR PairCrlList;
} GroupCrlList;
CSSM_CRLGROUP_TYPE CrlGroupType;
} CSSM_CRLGROUP, *CSSM_CRLGROUP_PTR;
Definitions
- CrlType
If all CRLs in the CrlList are of the same type, this variable lists
that type. Otherwise, the type should be CSSM_CRL_TYPE_MULTIPLE.
- CrlEncoding
If all CRLs in the
CrlList
are of the same encoding, this variable
gives that encoding. Otherwise, the type should be CSSM_CRL_ENCODING_MULTIPLE.
- NumberOfCrls
The number of entries in the
CrlList
array.
- GroupList
An array of CRLs. The array contains exactly
NumberOfCrls
entries.
CrlGroupType
defines the type of structure contained in the array. The group types
are described as follows:
| CrlGroupType Value
| Field Name
| Description
|
|---|
| CSSM_CRLGROUP_DATA
| CrlList
| (Legacy) A pointer to an array of CSSM_DATA structures. Each
CrlList array entry references a single CRL structure and
indicates the length of the structure. A single type and encoding apply
to all CRLs in this group. The type and encoding are indicated in
CrlType and CrlEncoding respectively.
|
| CSSM_CRLGROUP_ENCODED_CRL
| EncodedCrlList
| A pointer to an array of CSSM_ENCODED_CRL structures. Each
EncodedCrlList array entry references a CRL in an opaque, single
byte-array representation, and describes the format of the CRL
data contained in the byte-array. Each CRL encoding and type can
be distinct, as indicated in each array element.
|
| CSSM_CRLGROUP_PARSED_CRL
| ParsedCrlList
| A pointer to an array of CSSM_PARSED_CRL structures. Each
ParsedCrlList array entry references a CRL in a parsed representation, and
indicates the CRL type and parse format of that CRL.
|
| CSSM_CRLGROUP_CRL_PAIR
| PairCrlList
| A pointer to an array of CSSM_CRL_PAIR structures. Each PairCrlList array
entry aggregates two CRL representations: an opaque encoded CRL blob,
and a parsed CRL representation.
At least one of the two representations must be present in each array
entry. If both are present, they are assumed but not guaranteed to
correspond to one another. If the parsed form is being used in
a security sensitive operation, then it must have been verified
against the packed, encoded form, whose signature must have been verified.
|
CrlGroupType - The type of the group.
CSSM_FIELDGROUP
This data structure groups a set of OID/value pairs into a single
structure with a count of the number of fields in the array.
typedef struct cssm_fieldgroup {
int NumberOfFields ; /* number of fields in the array */
CSSM_FIELD_PTR Fields ; /* array of fields */
} CSSM_FIELDGROUP, *CSSM_FIELDGROUP_PTR ;
Definitions
- NumberOfFields
The number of entries in the array Fields.
- Fields
A pointer to an ordered array of OID/value pairs. Each structure
contains a single pair.
CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM
This type defines constants corresponding to known representations
of verification evidence returned by a verification function or
service. The constant values are used as type indicators in the
structure CSSM_EVIDENCE.
typedef uint32 CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM;
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_UNSPECIFIC 0x0
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CERT 0x1
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL 0x2
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CERT_ID 0x3
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_ID 0x4
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_VERIFIER_TIME 0x5
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_THISTIME 0x6
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_NEXTTIME 0x7
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_POLICYINFO 0x8
#define CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_TUPLEGROUP 0x9
CSSM_EVIDENCE
This structure contains certificates, CRLs and other information
used as audit trail evidence.
typedef struct cssm_evidence {
CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM EvidenceForm;
void *Evidence; /* Evidence content */
} CSSM_EVIDENCE, *CSSM_EVIDENCE_PTR;
Definitions
- EvidenceForm
An identifier indicating the type and the data structure of the evidence.
- Evidence
Buffer containing audit trail information.
The correspondence between the value of
EvidenceForm
and the structure type contained in the
Evidence
field is defined as follows:
| Value of EvidenceForm
| Data Type of Evidence
|
|---|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_UNSPECIFIC
| void *
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CERT
| CSSM_ENCODED_CERT
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL
| CSSM_ENCODED_CRL
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CERT_ID
| Big-endian integer
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_ID
| Big-endian integer
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_VERIFIER_TIME
| CSSM_TIMESTRING
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_THISTIME
| CSSM_TIMESTRING
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_CRL_NEXTTIME
| CSSM_TIMESTRING
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_TUPLEGROUP
| CSSM_TUPLEGROUP
|
| CSSM_EVIDENCE_FORM_POLICYINFO
| CSSM_TP_POLICYINFO
|
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT
This data structure contains all of the credentials and information required
as input to a verification service. The verification service verifies a
set of credentials for fitness to perform an application-defined action
on a specified data object.
typedef struct cssm_tp_verify_context {
CSSM_TP_ACTION Action;
CSSM_DATA ActionData;
CSSM_CRLGROUP Crls;
CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_PTR Cred;
} CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT, *CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_PTR;
Definitions
- Action
An application-specific and application-defined action to be performed
under the authority of the input credentials. If no action is specified,
the service provider module can define a default action and
performs verification assuming that action is being requested.
- ActionData
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the action-specific
data or a reference to the action-specific data upon which the
requested action should be performed. If no data is specified, and
the specified action requires a target data object, then the service
provider module defines one or more default data objects upon which the
action or default action would be performed.
- Crls
A group of one or more memory-resident Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs)
to be used in support of the verification process. Persistent CRLs
managed by a Data Storage Library module are referenced in
Cred.DbList.
- Cred
A pointer to a CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT structure containing one
or more credentials to be verified for fitness to perform the
requested action on the target data object. The structure also
contains control information to guide the credential verification process.
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT
This data structure contains the results of an evaluation by a
local trust policy. The trust policy evaluation process can return
to the requester the following:
-
description of the how the trust policy was applied during the
evaluation process
-
A set of evidence compiled during the evaluation process.
typedef struct cssm_tp_verify_context_result {
uint32 NumberOfEvidences;
CSSM_EVIDENCE_PTR Evidence;
} CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT, *CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR;
Definitions
- NumberOfEvidences
The number of entries in the Evidence list. The returned value is zero
if no evidence is produced. Evidence may be produced even when
verification fails. This evidence can describe why and how the
operation failed to verify the subject certificate.
- Evidence
A pointer to a list of CSSM_EVIDENCE objects containing an audit trail
of evidence constructed by the TP module during the verification process.
Typically this contains Certificates and CRLs that were used to establish
the validity of the Subject Certificate, but other objects may be
appropriate for other types of trust policies.
CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET
This data structure specifies the input data required when requesting
one or more requests from a Certification Authority. The initialized
structure is input to
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest().
typedef struct cssm_tp_request_set {
uint32 NumberOfRequests;
void *Requests;
} CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET, *CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET_PTR;
Definitions
- NumberOfRequests
The number of entries in the array
Requests.
- Requests
A pointer to an ordered array of service-specific certificate request
structures. Each structure contains a single request.
CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET
This data structure specifies the final output data returned by
a call to
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredAuthResult().
The structure contains an ordered array. Each array entry corresponds
to one request.
A call to
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredAuthResult()
must have a corresponding call to the request function
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest().
typedef struct cssm_tp_result_set {
uint32 NumberOfResults;
void *Results;
} CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET, *CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET_PTR;
Definitions
- NumberOfResults
The number of certificate service results contained in
Results.
- Results
A pointer to an ordered array of certificate service output structures.
The array is ordered corresponding to the array of input requests.
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS
This type defines constants used to indicate acceptance or rejection of
the results of a service authority.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS, *CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS_PTR;
#define CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS_UNKNOWN 0x0
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_ACCEPT 0x1
/* accept results of executing a submit-retrieve function pair */
#define CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_REJECT 0x2
/* reject results of executing a submit-retrieve function pair */
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE
This data structure specifies the input response vector required when
confirming the results returned by a Certification Authority through the
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
function. The response vector is ordered corresponding to the set of
returned results, one response per result. The valid response values include:
-
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_ACCEPT - indicates the corresponding result was accepted by the
requester
-
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_REJECT - indicates the corresponding result was rejected by the
requester
-
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS_UNKNOWN - indicates that the requester can not accept or
reject the returned result. The status of the returned result in indeterminate
typedef struct cssm_tp_confirm_response {
uint32 NumberOfResponses;
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_STATUS_PTR Responses;
} CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE, *CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR;
Definitions
- NumberOfResponses
The number of entries in the vector Responses.
- Responses
A pointer to an ordered vector of confirmation responses. Each response
corresponds to a result returned by a certificate-service authority.
CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN
The value used by an authority or process to indicate that an
estimated completion time can not be determined.
#define CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN -1
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN
A constant value indicating that the service provider module does not know
the time elapsed since a specific prior event.
#define CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN (-1)
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE
A constant value indicating that request has completed and the elapsed time
since a specific prior event is no longer of significance.
#define CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE (-2)
CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request
to issue a single new certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certissue_input {
CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID CSPSubserviceUid;
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
uint32 NumberOfTemplateFields;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR SubjectCertFields;
CSSM_TP_SERVICES MoreServiceRequests;
uint32 NumberOfServiceControls;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR ServiceControls;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR UserCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- CSPSubserviceUid
The identifier that uniquely describes the CSP module subservice where
the private key associated with the newly issued certificate is to
be stored. Optionally, an immediate service provider module can use
this CSP to perform additional cryptographic operations or may use another
default CSP for that purpose.
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service
provider that can be used to manipulate a certificate of the requested
type on the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this
request type.
- NumberOfTemplateFields
The number of entries in the
SubjectCertFields
array.
- SubjectCertFields
An array of OID/value pairs providing input values to the TP. The TP
can include these values in the new certificate or can use the values
to support the creation process without explicitly including them in the
new certificate. A count of the number of OID/value pairs is included
in the structure.
- MoreServiceRequests
A bit mask requesting additional certificate-creation-related services
from the Certificate Authority issuing the certificate. CSSM-defined
bit masks allow the caller to request backup or archive of the
certificate's private key, publication of the certificate in a
certificate directory service, request out-of-band notification of the need
to renew this certificate, etc.
- NumberOfServiceControls
The number of entries in the
ServiceControls
array.
- ServiceControls
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures. Each array element contains:
-
A CSSM_OID structure - the
Oid
value identifies one additional TP service associated with a primary TP service
request. The name space for OID values is defined by the TP service domain.
-
A CSSM_DATA structure - the
Data
value is input information to the additional TP service identified by the
Oid
value.
- UserCredentials
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials being presented for
authentication by the caller making the certificate request. The credentials
structure can contain multiple types of credentials, as required for
multi-factor authentication. The credential data can be an immediate
value, such as a passphrase, PIN, certificate, or template of user-specific
data, or the caller can specify a callback function a service provider
module can use to obtain one or more credentials. The
callback
function can be used to obtain a passphrase, a biometric input, or to
perform a challenge and response protocol. The type of credentials accepted
by a service provider module is defined and recorded in a record in the
Module Directory Service records describing that provider. If the service
provider module does not require credentials from a caller, then this field
can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_STATUS
This set of defined constants indicates the status of a service request
to issue a certificate.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_STATUS
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_STATUS_UNKNOWN 0x0
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OK 0x1
/* cert issued as requested */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OKWITHCERTMODS 0x2
/* cert issued but cert contents were updated by the
issuing authority */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OKWITHSERVICEMODS 0x3
/* cert issued but some requested backend services were
not performed by the issuing authority */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_REJECTED 0x4
/* cert was not issued due to some error condition */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_NOT_AUTHORIZED 0x5
/* cert was not issued, the request was not authorized */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_WILL_BE_REVOKED 0x6
/* cert was issued, but TP has initiated a revocation
of the certificate */
CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OUTPUT
This data structure aggregates the output information generated in
response to a single request to issue a new certificate. Each result
includes a certificate group composed of one or more certificates.
The first certificate in the group is the newly issued certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certissue_output {
CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_STATUS IssueStatus;
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR CertGroup;
CSSM_TP_SERVICES PerformedServiceRequests;
} CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTISSUE_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- IssueStatus
A value indicating the status of the newly issued certificate.
- CertGroup
A pointer to a structure containing a reference to a certificate group
and the number of certificates contained in that group. The certificate
group contains the newly issued certificate created in response to a request.
The certificate group can also contain supporting certificates related to
the newly issued certificate. By convention the new certificate is the
first member of the certificate group.
- PerformedServiceRequests
A bit mask indicating the additional certificate-creation-related services
that were performed by the Certificate Authority while issuing the
certificate. Possible services include:
-
Backup or archive of the private key associated with the newly
issued certificate
-
Publication of the new certificate in a certificate directory service
-
Registration for out-of-band certificate renewal notification
-
Other authority-provided services
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_ACTION
This type defines the constants identifying the certificates state changes
that are posted to a certificate revocation list for distribution to all
concerned systems.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_ACTION;
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_NONE (0x0) /* no change */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REVOKE (0x1) /* Revoke the certificate */
/* This action type indicates a request to revoke a single
certificate. Notice of the revocation operation remains
in affect until the certificate itself expires. Revocation
should be used to permanently remove a certificate from use. */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_HOLD (0x2) /* Hold/suspend the
certificate */
/* This action type indicates a request to suspend a
single certificate. A suspension operation implies
that the requester intends, at some time in the future,
to request that the certificate be released from hold,
making it available for use again. Placing a hold on
a certificate does not obligate the requester to
request a release. In practice, a certificate may
remain on hold until the certificate itself expires.
Revocation should be used to permanently remove a
certificate from use. */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_RELEASE (0x3) /* Release the held
certificate */
/* This action type indicates a request to release a
single certificate currently on hold. A release
operation makes a certificate available for use again.
Revocation should be used to permanently remove a
certificate from use. */
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON
This type defines the constants reasons for a change in certificate state.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON;
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_UNKNOWN (0x0)
/* unspecified */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_KEYCOMPROMISE (0x1)
/* Subject key believed to be compromised */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_CACOMPROMISE (0x2)
/* CA's key believed to be compromised */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_CEASEOPERATION (0x3)
/*certificate holder ceases operation under the
jurisdiction of this certificate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_AFFILIATIONCHANGE (0x4)
/*certificate holder has moved from this jurisdiction */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_SUPERCEDED (0x5)
/*certificate holder as issued a new, superceding
certificate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_SUSPECTEDCOMPROMISE (0x6)
/*certificate could be compromised */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON_HOLDRELEASE (0x7)
/*certificate holder resumes operation under
the jurisdiction of this certificate */
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request to
change the state of a single certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certchange_input{
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_ACTION Action;
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason;
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
CSSM_DATA_PTR Cert;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR ChangeInfo;
CSSM_TIMESTRING StartTime;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR CallerCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- Action
An identifier indicating a state change that is posted to a
certificate revocation list for distribution to all concerned systems.
- Reason
An identifier indicating why the certificate state should be changed.
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service
provider that can be used to manipulate a certificate of the requested
type on the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this
request type.
- Cert
The certificate that is the target of the status change.
- ChangeInfo
A pointer to a CSSM_FIELD structure containing optional information for
inclusion in an authority's record regarding the status of
Cert.
The structure contains an OID and a value. The OID identifies the contents
of the value field.
- StartTime
The time at which the external event that created the need for a
certificate state change took place.
- CallerCredentials
A set of credentials that can be submitted to the certificate authority
process for verification when processing the status change request.
The supplied credentials must be transportable, because the certificate
authority process can be remote. Verification determines whether the
requester is authorized to submit the revocation request. If no
credentials are required by the certificate authority, then this value
can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_STATUS
These constants define the change values that can be returned by a
certificate authority that provides state change services for certificates.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_STATUS;
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_STATUS_UNKNOWN (0x0)
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_OK (0x1)
/* cert state was successfully changed
beginning at the specified time */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_OKWITHNEWTIME (0x2)
/* cert state was successfully changed, at
a modified effective time */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_WRONGCA (0x3)
/* cert state was not changed, the selected
CA is not authorized to change the cert state */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REJECTED (0x4)
/* cert state was not changed due to some
error condition */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_NOT_AUTHORIZED (0x5)
/* cert state was not changed, the requester is
not authorized to change the cert state */
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_OUTPUT
This type defines the output results returned by a certificate authority
in response to an action request to revoke, hold, or release a hold on
a certificate. An array of output values is aggregated in a
CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET structure and is an output parameter of the
function
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult().
typedef struct cssm_tp_certchange_output {
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_STATUS ActionStatus;
CSSM_FIELD RevokeInfo;
} CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- ActionStatus
A CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_STATUS value indicating success or specifying a
particular error condition.
- RevokeInfo
A pointer to a CSSM_FIELD structure containing optional suspension
information provided by the Certification Authority to the requester.
CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request
to verify a single target certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certverify_input{
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
CSSM_DATA_PTR Cert;
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_PTR VerifyContext;
} CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service provider
that can be used to manipulate a certificate of the requested type on
the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this request type.
- Cert
The certificate that is the target of a verification operation.
- VerifyContext
A pointer to a CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT structure containing additional
credentials and information to be used in the verification process
carried out by the verification authority. The verification request
can include:
-
An Action - an indicator of the action for which verification is being performed
-
An ActionData Object- the data object that is the target of the action
CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_STATUS
These constants define the status values that can be returned by a
certificate authority that provides a credential verification service.
The status CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_REVOKED indicates that the certificate in
question is explicitly revoked by a revocation record. A certificate
can be invalid for one of several reasons, including expiration,
unrecognized certificate issuer, invalid signature (implying tampering),
unrecognized certificate contents, etc.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_STATUS
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_UNKNOWN (0x0)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_VALID (0x1)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID (0x2)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_REVOKED (0x3)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_SUSPENDED (0x4)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_EXPIRED (0x5)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_NOT_VALID_YET (0x6)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_AUTHORITY (0x7)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_SIGNATURE (0x8)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_CERT_VALUE (0x9)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_CERTGROUP (0xA)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_POLICY (0xB)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_POLICY_IDS (0xC)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_BASIC_CONSTRAINTS (0xD)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_CRL_DIST_PT (0xE)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_INVALID_NAME_TREE (0xF)
#define CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_UNKNOWN_CRITICAL_EXT (0x10)
CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_OUTPUT
This data structure aggregates the verification status of a single
target certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certverify_output {
CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_STATUS VerifyStatus;
uint32 NumberOfEvidence;
CSSM_EVIDENCE_PTR Evidence;
} CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTVERIFY_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- VerifyStatus
The status result of a certificate verification process.
- NumberOfEvidence
The number of entries in
Evidence
- Evidence
A pointer to a CSSM_EVIDENCE structure containing an audit trail and
conditional information supporting the
VerifyStatus
of a certificate. This can include:
-
Certificates (or the unique identifiers for certificates) used as the
basis of verification
-
CRLs (or the unique names for a CRL) searched during the verification process
-
Conditional information such as the timeframe for which the
VerifyStatus
applies
Other domain-specific conditions
CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request to
notarize a certificate and optionally add more field values to the
certificate prior to over-signing by a CA process.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certnotarize_input {
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
uint32 NumberOfFields;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR MoreFields;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR SignScope;
uint32 ScopeSize;
CSSM_TP_SERVICES MoreServiceRequests;
uint32 NumberOfServiceControls;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR ServiceControls;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR UserCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service
provider that can be used to manipulate a certificate of the requested
type on the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this
request type.
- NumberOfFields
The number of certificate field values specified in
MoreFields.
- MoreFields
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs providing new, additional
certificate field values that can be added to an existing certificate prior
to over-signing the existing certificate and the newly added fields.
The specified fields can not replace any existing certificate fields.
Only appended field values are permitted. These fields are optional.
- SignScope
A pointer to the CSSM_FIELD array containing the OID/value pairs
specifying the certificate fields to be signed. When the input value
is NULL, the CA assumes and includes a default set of certificate fields in
the signing process.
- ScopeSize
The number of entries in the sign scope list. If no signing scope is
specified, then
ScopeSize
must be zero.
- MoreServiceRequests
A bit mask requesting additional certificate-notary-related services from
the Certificate Authority performing the operation.
- NumberOfServiceControls
The number of entries in the
ServiceControls
array.
- ServiceControls
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures. Each array element contains:
-
A CSSM_OID structure - the
Oid
value identifies one additional CA service associated with the notary
request. The name space for OID values is defined by the CA service domain.
-
A CSSM_DATA structure - the
Data
value is input information to the additional CA service identified by the
Oid
value.
- UserCredentials
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials being presented for
authentication by the caller making the certificate request. The
credentials structure can contain multiple types of credentials, as
required for multi-factor authentication. The credential data can be an
immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN, certificate, or template of
user-specific data, or the caller can specify a callback function a
service provider module can use to obtain one or more credentials.
The callback function can be used to obtain a passphrase, a biometric
input, or to perform a challenge and response protocol. The type of
credentials accepted by a service provider module is defined and recorded
in a record in the Module Directory Service records describing that provider.
If the service provider module does not require credentials from a caller,
then this field can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_STATUS
This set of defined constants indicates the status of a service request
to notarize an existing certificate by over-signing the certificate and
one or more of its current signatures.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_STATUS;
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_STATUS_UNKNOWN (0x0)
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OK (0x1)
/* cert fields were added and the result was notarized
as requested */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OKWITHOUTFIELDS (0x2)
/* non-conflicting cert fields were added,
conflicting cert fields were ignored,
and the result was notarized as requested */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OKWITHSERVICEMODS (0x3)
/* cert fields were added and the result was notarized
as requested, but some requested backend services
were not performed by the notary */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_REJECTED (0x4)
/* cert was not notarized due to some error condition */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_NOT_AUTHORIZED (0x5)
/* cert was not notarized, the request was not authorized */
CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OUTPUT
This data structure aggregates the output information generated in response
to a single request to notarize an existing certificate. Each result includes
a certificate group composed of one or more certificates. The first
certificate in the group is the notarized certificate.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certnotarize_output {
CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_STATUS NotarizeStatus;
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR NotarizedCertGroup;
CSSM_TP_SERVICES PerformedServiceRequests;
} CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- NotarizeStatus
A CSSM_TP_CERTNOTARIZE_STATUS value indicating the status of the newly
notarized certificate.
- NotarizedCertGroup
A pointer to a structure containing a reference to a certificate group and
the number of certificates contained in that group. The certificate group
contains the notarized certificate created in response to a notary request.
The certificate group can also contain supporting certificates related to
the newly notarized certificate. By convention the new notarized certificate
is the first member of the certificate group.
- PerformedServiceRequests
A bit mask indicating the additional certificate-notary-related services
that were performed by the Certificate Authority while notarizing the
certificate. Possible services include:
-
Publication of the notarized certificate in a certificate directory service
-
Auditing of the notary operation
-
Other authority-provided services
CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request to
reclaim an existing certificate and recover its associated private key.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certreclaim_input {
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
uint32 NumberOfSelectionFields;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR SelectionFields;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR UserCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service
provider that can be used to manipulate a certificate of the requested type
on the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this request type.
- NumberOfSelectionFields
The number of certificate field values in the
SelectionFields
array.
- SelectionFields
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs providing search values for
selecting one or more caller-owner certificates issued by a certificate
authority. These fields are optional. If no selection fields are provided,
then all caller-owner certificates from the CA will be returned for
possible reclamation.
- UserCredentials
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials being presented for
authentication by the caller making the certificate request. The
credentials structure can contain multiple types of credentials, as
required for multi-factor authentication. The credential data can be an
immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN, certificate, or template
of user-specific data, or the caller can specify a callback function a
service provider module can use to obtain one or more credentials. The
callback function can be used to obtain a passphrase, a biometric input,
or to perform a challenge and response protocol. The type of credentials
accepted by a service provider module is defined and recorded in a
record in the Module Directory Service records describing that provider.
If the service provider module does not require credentials from a caller,
then this field can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_STATUS
This set of defined constants indicates the status of a service request
to reclaim a certificate.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_STATUS;
#define CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_STATUS_UNKNOWN (0x0)
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_OK (0x1)
/* a set of one or more certificates were returned by the CA
for local recovery of the associated private key */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_NOMATCH (0x2)
/* no certificates owned by the requester were found matching
the specified selection fields */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_REJECTED (0x3)
/* certificate reclamation failed due to some error condition */
#define CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_NOT_AUTHORIZED (0x4)
/* certificate reclamation was not performed, the request
was not authorized */
CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_OUTPUT
This data structure aggregates the output information generated in response
to a single request to reclaim a set of certificates and recovery the use
of each associated private key. The returned certificates must be scanned
and reclaimed individually using the functions
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey()
and
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort()
to recover the private key to the local system.
typedef struct cssm_tp_certreclaim_output {
CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_STATUS ReclaimStatus;
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR ReclaimedCertGroup;
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle;
} CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CERTRECLAIM_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- ReclaimStatus
A value indicating the status of the certificate reclamation request.
- ReclaimedCertGroup
A pointer to a structure containing a reference to a group of certificates
and the number of certificates contained in that group. The certificate
group contains all certificates that are candidates for reclamation.
A certificate is a candidate if it satisfies at least the following criteria:
-
The certificate is owned by the requester
-
Recovery of the certificate is within the jurisdiction of the responding
Certification Authority
-
The certificate matched the input selection criteria
- KeyCacheHandle
A handle to a cache of protected private keys. The cache is managed by
the service provider. Each key is associated with one of the certificates in
ReclaimedCertGroup.
CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_INPUT
This data structure aggregates the input information for a request to
issue the most current certificate revocation list (CRL). The desired CRL
is identified by at least one of the following input values:
-
CrlIdentifier
- requesting the most current CRL issued after the CRL named by this identifier
-
CrlThisTtime
- requesting the most current CRL issued after this time
-
PolicyIdentifier
- requesting the most current CRL governing the policy domain indicated by
this Policy identifier.
If CRL retrieval is a controlled operation, the caller can present the
necessary credentials in
CallerCredentials.
typedef struct cssm_tp_crlissue_input {
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle;
uint32 CrlIdentifier;
CSSM_TIMESTRING CrlThisTime;
CSSM_FIELD_PTR PolicyIdentifier;
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR CallerCredentials;
} CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_INPUT, *CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_INPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- CLHandle
The identifier that uniquely describes a Certificate Library service provider
that can be used to manipulate certificates and CRLs of the requested type on
the local system. This is an optional input parameter for this request type.
- CrlIdentifier
An integer that uniquely identifies the most current certificate revocation
list known or held by the requester. If the CRL identifier is not known,
or the requester has no previous local copy of a CRL, then this value can
be zero.
- CrlThisTime
A CSSM_TIMESTRING_PTR referencing a string containing the date and time
of the most current certificate revocation list known or held by the
requester. If the time is not known, or the requester has no previous
local copy of a CRL from which to extract a time, then this pointer value
can be NULL.
- PolicyIdentifier
The policy identifier is an OID-value pair. The CSSM_OID structure contains
the name of the policy and the value (contained in a CSSM_DATA structure)
is an optional, caller-specified input value governing the interpretation and
application of the policy. The name space for policy identifiers is defined
externally by the application domains served by the Certification Authority.
If the policy domain is implied by
CrlIdentifier
or can be determine by the jurisdiction of the requester's
CallerCredentialsi,
then this pointer value can be NULL.
- CallerCredentials
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials being presented for
authentication by the caller requesting a CRL from a Certification Authority.
The credentials structure can contain multiple types of credentials,
as required for multi-factor authentication. The credential data can be
an immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN, certificate, or template
of user-specific data, or the caller can specify a callback function a
service provider module can use to obtain one or more credentials.
The callback function can be used to obtain a passphrase, a biometric input,
or to perform a challenge and response protocol. The type of credentials
accepted by a service provider module is defined and recorded in a record in
the Module Directory Service records describing that provider. If
the service provider module does not require authenticated callers, then
this field can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_STATUS
This set of defined constants indicates the status of a service request
to issue the most recent certificate revocation list.
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_STATUS;
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_STATUS_UNKNOWN (0x0)
/* indeterminate */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_OK (0x1)
/* a copy of the most current CRL was issued as requested
and the time for issuing the next CRL is also returned */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_NOT_CURRENT (0x2)
/* either no CRL has been issued since the CRL identified
in the request, or it is not time to issue an updated CRL.
no CRL has been returned, but the time for issuing the
next CRL is included in the results */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_INVALID_DOMAIN (0x3)
/* CRL domain was not recognized or was outside the
CA jurisdiction, no CRL or time for the next CRL
has been returned */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_UNKNOWN_IDENTIFIER (0x4)
/* unrecognized CRL identifier,
no CRL or time for the next CRL has been returned */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_REJECTED (0x5)
/* CRL was not issued due to some error condition,
no CRL or time for the next CRL has been returned */
#define CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_NOT_AUTHORIZED (0x6)
/* CRL was not issued, the request was not authorized,
no CRL or time for the next CRL has been returned */
CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_OUTPUT
This data structure aggregates the output information generated in response
to a single request to issue a copy of the most recent certificate
revocation list (CRL).
typedef struct cssm_tp_crlissue_output {
CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_STATUS IssueStatus;
CSSM_ENCODED_CRL_PTR Crl;
CSSM_TIMESTRING CrlNextTime;
} CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_OUTPUT, *CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_OUTPUT_PTR;
Definitions
- IssueStatus
A CSSM_TP_CRLISSUE_STATUS value indicating the status of a copy of the
newly issued CRL and the time specified for issuing the next CRL update.
- Crl
A pointer to a structure containing the encoded certificate revocation
list and indicators specifying the type and encoding of the CRL
representation. If the request failed and no CRL is returned, then
this pointer value is NULL.
- CrlNextTime
A CSSM_TIMESTRING referencing a string containing the anticipated date and
time for issuing the next CRL update in the domain of the returned CRL.
If the time is not known, then this pointer value can be NULL.
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE
typedef uint32 CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE;
#define CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE_GENERIC (0x0)
#define CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE_REGISTRATION (0x1)
Error Codes and Error Values
The Error Values that can be returned by TP functions can be either
derived from the Common Error
Codes defined in
CSSM Error Handling,
or from a Common set that more than one TP function
can return, or they are specific to a TP function.
The TP Error Values defined in this section list the TP Error Values
in the Common set, plus any Error Values that are specific to a function.
TP Error Values Derived from Common Error Codes
#define CSSMERR_TP_INTERNAL_ERROR \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INTERNAL_ERROR)
#define CSSMERR_TP_MEMORY_ERROR \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR)
#define CSSMERR_TP_MDS_ERROR \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_INPUT_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_INPUT_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_FUNCTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_FUNCTION_NOT_IMPLEMENTED)
#define CSSMERR_TP_SELF_CHECK_FAILED \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_SELF_CHECK_FAILED)
#define CSSMERR_TP_OS_ACCESS_DENIED \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_OS_ACCESS_DENIED)
#define CSSMERR_TP_FUNCTION_FAILED \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_FUNCTION_FAILED)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DATA \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DATA)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DB_LIST)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CERT_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CRL_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DATA \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DATA)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR)
#define CSSMERR_TP_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS)
#define CSSMERR_TP_VERIFICATION_FAILURE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_VERIFICATION_FAILURE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DB_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_UNKNOWN_FORMAT)
#define CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_TAG \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_UNKNOWN_TAG)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR + CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DL_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_CL_HANDLE)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER)
Common TP Error Values
These values can be returned by one or more TP APIs.
#define CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_ERROR+CSSM_ERRORCODE_COMMON_EXTENT)
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER \
(CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+1)
Invalid context pointer
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+2)
Invalid identifier pointer
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_KEYCACHE_HANDLE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+3)
Invalid key cache handle
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+4)
Invalid structure or unknown format for certificate group or certificates in the group
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+5)
Invalid structure or unknown format for CRL group or CRLs in the group
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+6)
Invalid CRL group pointer
#define CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+7)
Invalid/unauthorized credentials
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+8)
Incomplete certificate group
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+9)
Cannot perform the requested operation (sign/verify/database-apply)
with input signer or revoker certificate
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+10)
Certificate has expired
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+11)
Certificate not valid until a future date
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+12)
Certificate has been revoked
#define CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+13)
Certificate is currently suspended from use
#define CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+14)
Insufficient caller credentials for this operation
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+15)
Invalid action
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+16)
Invalid data specified for this action
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+17)
Invalid anchor certificate
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+18)
Invalid or unreachable authority
#define CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+19)
Unable to determine trust for action
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+20)
Invalid certificate
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+21)
Certificate group is not signed by a recognized issuing authority
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+22)
Certificate Revocation List is from an unrecognized issuing authority.
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+23)
Invalid encoding for CRL
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+24)
Invalid type for CRL
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+25)
Invalid CRL
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FORM_TYPE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+26)
Invalid argument for form type
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ID (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+27)
Invalid pass through ID
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+28)
Unknown reference identifier
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_INDEX (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+29)
Certficate index is invalid
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+30)
Certificate contains unrecognized names
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+31)
Invalid policy identifier
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+32)
Invalid CSSM_TIMESTRING
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REASON (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+33)
Invalid argument for reason
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REQUEST_INPUTS (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+34)
Invalid request input parameters
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_RESPONSE_VECTOR (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+35)
Invalid vector of responses
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+36)
Certificate signature is invalid
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+37)
Invalid stop on policy
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+38)
Invalid callback
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+39)
Invalid tuple
#define CSSMERR_TP_NOT_SIGNER (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+40)
Signer certificate is not signer of subject
#define CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+41)
Signature can not be trusted
#define CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+42)
Unspecified authority with no default authority
#define CSSMERR_TP_REJECTED_FORM (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+43)
Form was rejected
#define CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_LOST (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+44)
Authority lost the request. Must resubmit
#define CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_REJECTED (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+45)
Authority rejected the request with no specific results returned
#define CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+46)
Unsupported type of network address
#define CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_SERVICE (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+47)
Unsupported TP service requested
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP_POINTER (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+48)
Invalid tuple group pointer
#define CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP (CSSM_TP_BASE_TP_ERROR+49)
Invalid structure or unknown format for tuple group or tuples in the group
Trust Policy Operations
The man-page definitions for Trust Policy operations are
presented in this section.
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest for the CSSM API
TP_SubmitCredRequest for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType,
const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ReferenceIdentifier)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_SubmitCredRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType,
const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ReferenceIdentifier)
DESCRIPTION
If the caller is successfully authenticated, then this function submits
a request to the Authority identified by
PreferredAuthority.
The authority service can be local or remote. If the Authority is
not specified, then the TP module can assume a default authority based
on the
RequestType
and the
CallerAuthContext.
RequestType
indicates the type of Authority request and
RequestInput
specifies the input parameters needed by the authority to perform the request.
The request is submitted to the authority only if the TP module can
successfully authenticate the caller. The
CallerAuthContext
presents the caller's credentials and a list of one or more policies
under which the caller should be authenticated. Caller credentials
can be presented in several forms:
-
Memory-resident credential values, directly referenced by the structure
-
Data bases containing credentials
-
Callback functions that can be invoked to obtain credentials from
an active entity
The local service provider must select and forward the credentials
required by the Authority. The caller must provide all necessary
credentials through the
CallerAuthContext
parameter.
If the caller can not be authenticated by the local service provider,
the function fails and the request is not submitted to the selected authority.
This function returns a
ReferenceIdentifier
and an
EstimatedTime
(specified in seconds).
ReferenceIdentifier
is an ID for the submitted request.
EstimatedTime
defines the expected time to process the request. This time may be
substantial when the request requires offline authentication procedures
by the Authority process. In contrast, the estimated time can be zero,
meaning the result can be obtained immediately using
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI).
After the specified time has elapsed, the caller must use the function
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSMAPI) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI)
with the reference identifier, to obtain the result of the request.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to
perform this function.
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Certificate Service Authority
to submit the request to.
- RequestType (input)
The identifier of the type of request to submit.
- RequestInput (input)
A pointer to the input parameters to be submitted to the authority
who will perform the requested service.
- CallerAuthContext (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials.
The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed
registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific data.
The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module
and recorded in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials can be
required. If the local service provider module does not require credentials
from a caller, then the
CallerCredentials
field of this verification context structure can be NULL. The
structure optionally contains additional credentials that can be used
to support the authentication process. Authentication credentials required
by the authority should be included in the
RequestInput.
The local service provider module can forward this credential information
to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The number of estimated seconds before the service results are ready
to be retrieved. A (default) value of zero indicates that the results
can be retrieved immediately via the corresponding
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI)
function call. When the local service provider module or the authority
cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service,
the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- ReferenceIdentifier (output)
A reference identifier, which uniquely identifies this specific request.
The handle persists across application executions and becomes undefined
when all local processing of the request has completed. Local processing
is completed in one of two ways:
-
For certificate services that do not require explicit confirmation
by the requester, the reference identifier is invalidated when the
corresponding
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI)
function completes (by returning valid results or by failure, which
blocks returned results)
-
For certificate services that require explicit confirmation by the
requester, the reference identifier is invalidated by successfully
invoking the function
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResu()
(CSSM API) or
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
(TP SPI).
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_SERVICE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REQUEST_INPUTS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
For the TP SPI:
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult
SYNOPSIS
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_BOOL *ConfirmationRequired,
CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET_PTR *RetrieveOutput)
DESCRIPTION
This function returns the results of a
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
call.
The single identifier
ReferenceIdentifier
denotes the
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
invocation that initiated the request.
It is possible that the results are not ready to be retrieved when this
call is made. In that case, an
EstimatedTime
to complete processing is returned. The caller must attempt to retrieve
the results again after the estimated time to completion has elapsed.
This function can fail in total for any one of the following reasons:
-
The reference identifier is invalid
-
The TP process can not be located
-
The TP process encountered a fatal error when attempting to process the request.
When this function completes, the set of return results is ordered
corresponding to the order of the originating request.
Some certificate services require the requester to confirm retrieval of
the results.
ConfirmationRequired
indicates whether the caller must confirm completion of
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
by calling
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult().
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to
perform this function.
- ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies the
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
call that initiated the certificate service request whose results are
returned by this function. The identifier persists across application
executions and becomes undefined when all local processing of the request
has completed. Local processing is completed in one of two ways:
-
For certificate services that do not require explicit confirmation by
the requester, the reference identifier is invalidated when the
corresponding
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
function completes (by returning valid results or by failure, which
blocks returned results)
-
For certificate services that require explicit confirmation by the
requester, the reference identifier is invalidated by successfully
invoking the function
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult().
- CallerAuthCredentials (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials.
The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed
registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific data.
The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module
and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials
can be required. If the local service provider module does not require
credentials from a caller, then the
Credentials
field of this verification context structure can be NULL. The
structure optionally contains additional credentials that can be used
to support the authentication process. Authentication credentials required
by the authority should be included in the
RequestInput.
The local TP module can forward information from the
CallerAuthCredentials
to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The number of seconds estimated before the results of a requested service
will be returned to the requester.
When the local TP module or the authority process cannot estimate the
time required to perform the requested service, the output value for
estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- ConfirmationRequired (output)
A boolean value indicating whether the caller must invoke
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
to acknowledge retrieving the results of the service request. CSSM_TRUE
indicates the caller must call
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult().
CSSM_FALSE indicates that the caller must not call
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult().
The value of this output parameter is not applicable until the
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
completes by returning results of the request or terminates in
unrecoverable failure.
- RetrieveOutput (output)
A pointer to the results returned by the authority in response to the
service requests submitted by
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest().
The output results are ordered corresponding to the requests. The structure
of the response set is determined by the type of request. The caller and
the service provider must retain knowledge of the request type associated
with the
ReferenceIdentifier.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value combined with estimated time to indicate one of
three results:
| Complete Function
| Function Return
| RetrieveOutput
| EstimatedTime
|
|---|
| Result
| Value
|
|
|
|---|
| Request results returned to caller
| CSSM_OK
| Non-NULL pointer
| NA
|
| Request results not ready, but expected in the future
| CSSM_OK
| NULL pointer
| CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_
UNKNOWN or <estimated seconds>
|
| Fatal Error, results will never be returned
| (!CSSM_OK)
| NA
| NA
|
For a return value of (!CSSM_OK) the return value represents a specific
error code.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_LOST
CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_REJECTED
SEE
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
For the TP SPI:
TP_SubmitCredRequest()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult for the CSSM API
TP_ConfirmCredResult for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ConfirmCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority)
DESCRIPTION
This function submits a vector of acknowledgements to a Certificate
Authority for a set of requests and corresponding results identified by
ReferenceIdentifier.
The caller must execute the call sequence
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
and
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(or the equivalent TP SPI calls)
to submit a set of requests and to retrieve the results of those requests.
Some Certificate Authority services accessed through the request and
retrieve functions require confirmation. The function
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI)
returns a value indicating whether the caller must invoke
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_ConfirmCredResult()
(TP SPI)
to successfully complete the service.
The
Responses
vector accepts or rejects each result independently. If the caller
rejects a returned result, the action taken by the authority depends
on the requested type of service.
The
ReferenceIdentifier
also identifies the authority process state associated with the function
pair
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
and
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(or the equivalent TP SPI calls).
The
PreferredAuthority
information can be used to further identify the authority to receive
the acknowledgement. After successful execution of this function,
the value of the
ReferenceIdentifier
is undefined and should not be used in subsequent operations in the
current module attach session.
This function fails if
ReferenceIdentifier
is invalid or the Authority process can not be located.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to
perform this function.
- ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies execution of the call
sequence
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
and
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(or the equivalent TP SPI call pair)
to submit a set of requests and to retrieve the results of those requests.
- CallerAuthCredentials (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials.
The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed
registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific data.
The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module
and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials
can be required. If the local service provider module does not require
credentials from a caller, then the
Credentials
field of this verification context structure can be NULL. The structure
optionally contains additional credentials that can be used to support
the authentication process. Authentication credentials required by the
authority should be included in the
RequestInput.
The local TP module can forward information from the
CallerAuthCredentials
to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
- Responses (input)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the caller's acceptance or
rejection of results. The vector contains one acknowledgement per result
returned by
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
(TP SPI).
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Authority to receive
the acknowledgements. The structure can include:
-
An identity certificate for the authority
-
The location of the authority
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_RESPONSE_VECTOR
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest()
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation()
For the TP SPI:
TP_SubmitCredRequest()
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
TP_ReceiveConfirmation()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation for the CSSM API
TP_ReceiveConfirmation for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses,
sint32 *ElapsedTime)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ReceiveConfirmation
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses,
sint32 *ElapsedTime)
DESCRIPTION
A certificate authority uses this function to poll for confirmation from
a requester who has been served by the authority. A requester sends a
confirmation to the authority by successfully invoking the function
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
(CSSM API) or
TP_ConfirmCredResult()
(TP SPI).
The
ReferenceIdentifier
uniquely identifies the service request and corresponding results for which
confirmation is expected. This reference identifier need not be identical
to the reference identifier used by the requester, but a one-to-one
mapping between the two name spaces must be well-defined.
Responses
is an ordered vector of acknowledgements indicating, for each returned
result, whether the result was accepted or rejected by the original
requester for whom the service was performed. If a result is rejected
by the receiver, then the authority process must undo the service if
a reverse operation is possible and available.
If a fatal error occurs, this function returns an error code, indicating
that the function call can never be completed. If confirmation has not
been received, the function return value is CSSM_OK and the
ElapsedTime
is returned to the caller of this function. The time represents elapsed
seconds since the service results were produced by the authority process.
Note that there can be a difference between the time the authority
process produces the results and the time the results are actually
received by the requester. Elapsed time is relative and should increase
with consecutive calls using the same
ReferenceIdentifier.
If the TP module has no knowledge of the elapsed time, the value
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN must be returned. If the service requester
has confirmed receipt of the service results, this function returns
CSSM_OK and
ElapsedTime
is CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
This function can be invoked repeatedly until the confirmation is received
or until the caller decides the acknowledgement may be lost and chooses
to undo the results of the original service request.
This function fails if the
ReferenceIdentifier
is invalid or does not match any requested service for which confirmation
is expected.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to
perform this function.
- ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies a set of service requests
and the results created in response to those requests.
- Responses (output)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the caller's acceptance
or rejection of results. The vector contains one acknowledgement per
result created by the certificate authority.
- ElapsedTime (output)
- If the confirmation has not been received, this output value is the
number of seconds elapsed since the certificate authority created the
results or CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN. If the confirmation has been
received, this output value is CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM return value combined with elapsed time to indicate one of
three results:
| Complete Function
| Function Return
| RetrieveOutput
| EstimatedTime
|
|---|
| Result
| Value
|
|
|
|---|
| Confirmation Received
| CSSM_OK
| CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE
|
|
| Confirmation not received, but expected in the future
| CSSM_OK
| CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN
or <elapsed seconds>
|
|
| Fatal Error, Confirmation is not expected
| (!CSSM_OK)
| NA
|
|
For a return value of (!CSSM_OK) the return value is an error code.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
For the TP SPI:
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey for the CSSM API
TP_CertReclaimKey for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
uint32 CertIndex,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimKey
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
uint32 CertIndex,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry)
DESCRIPTION
This function recovers the private key associated with a certificate and
securely stores that key in the specified cryptographic service provider.
The key and its associated certificate are among a set of certificates and
private keys reclaimed from a certificate authority.
The particular private key to be recovered to the local system is
identified by its associated certificate. The certificate is identified by
its
CertIndex
position within the
CertGroup.
The reclamation process associates the private key with the public key
contained in the certificate, and securely stores the private key in the
specified cryptographic service provider.
The CSP can require that the caller provide access credentials authorizing
inserting a new key into the CSP through an
UnwrapKey
operation. The caller should also provide an initial Access Control List
(ACL) entry for the newly inserted key. The ACL entry is used to
control future use of the recovered private key. These inputs are provided
in
CredAndAclEntry.
When all required private keys have been reclaimed, the key cache can be
discarded using the function
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort()
(CSSM API) or
TP_CertReclaimAbort()
(TP SPI).
The caller must free the
CertGroup
when it is no longer needed.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider module used to perform this
operation.
- CertGroup (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a reference to a group of certificates
and the number of certificates contained in that group. The certificate group
contains all certificates that are candidates for reclamation.
- CertIndex (input)
An index value that identifies the certificate whose associated private key
is to be recovered and stored in the local CSP. This index value I references
the I-th certificate in
CertGroup.
- KeyCacheHandle (input)
A reference handle that uniquely identifies the cache of protected private
keys associated with the reclaimed certificates contained in
CertGroup.
The structure of the cache is opaque to the caller.
- CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the CSP module where the private key is to be
stored. Optionally, the CA service provider can use this CSP to perform
additional cryptographic operations or may use another default CSP for
that purpose.
- CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials authorized for creating
a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control future use of the
newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype can
be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided for
use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry
interactively. If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then
the credentials can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry
for the new key, then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_INDEX
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_KEYCACHE_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult()
CSSM_TP_Cert_ReclaimAbort()
For the TP SPI:
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
TP_Cert_ReclaimAbort()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort for the CSSM API
TP_CertReclaimAbort for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimAbort
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle)
DESCRIPTION
This function terminates the iterative process of reclaiming certificates
and recovering their associated private keys from a protected key cache.
This function must be called even if all private keys are recovered from
the cache. This function destroys all intermediate state and secret
information used during the reclamation process. At completion of this
function, the cache handle is invalid.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider module used to perform this
function.
- KeyCacheHandle (input)
An opaque handle that identifies the cache of protected private keys
reclaimed from a certificate authority for potentially recovery on the
local system.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_KEYCACHE_HANDLE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertReclaimKey()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_FormRequest for the CSSM API
TP_FormRequest for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_FormRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm)
DESCRIPTION
This function returns a blank form of type
FormType
from an Authority. If the
PreferredAuthority
list is NULL, the CA module can use a default authority name and location
based on
FormType.
The CA module must incorporate knowledge of the interface protocol
for communicating with the authority.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to
perform this function.
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate that
identifies the Authority process, or a network address directly or
indirectly identifying the location of the authority. If the input
is NULL, the module can assume a default authority location. If a default
authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated and the
operation fails.
- FormType (input)
- ,br
Indicates the type of form being requested.
- BlankForm (output)
A CSSM_DATA structure containing the requested form. The caller must
have knowledge of the structure of the form based on
FormType.
RETURN VALUE
ERRORS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FORM_TYPE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_FormSubmit()
For the TP SPI:
TP_FormSubmit()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_FormSubmit for the CSSM API
TP_FormSubmit for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_FormSubmit
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
const CSSM_DATA *Form,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority,
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormSubmit
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
const CSSM_DATA *Form,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority,
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials)
DESCRIPTION
The completed Form is submitted to a
ClearanceAuthority,
who is acting on behalf of a
RepresentedAuthority.
Typically the submitted form is requesting an authorization credential
required as input to future service requests to the
RepresentedAuthority.
If the form is honored by the
ClearanceAuthority,
then a set of one or more
Credentials
is returned to the requester.
These credential can be used as the input credential in future service
requests submitted to the
RepresentedAuthority.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
A handle for the service provider module that will perform the operation.
- FormType (input)
Indicates the type of form being submitted.
- Form (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the completed form to
be submitted to the
ClearanceAuthority.
- ClearanceAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate
that identifies the clearance authority process, or a network address
directly or indirectly identifying the location of the authority.
If the input is NULL, the service provider module can assume a default
authority based on the
FormType
and contents of
Form.
If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be
initiated and the operation fails.
- RepresentedAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate
that identifies the authority represented by the
ClearanceAuthority,
or a network address directly or indirectly identifying the location
of the authority.
If the input is NULL, the service provider module can assume a default
authority based on the
FormType
and contents of
Form.
If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be
initiated and the operation fails.
- Credentials (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing one or more
credentials issued in response to the contents of the
Form.
If the output is NULL, either no credentials were returned or an
error occurred.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FORM_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_REJECTED_FORM
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_FormRequest()
For the TP SPI:
TP_FormRequest()
Local Application-Domain-Specific Trust Policy Functions
The man-page definitions for Local Application-Domain-Specific Trust Policy
functions are presented in this section.
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify for the CSSM API
TP_CertGroupVerify for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult)
DESCRIPTION
This function determines whether the certificate is trusted. The
actions performed by this function differ based on the trust policy
domain. The factors include practices,
procedures and policies defined by the certificate issuer.
Typically certificate verification involves the verification of
multiple certificates. The first certificate in the group is the
target of the verification process. The other certificates in the
group are used in the verification process to connect the target
certificate with one or more anchors of trust. The supporting
certificates can be contained in the provided certificate group
or can be stored in the data stores specified in the
VerifyContext
DBList. This
allows the trust policy module to construct a certificate group
and perform verification in one operation. The data stores
specified by DBList can also contain certificate revocation lists
used in the verification process. It is also possible to provide
a data store of anchor certificates. Typically the points of
Trust are few in number and are embedded in the caller or in the
TPM during software manufacturing or at runtime
The caller can select to be notified incrementally as each
certificate is verified. The
CallbackWithVerifiedCert
parameter
(in the
VerifyContext)
can specify a caller function to be
invoked at the end of each certificate verification, returning
the verified certificate for use by the caller.
Anchor certificates are a list of implicitly trusted certificates.
These include root certificates, cross certified certificates, and
locally defined sources of trust. These
certificates form the basis to determine trust in the subject certificate.
A policy identifier can specify an additional set of conditions that
must be satisfied by the subject certificate in order to meet the trust
criteria. The name space for policy identifiers is defined by the
application domains to which the policy applies. This is outside of
CSSM. A list of policy identifiers can be specified and the stopping
condition for evaluating that set of conditions.
The evaluation and verification process can produce a list of evidence.
The evidence can be selected values from the certificates examined in
the verification process, entire certificates from the process or other
pertinent information that forms an audit trail of the verification
process. This evidence is returned to the caller after all steps in the
verification process have been completed.
If verification succeeds, the trust policy module may carry out the
action on the specified data or may return approval for the action
requiring the caller to perform the action. The caller must consult TP
module documentation outside of this specification to
determine all module-specific side effects of this operation.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate the subject certificate and anchor
certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP
module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider
module that can be used to perform the cryptographic operations
required to carry out the verification. If no
CSP handle is specified, the TP module allocates a suitable CSP.
- CertGroupToBeVerified (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be verified. The first
certificate in the group is the primary target certificate for
verification. Use of the subsequent certificates during the
verification process is specific to the trust domain.
- VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual
information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values
in the context are optional except
Action.
The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate
without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The
operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the
service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- VerifyContextResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during
the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate for the CSSM API
TP_CertCreateTemplate for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
DESCRIPTION
This function allocates and initializes memory for an encoded certificate
template output in
CertTemplate->Data.
The template values are specified by the input OID/value pairs contained in
CertFields.
The initialization process includes encoding all certificate field values
according to the certificate type and certificate template encoding supported
by the trust policy library module.
The
CertTemplate
output is an unsigned certificate template in the format supported by the TP.
The memory for
CertTemplate->Data
is allocated by the service provider using the calling application's
memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library module used to perform
this function.
- NumberOfFields (input)
The number of certificate field values specified in the
CertFields.
- CertFields (input)
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs that identifies the field
values to initialize a new certificate.
- CertTemplate (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure that will contain the unsigned
certificate template as a result of this function.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields()
CSSM_TP_CertSign()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields()
TP_CertSign()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields for the CSSM API
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
DESCRIPTION
This function extracts and returns all field values from
CertTemplate.
CertTemplate
is an unsigned certificate template in the format supported by the TP.
Fields are returned as a set of OID-value pairs. The OID identifies
the TP certificate template field and the data format of the value
extracted from that field.
The Trust Policy module defines and uses a preferred data format for
returning field values from this function.
Memory for the
CertFields
output is allocated by the service provider using
the calling application's memory management routines. The application must
deallocate the memory, by calling
CSSM_CL_FreeFields()
(CSSM API) or
CL_FreeFields()
(TP SPI).
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform
this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library module used to perform
this function.
- CertTemplate (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the packed, encoded
certificate template.
- NumberOfFields (output)
The length of the output array of fields.
- CertFields (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures which contains the OIDs
and values of the fields of the input certificate template.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate()
CSSM_TP_CertSign()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertCreateTemplate()
TP_CertSign()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertSign for the CSSM API
TP_CertSign for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
DESCRIPTION
The TP module decides whether the signer certificate is trusted to
sign the
CertTemplateToBeSigned.
The signer certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability
to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established,
this operation signs the entire certificate. The caller must provide
a credential that permits the caller to use the private key for
this signing operation. The credential can be provided in the
cryptographic context
CCHandle.
If
CCHandle
is NULL, the credentials in the
SignerVerifyContext
specify the credential value.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform
this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used
to perform this function.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context for signing
the certificate. This context also identifies the cryptographic
service provider to be used to perform the signing operation.
If this handle is not provided by the caller, the trust policy module
can assume a default signing algorithm and a default CSP.
If the trust policy module does not assume defaults or the default
CSP is not available on the local system, an error occurs.
- CertTemplateToBeSigned (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a certificte template to be signed.
The CRL type and encoded are included in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent
the signer for this operation. The first certificate in the group is the
target certificate representing the signer. Use of subsequent
certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a
hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates
of a certificate chain.
- SignerVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual
information to be used in the verification process. All of the input
values in the context are optional. The service provider can define
default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the
other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a
necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define
an appropriate default value.
- SignerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the
verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- SignedCert (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the signed certificate.
The
SignedCert->Data
is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the
application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate()
CSSM_TP_CrlSign()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertCreateTemplate()
TP_CrlSign()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CrlVerify for the CSSM API
TP_CrlVerify for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CrlVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult)
DESCRIPTION
This function verifies the integrity of the certificate revocation list
and determines whether it is trusted. The conditions for trust are part
of the trust policy module. It can include conditions such as validity
of the signer's certificate, verification of the signature on the CRL,
the identity of the signer, the identity of the sender of the CRL, date
the CRL was issued, the effective dates on the CRL, and so on.
The caller can specify additional points of trust represented by
anchor certificates in the
VerifyContext.
The trust policy module can
use these additional points of trust in the verification process.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate the certificates to be verified. If no
certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed
CL module, if required.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service Provider to be used to
verify signatures on the signer's certificate and on the CRL. The TP
module is responsible for creating the cryptographic context structure
required to perform the verification operation. If no CSP is specified,
the TP module uses an assumed CSP to perform the operations.
- CrlToBeVerified (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing a signed certificate
revocation list to be verified.
The CRL type and encoding are included in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_CERTGROUP structure containing one or more
related certificates that paretially or fully represent the signer
of the certificate revocation list.
The first certificate
in the group is the target certificate representing the CRL signer.
Use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For
example, in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are
intermediate
certificates of a certificate chain -
the caller can specify additional points of trust represented by
anchor certificates in the
VerifyContext.
The trust policy module can
use these additional points of trust in the verification process.
- VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual
information to be used in the verification process. All of the input
values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default
values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other
fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary
input value is omitted and the service module can not define an
appropriate default value
- RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generation during
the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlVerify()
For the TP SPI:
CL_CrlVerify()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CrlCreateTemplate for the CSSM API
TP_CrlCreateTemplate for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
DESCRIPTION
This function creates an unsigned, memory-resident CRL template.
Fields in the CRL are initialized based on the descriptive data
specified by the OID/value input pairs in
CrlFields
and the local domain policy of the TP. The specified OID/value pairs
can initialize all or a subset of the general attribute fields in
the new CRL, though the module developer may specify a set of fields
that must be or cannot be set using this operation. The
NewCrlTemplate
output is an unsigned CRL template in the format supported by the TP.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform
this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used
to perform this function.
- NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID/value pairs specified in the
CrlFields
input parameter.
- CrlFields (input)
Any array of field OID/value pairs containing the values to initialize
the CRL attribute fields
- NewCrlTemplate (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the new CRL. The
NewCrl->Data
is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by
the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CrlSignWithKey()
CSSM_TP_CrlSignWithCert()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CrlSignWithKey()
TP_CrlSignWithCert()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertRevoke for the CSSM API
TP_CertRevoke for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertRevoke
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRevoke
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
DESCRIPTION
The TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can
revoke the subject certificate group. The revoker certificate group
is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is
determined. Once the trust is established, the TP revokes the
subject certificate by adding it to the certificate revocation list.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform
this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider
module used to perform this function.
- OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing an existing certificate
revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list is created or the
operation fails.
- CertGroupToBeRevoked (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent
the certificate to be revoked by this operation. The first certificate
in the group is the target certificate. The use of subsequent certificates
is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model
subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
- RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent
the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate in
the group is the target certificate representing the revoker.
The use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
- RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in verifying certificates
and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional elements in
the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default
values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module vendor
release documents.
This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
- RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during
the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- Reason (input/optional)
The reason for revoking the subject certificate.
- NewCrlTemplate (outputl)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the updated certificate
revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error has occurred.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REASON
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert()
For the TP SPI:
CL_CrlAddCert()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate for the CSSM API
TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
DESCRIPTION
The TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can
remove the subject certificate group from the CRL template. The
revoker certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability
to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established,
the TP
removes the certificates from the CRL template.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform
this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used
to perform this function.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider module
used to perform this function.
- OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing an existing certificate
revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list is created or
the operation fails.
- CertGroupToBeRemoved (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be removed from the the CRL template.
- RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent
the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate in
the group is the target certificate representing the revoker.
The use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
- RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in verifying certificates
and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional elements in
the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default
values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module
vendor release documents.
This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
- RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during
the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- NewCrlTemplate (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the updated certificate
revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error has occurred.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert()
For the TP SPI:
CL_CrlAddCert()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CrlSign for the CSSM API
TP_CrlSign for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CrlSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl)
DESCRIPTION
The TP module decides whether the signer certificate is trusted to sign
the entire certificate revocation list. The signer certificate group is
first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is
determined. Once the trust is established, this operation signs the
entire certificate revocation list. Individual records within the
certificate revocation list were
signed when they were added to the list.
The caller must provide a credential that permits the caller to use
the private key for this signing operation. The credential can be
provided in the cryptographic context
CCHandle.
If
CCHandle
is NULL,
the credentials in the
SignerVerifyContext
specify the credential value.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate the certificates to be verified. If no
certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed
CL module, if required.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context for signing
the CRL. This context also identifies the cryptographic service
provider to be used to perform the signing operation. If this
handle is not provided by the caller, the trust policy module
can assume a default signing algorithm and a default CSP. If the
trust policy module does not assume defaults or the default CSP
is not available on the local system an error occurs.
- CrlToBeSigned (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing a certificate
revocation list to be signed.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_CERTGROUP structure containing one or more
related certificates that partially or fully represent the signer of the
certificate revocation list. The first certificate in
the group is the target certificate representing the CRL signer.
Use of
subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example,
in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate
certificates of a certificate chain.
- SignerVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual
information to be used in the verification process. All of the
input values in the context are optional. The service provider can
define default values or can attempt to operate without input for
all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail
if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not
define an appropriate default value.
- SignerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generation during
the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- SignedCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the signed certificate
revocation list. The
SignedCrl->Data
is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlSign()
For the TP SPI:
CL_CrlSign()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_ApplyCrlToDb for the CSSM API
TP_ApplyCrlToDb for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ApplyCrlToDb
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ApplyCrlToDb
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult)
DESCRIPTION
This function updates persistent storage to reflect entries in the
certificate revocation list. The TP module determines whether the
memory-resident CRL is trusted, and if it should be applied to one or
more of the persistent databases. Side effects of this function can
include saving a persistent copy of the CRL in a data store, or
removing certificate records from a data store.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate the CRL as it is applied to the data store
and to manipulate the certificates effected by the CRL, if required. If
no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an
assumed CL module, if required.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service Provider to be used to
verify signatures on the CRL determining whether to trust the CRL and
apply it to the data store. The TP module is responsible for creating
the cryptographic context structures required to perform the
verification operation. If no CSP is specified, the TP module uses an
assumed CSP to perform these operations.
If optional, the caller will set this value to 0.
- CrlToBeApplied (input)
A pointer to a structure containing the encoded certificate revocation
list to be applied to the data store. The CRL type and encoding are included
in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_CERTGROUP structure containing one or more
related certificates that partially or fully represent the signer of the
certificate revocation list. The first certificate in
the group is the target certificate representing the CRL signer.
Use of
subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example,
in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate
certificates of a certificate chain.
- ApplyCrlVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual
information to be used in the verification process. All of the input
values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default
values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields
of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input
value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate
default value.
- ApplyCrlVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during
the verification process. The information can include:
| Evidence
| (output/optional)
|
| NumberOfEvidences
| (output/optional)
|
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstItem()
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextItem()
CSSM_DL_CertRevoke()
For the TP SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstItem()
CL_CrlGetNextItem()
DL_CertRevoke()
Group Functions
The man-page definitions for TP Group functions are
presented in this section.
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct for the CSSM API
TP_CertGroupConstruct for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const void *ConstructParams,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupConstruct
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const void *ConstructParams,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
DESCRIPTION
This function builds a collection of certificates that together make up
a meaningful credential for a given trust domain. For example, in a
hierarchical trust domain, a certificate group is a chain of
certificates from an end entity to a top level certification authority.
The constructed certificate group format (such as ordering) is
implementation specific. However, the subject or end-entity is always
the first certificate in the group.
A partially constructed certificate group is specified in
CertGroupFrag.
The first certificate is interpreted to be the subject
or end-entity certificate. Subsequent certificates in the
CertGroupFrag
structure may be used during the construction of a certificate group in
conjunction with certificates found in the data stores specified in
DBList.
The trust policy defines the certificates that will be included
in the resulting set.
The output set is a sequence of certificates ordered by the
relationship among them. The result set can be augmented by adding
semantically-related certificates obtained by searching the
certificate data stores specified in
DBList.
The data stores are
searched in order of appearance in
DBList.
If the TP supports a hierarchical model of certificates, the function
output is an uninterrupted, ordered chain of certificates based on
the first certificate as the leaf of the certificate chain.
If the certificate is multiply-signed, then the ordered chain
will follow the first signing certificate. The function should also
detect cross-certificate pairs and should include both certificates
without duplicating either certificate.
Extraneous certificates in the
CertGroupFrag
fragment or contained in the
DBList
data stores are ignored. The certificate group returned by this
function can be used as input to the function
CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify()
(CSSM API) or
TP_CertGroupVerify()
(TP SPI).
The constructed certificate group can be consistent locally or
globally. Consistency can be limited to the local system if
locally-defined points of trust are inserted into the group.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle to the trust policy module to perform this operation.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle to the certificate library module that can be used to
manipulate and parse values in stored in the certgroup certificates. If
no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an
assumed CL module.
- CSPHandle (input./optional)
A handle specifying the Cryptographic Service Provider to be
used to verify certificates as the certificate group is
constructed. If the a CSP handle is not specified, the trust
policy module can assume a default CSP. If the module cannot
assume a default, or the default CSP is not available on the
local system, an error occurs.
- DBList (input)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage library module and a
data store, identifying certificate databases containing certificates
(and possibly other security objects) that
are managed by that module.
certificates (and possibly other security objects). The data stores
should be searched to complete construction of a semantically-related
certificate group.
- ConstructParams (input/optional)
A pointer to data that can be used by the add-in trust policy module
in constructing the
CertGroup.Thesemanticsofthisparameteraredefinedby
the trust policy and the credential model supported by that policy.
The input parameter can consist of a set of values, each guiding
some aspect of the construction process. Parameter values can:
-
Limit the certificates that are added to the constructed set.
-
Identify other sources of certificates for inclusion in the constructed set.
- CertGroupFrag (input)
A list of certificates that form a possibly incomplete set of
certificates. The first certificate in the group represents the target
certificate for which a group of semantically related certificates will
be assembled. Subsequent intermediate certificates
can be supplied by the caller. They need not be in any particular order.
- CertGroup (output)
A pointer to a
complete certificate group based on the original subset of
certificates and the certificate data stores. The
CSSM_CERTGROUP and its sub-structure is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune()
CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertGroupPrune()
TP_CertGroupVerify()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune for the CSSM API
TP_CertGroupPrune for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupPrune
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup)
DESCRIPTION
This function removes any locally issued anchor
certificates from a constructed certificate group. The prune
operation can remove those certificates that have been signed by any
local certificate authority, as it is possible that these certificates
will not be meaningful on other systems.
This operation can also remove additional certificates that can be
added to the certificate group again using the
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct()
(CSSM API) ot
TP_CertGroupConstruct()
(TP SPI)
operation. The pruned certificate group should be suitable for
export to external hosts/entities, which can in turn reconstruct and
verify the certificate group.
The
DBList
parameter specifies a set of data stores containing
certificates that should be pruned from the group.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle to the trust policy module to perform this operation.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle to the certificate library module that can be used to
manipulate and parse the certgroup certificates and the certificates in
the specified data stores. If no certificate library module is
specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module.
- DBList (input)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage library module and a
data store, identifying certificate databases containing certificates (and
possibly other security objects) that are managed by that module.
The data stores are
searched for anchor certificates restricted to have local scope. These
certificates are candidates for removal from the subject certificate
group.
- OrderedCertGroup (input)
The initial complete set of semantically-related certificates
- for example, the result of a
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct()
(CSSM API) or
TP_CertGroupConstruct()
(TP SPI) call -
from which certificates will be selectively removed.
- PrunedCertGroup (output)
A pointer to a certificate group containing those certificates which
are verifiable credentials outside of the local system.
The CSSM_CERTGROUP and its sub-structure is allocated by the
service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct()
CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertGroupConstruct()
TP_CertGroupVerify()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup for the CSSM API
TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup)
DESCRIPTION
This function creates a set of authorization tuples based on
a set of input certificates. The certificates must be of the
type managed by the Trust Policy module. The trust policy module
may require that the input certificates be successfully verified
before being translated to tuples. It is assumed that the
certificates carry authorizations. The trust policy service
provider interprets the certificate authorization fields and
generates one or more tuples corresponding to those authorizations.
The certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy module.
The resulting tuples can be input to an authorization evaluation
function, such as
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute()
(CSSM API) or
AC_AuthCompute()
(AC SPI),
which determines whether a particular action is authorized
under a basic set of authorization assumptions.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service module used
to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library module that
can be used to scan the certificate fields for values.
If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module
uses an assumed CL module.
- CertGroup (input)
A group of certificates in the native certificate format supported
by the Trust Policy module. The certificates carry authorizations
for one or more certificate subjects.
- TupleGroup (output)
A pointer to a structure containing references
to one or more tuples resulting from the translation process.
Storage for structure and the tuples is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup()
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute()
For the TP SPI:
TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup()
AC_AuthCompute()
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup for the CSSM API
TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates)
DESCRIPTION
This function creates a set of certificate templates based on a
set of input tuples. The tuples describe a set of authorizations
for one or more subjects. The trust policy service provider maps
these authorizations to appropriate template values for one
or more certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy module.
The resulting certificate templates can be input to a certificate
creation function, such as
CSSM_CL_CertSign()
(CSSM API) or
CL_CertSign()
(TP SPI).
The signed certificates created by these functions should carry
the authorizations described in the input tuples.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service module used
to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library module that
can be used to assist in the creation of field values.
If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module
uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- TupleGroup (input)
A pointer to a group of CSSM_TUPLE describing authorizations for
one or more subjects.
- CertTemplates (output)
A pointer to a structure containing references
to one or more certificate templates resulting from the
translation process. Storage for the structure and certificate templates
is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated
by the application.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLE
SEE ALSO
For the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup()
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute()
For the TP SPI:
TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup()
AC_AuthCompute()
Extensibility Functions
The man-page definition for the
CSSM_TP_PassThrough()
Extensibility function is presented in this section.
Previous section.
NAME
CSSM_TP_PassThrough for the CSSM API
TP_PassThrough for the TP SPI
SYNOPSIS
API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_PassThrough
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_PassThrough
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
DESCRIPTION
This function allows applications to call trust policy module-specific
operations that have been exported. Such operations may include
queries or services specific to the domain represented by the TP
module.
PARAMETERS
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to
perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate the subject certificate and anchor
certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP
module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of the cryptographic operation.
If the module-specific operation does not perform any cryptographic
operations, a cryptographic context is not required
- DBList (input/optional)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage library module and a
data store, identifying certificate databases containing certificates (and
possibly other security objects) that may be used by the
pass-through
function.
If no DL and DB handle pairs are specified, the TP module can
use an assumed DL module and an assumed data store for this operation.
- PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by the TP module to indicate the exported
function to perform.
- InputParams (input/optional)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing
parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner by the
requested TP module.
- OutputParams (output/optional)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing
the output data. The service provider allocates the memory
for sub-structures. The application must free the
memory for the sub-structures.
RETURN VALUE
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
ERRORS
See the Error Codes and Error Values section earlier in this Chapter.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID

