Add-in modules provide one or more categories of security services to applications. The service categories are Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) services, Trust Policy (TP) services, Certificate Library (CL) services, and Data Storage Library (DL) services. Each security service contains one or more implementation instances, called sub-services. For a CSP service providing access to hardware tokens, a sub-service would represent a slot. For a CL service provider, a sub-service would represent a specific certificate format. These sub-services each support the module interface for their respective service categories. This documentation-part describes the module interface functions in the KR service category.
Each module, regardless of the security services it offers, has the same set of administrative responsibilities. Every module must expose functions which allow CSSM to indicate events such as module attach and detach. In addition, as part of the attach operation, every module must be able to verify its own integrity, verify the integrity of CSSM, and register with CSSM. Detailed information about add-in module structure, administration, and interfaces can be found in the CSSM Add-in Module Structure and Administration Specification.

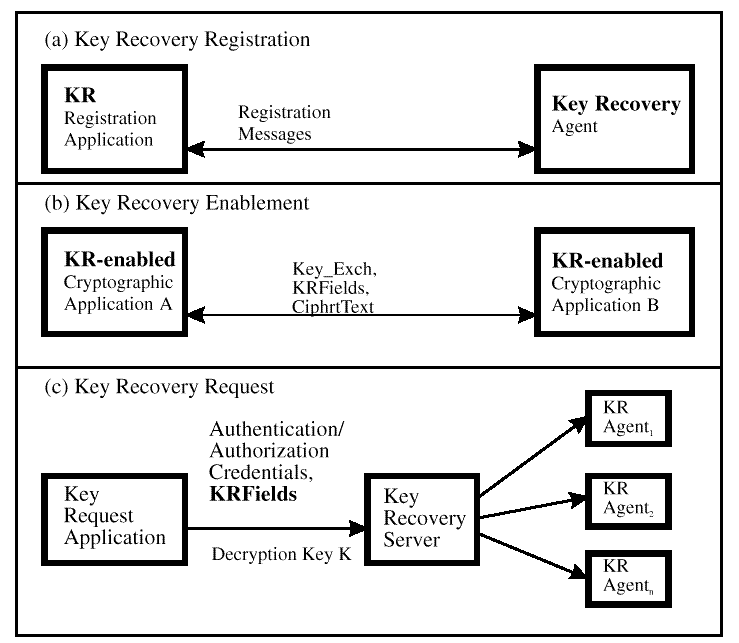
The process of cryptographic key recovery involves three major phases. First, there is an optional key recovery registration phase where the parties that desire key recovery perform some initialization operations with the escrow or recovery agents; these operations include obtaining a user public key certificate (for an escrowed key pair) from an escrow agent, or obtaining a public key certificate from a recovery agent . Next, parties that are involved in cryptographic associations have to perform operations to enable key recovery (such as the generation of key recovery fields, and so on)-this is typically called the key recovery enablement phase. Finally, authorized parties that desire to recover the data keys, do so with the help of a recovery server and one or more escrow agents or recovery agents-this is the key recovery request phase.
It is envisioned that governments or organizations will operate their own recovery server hosts independently, and that key recovery servers may support a single or multiple key recovery mechanisms. There are a number of important issues specific to the implementation and operation of the key recovery servers, such as vulnerability and liability. The focus of this documentation-part is a framework based approach to implementing the key recovery operations pertinent to end parties that use encryption for data confidentiality. The issues with respect to the key recovery server and agents will not be discussed further here.
-
-
typedef struct cssm_spi_kr_funcs {
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RegistrationRequest)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE KRRegistrationContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *KRRegistrationContext,
const CSSM_DATA *KRInData,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials,
CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ReferenceHandle);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RegistrationRetrieve)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ReferenceHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_KR_PROFILE_PTR KRProfile);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *GenerateRecoveryFields)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE KREnablementContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *KREnablementContext,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext,
const CSSM_DATA *KRSPOptions,
CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags,
CSSM_DATA_PTR KRFields);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *ProcessRecoveryFields)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE KREnablementContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *KREnablementContext,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext,
const CSSM_DATA *KRSPOptions,
CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags,
CSSM_DATA *KRFields);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RecoveryRequest)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE KRRequestContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *KRRequestContext,
const CSSM_DATA *KRInData,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ReferenceHandle);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RecoveryRetrieve)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ReferenceHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CacheHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfRecoveredKeys);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *GetRecoveredObject)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CacheHandle,
uint32 IndexInResults,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
uint32 Flags,
CSSM_KEY_PTR RecoveredKey,
CSSM_DATA_PTR OtherInfo);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RecoveryRequestAbort)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *PassThrough)
(CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE KeyRecoveryContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *KeyRecoveryContext,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams);
} CSSM_SPI_KR_FUNCS, *CSSM_SPI_KR_FUNCS_PTR;
KR service modules store information in two MDS relations:
CSSM uses the Primary EMM Service Provider Relation during module management operations. This relation is defined in Module Directory Services. Applications use the KR Primary Relation to locate and select specific KR modules.
| Field Name | Field Data Type | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|
| * | ModuleID | STRING | GUID (in string format) uniquely identifying service provider modules |
| * | SSID | UINT32 | 4 byte Subservice ID
A subservice can be used to support different KR mechanisms. Examples
include:
|
| Manifest | BLOB | Signed-manifest describing the dynamic components of a service provider | |
| ModuleName | STRING | Manifest Section Name. | |
| CompatCSSMVersion | STRING | Lowest compatible CSSM version | |
| Version | STRING | Service provider version string (in dotted high/low format - e.g. 2.0). | |
| Vendor | STRING | Service provider vendor name in ASCII text. | |
| Description | STRING | Human-readable description of this KR subservice. |
KRSP_RegistrationRequest
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RegistrationRequest (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE KRRegistrationContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *KRRegistrationContext, CSSM_DATA *KRInData, const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials, CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags, sint32 *EstimatedTime, CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ReferenceHandle)
This function performs a key recovery registration operation. The KRInData contains known input parameters for the recovery registration operation. A UserCallback function may be supplied to allow the registration operation to interact with the user interface, if necessary. When this operation is successful, a ReferenceHandle and an EstimatedTime parameter are returned; the ReferenceHandle is to be used to invoke the KRSP_RegistrationRetrieve function, after the EstimatedTime in seconds.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- KRRegistrationContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this key recovery operation used to link to the KRSP-managed information.
- KRRegistrationContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes with this key recovery context.
- KRInData (input)
Input data for key recovery registration.
- AccessCredentials (input/optional)
User access credentials, including certificates, samples (password, biometrics) and callback function and context pointers used to authenticate the caller.
- KRFlags (input)
Flag values for recovery registration. Defined values are:
- KR_INDIV-signifies that the registration is for the IND scenario.
- KR_ENT-signifies that the registration is for the ENT scenario.
- KR_LE-signifies that the registration is for the LE scenario.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The estimated time after which the CSSM_KR_RegistrationRetrieve call should be invoked to obtain registration results. When the local service provider module or the key recovery server cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- ReferenceHandle (output)
The handle to use to invoke the CSSM_KR_RegistrationRetrieve function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid registration handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_POINTER
Invalid pointer.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
KRSP_RegistrationRetrieve
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RegistrationRetrieve (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_HANDLE ReferenceHandle, const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredential, sint32 *EstimatedTime, CSSM_KR_PROFILE_PTR *KRProfile)
This function completes a key recovery registration operation. The results of a successful registration operation are returned through the KRProfile parameter, which may be used with the profile management API functions.If the results are not available when this function is invoked, the KRProfile parameter is set to NULL, and the EstimatedTime parameter indicates when this operation should be repeated with the same ReferenceHandle.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- ReferenceHandle (input)
Indicates which outstanding recovery request is to be completed.
- AccessCredentials (input/optional)
User access credentials, including certificates, samples (password, biometrics) and callback function and context pointers used to authenticate the caller.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The estimated time after which this call should be repeated to obtain registration results. This is set to a non-zero value only when the KRProfile parameter is NULL. When the local service provider module or the key recovery server cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- KRProfile (input/output)
Key recovery profile that is filled in by the registration operation.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid reference handle.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
KRSP_GenerateRecoveryFields
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_GenerateRecoveryFields (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE KREnablementContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *KREnablementContext, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext, CSSM_DATA *KRSPOptions, CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags, CSSM_DATA_PTR KRFields)
This function generates the key recovery fields for a cryptographic association given the key recovery context, and the cryptographic context containing the key that is to be made recoverable. The session attribute and the flags are interpreted by the KRSP. A set of key recovery fields (KRFields) is returned if the function is successful. The KRFlags parameter may be used to fine tune the contents of the KRFields produced by this operation.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- KREnablementContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this key recovery operation used to link to the KRSP-managed information.
- KREnablementContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes with this key recovery context.
- CryptoContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context used to link to the CSP-managed information.
- CryptoContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes of the cryptographic context.
- KRSPOptions (input)
The key recovery service provider specific options. These options are uninterpreted by the SKMF, but passed on to the KRSP.
- KRFlags (input)
Flag values for key recovery fields generation. Defined values are:
- KR_INDIV-signifies that the individual key recovery fields should be generated.
- KR_ENT-signifies that the enterprise key recovery fields should be generated.
- KR_LE_MAN-signifies that the law enforcement key recovery fields pertaining to the manufacturing jurisdiction should be generated.
- KR_LE_USE-signifies that the law enforcement key recovery fields pertaining to the jurisdiction of use should be generated.
- KR_OPTIMIZE-signifies that performance optimization options are to be adopted by a KRSP while implementing this operation.
- KR_DROP_WORKFACTOR-signifies that the key recovery fields should be generated without using the key size work factor.
- KRFields (output)
The key recovery fields in the form of a data blob.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_CC_HANDLE
Invalid crypto context handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_KRC_HANDLE
Invalid key recovery context handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_OPTIONS
Invalid recovery options.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
KRSP_ProcessRecoveryFields
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_ProcessRecoveryFields (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE KREnablementContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *KREnablementContext, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext, CSSM_DATA_PTR KRSPOptions, CSSM_KR_POLICY_FLAGS KRFlags, CSSM_DATA_PTR KRFields)
This call processed a set of key recovery fields given the key recovery context, and the cryptographic context for the encryption operation, and returns a non-NULL cryptographic context handle if the processing was successful. The returned handle may be used for the decrypt API calls of the CSSM.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- KREnablementContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this key recovery operation used to link to the KRSP-managed information.
- KREnablementContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes with this key recovery context.
- CryptoContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context used to link to the CSP-managed information.
- CryptoContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes of the cryptographic context.
- KRSPOptions (input)
The key recovery service provider specific options. These options are uninterpreted by the SKMF, but passed on to the KRSP.
- KRFlags (input)
Flag values for key recovery fields generation. Defined values are:
- KR_ENT-signifies that only the enterprise key recovery fields should be processed.
- KR_LE-signifies that only the law enforcement key recovery fields should be processed.
- KR_ALL-signifies that LE, and ENT key recovery fields should be processed.
- KR_OPTIMIZE-signifies that available optimization options are to be adopted.
- KRFields (input)
The key recovery fields to be processed in the form of a data blob.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_CC_HANDLE
Invalid crypto context handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_KRC_HANDLE
Invalid key recovery context handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_OPTIONS
Invalid recovery options.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
KRSP_RecoveryRequest
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRequest (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE KRRequestContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *KRRequestContext, const CSSM_DATA *KRInData, const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials, sint32 *EstimatedTime, CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ReferenceHandle)
This function performs a key recovery request operation. The KRInData contains known input parameters for the recovery request operation. A UserCallback function may be supplied to allow the recovery operation to interact with the user interface, if necessary. If the recovery request operation is successful, a ReferenceHandle and an EstimatedTime parameter is returned; the ReferenceHandle is to be used to invoke the KRSP_RecoveryRetrieve function, after the EstimatedTime in seconds.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- KRRequestContextHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this key recovery operation used to link to the KRSP-managed information.
- KRRequestContext (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes with this key recovery context.
- KRInData (input)
Input data for key recovery requests. For encapsulation schemes, the key recovery fields are included in this parameter.
- AccessCredentials (input/optional)
User access credentials, including certificates, samples (password, biometrics) and callback function and context pointers used to authenticate the caller.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The estimated time after which the CSSM_KR_RecoveryRetrieve call should be invoked to obtain recovery results. When the local service provider module or the key recovery server cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- ReferenceHandle (output)
Handle returned when recovery request is successful. This handle may be used to invoke the CSSM_KR_RecoveryRetrieve function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_INVALID_KR_HANDLE
Invalid handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid recovery context handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_RECOVERY_CONTEXT
Invalid context value.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_POINTER
Invalid pointer.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
KRSP_RecoveryRetrieve
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRetrieve (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCredentials, sint32 *EstimatedTime, CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CacheHandle, uint32 *NumberOfResults)
This function completes a key recovery request operation. The ReferenceHandle parameter indicates which outstanding recovery request is to be completed. The results of a successful recovery operation are referenced by the CacheHandle parameter, which may be used with the KRSP_GetRecoveredObject function to retrieve the recovered keys.If the results are not available at the time this function is invoked, the CacheHandle is NULL, and the EstimatedTime parameter indicates when this operation should be repeated with the same ReferenceHandle.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- AccessCredentials (input/optional)
User access credentials, including certificates, samples (password, biometrics) and callback function and context pointers used to authenticate the caller.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The estimated time after which this call should be repeated to obtain recovery results. This is set to a non-zero value only when the ResultsHandle parameter is NULL. When the local service provider module or the key recovery server cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- CacheHandle (output)
Handle returned when recovery operation is successful. This handle may be used to get individual keys using theKRSP_GetRecoveredObject() function. This handle is NULL, if EstimatedTime parameter is not zero.
- NumberOfResults (output)
The number of recovered key objects that may be obtained using the ResultsHandle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_INVALID_KR_HANDLE
Invalid KR handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid reference handle.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Memory error.
- CSSM_KR_FAIL
Function failed.
KRSP_GetRecoveredObject
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_GetRecoveredObject (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_HANDLE CacheHandle, uint32 IndexInResults, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry, uint32 Flags, CSSM_KEY_PTR RecoveredKey, CSSM_DATA_PTR OtherInfo)
This function is used to step through the results of a recovery request operation in order to retrieve a single recovered key at a time along with its associated meta information. The cache handle returned from a successful KRSP_RecoveryRetrieve operation is used . When multiple keys are recovered by a single recovery request operation, the index parameter indicates which item to retrieve through this function.The RecoveredKey parameter serves as an input template for the key to be returned. If a private key is to be returned by this operation, the PassPhrase parameter is used to inject the private key into the CSP indicated by the RecoveredKey template; the corresponding public key is returned in the RecoveredKey parameter. Subsequently, the PassPhrase and the public key may be used to reference the private key when operations using the private key are required. The OtherInfo parameter may be used to return other meta data associated with the recovered key.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- CacheHandle (input)
The handle returned from a successful CSSM_KR_RecoveryRequest operation.
- IndexInResults (input)
The index into the results that are referenced by the ResultsHandle parameter.
- CSPHandle (input/optional )
This parameter identifies the CSP that the recovered key should be injected into. It may be set to NULL if the key is to be returned in raw form to the caller.
- CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype can be presented as immediate values, or callback functions can be provided for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively. If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key, then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
- Flags (input)
Flag values relevant for recovery of a key. Possible values are: CERT_RETRIEVE-if the recovered key is a private key, return the corresponding public key certificate in the OtherInfo parameter.
- RecoveredKey (output)
This parameter returns the recovered key.
- OtherInfo (output)
This parameter is used if there are additional information associated with the recovered key (such as the public key certificate when recovering a private key) that is to be returned.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_INVALID_KR_HANDLE
Invalid KR Handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
Invalid CSP Handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid cache handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_INDEX
Cache index value is out of range.
- CSSM_KR_PRIVATE_KEY_STORE_FAIL
Unable to store private key in CSP.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Not enough memory.
KRSP_RecoveryRequestAbort
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRequestAbort (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
This function is invoked after a successful call to theCSSM_KR_RecoveryRetrieve() API, and after all desired keys were recovered usingCSSM_KR_GetRecoveredObject() . The function also destroys all intermediate state and secret information used during the key recovery process.
- KRSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- ResultsHandle (input)
The handle returned from a successful KRSP_RecoveryRequest operation.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_INVALID_KR_HANDLE
Invalid KR handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid cache handle.
KRSP_PassPrivFunc
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_PassPrivFunc (CSSM_PRIV_FUNC_PTR CSSM_SetContextPriv)
This function is used to provide the KRSP with the CSSM_SetContextPriv callback function. This callback is implemented by the CSSM and allows the setting or dropping of the privilege state flag for a given cryptographic context. This is used by the KRSP to make a cryptographic context privileged with respect to key recovery policy enforcement decisions, so that the KRSP itself is allowed to bypass the key recovery policy controls. The KRSP is expected to reset the privilege state flag as soon as the need for the privilege is over.
- CSSM_SetContextPriv (input)
The callback that is used by the KRSP to set or drop the privilege state flag for a given cryptographic context.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Not enough memory.
KRSP_PassThrough
CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_PassThrough (CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE KRSPHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE KeyRecoveryContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *KeyRecoveryContext, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CryptoContextHandle, const CSSM_CONTEXT *CryptoContext, uint32 PassThroughId, const void *InputParams, void **OutputParams)
The KRSP_PassThrough function is provided to allow KRSP developers to extend the key recovery functionality of the CSSM API.
- KRHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this key recovery operation.
- KeyRecoveryContextHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in key recovery service provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions managed by CSSM.
- KeyRecoveryContext (input/optional)
Pointer to the CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes with this key recovery context.
- CryptoContextHandle (Input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context used to link to the CSP-managed information.
- CryptoContext (input/optional)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes the attributes of the cryptographic context.
- PassThroughId (input)
An identifier specifying the custom function to be performed.
- InData (input)
A pointer to a void structure containing the input data.
- OutData (output)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing the output data. The service provider will allocate the memory for this structure. The application should free the memory for the structure.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_HANDLE
Invalid handle.
- CSSM_KR_INVALID_POINTER
Invalid pointer for input data.
- CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Not enough memory to allocate.
- CSSM_KR_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATION
Add-in does not support this function.
- CSSM_KR_PASS_THROUGH_FAILED
Unable to perform custom function.
| Contents | Next section | Index |