Vendors providing add-in security service modules are
developing products that provide services in more than one
functional category. Vendors may not want to partition their
products in this manner. More pointedly, they can be unable
to do so. Consider a class 2 PKCS#11 cryptographic device.
This device performs cryptographic operations and provides
persistent storage for keys, certificates, and other
security-related objects. These services are logically
partitioned between the CSP-APIs and the DLM-APIs.
Implementing two separate add-in modules is not feasible. In
order to provide correct service, the two modules must share
execution state, such as PKCS#11 session identifiers.
Additional examples exist, as shown in

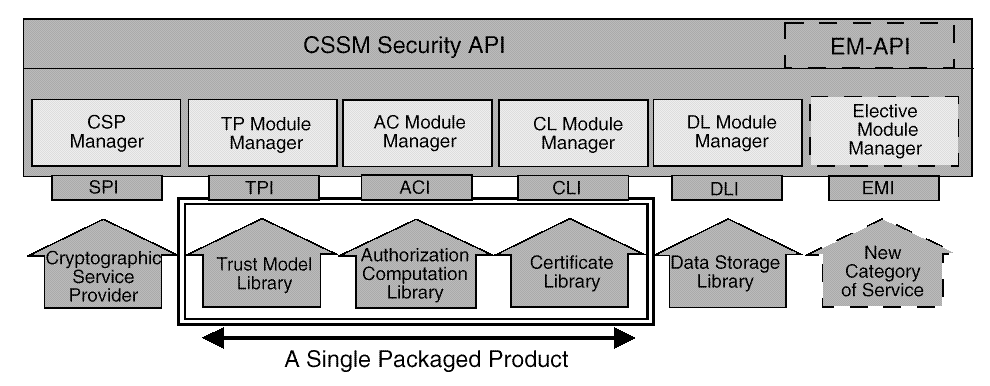
Multi-service add-in modules separate module packaging from the application developers functional view of CSSM APIs. A multi-service module is a single, dynamic add-in module that implements CSSM functions from two or more functional categories of the CSSM APIs.
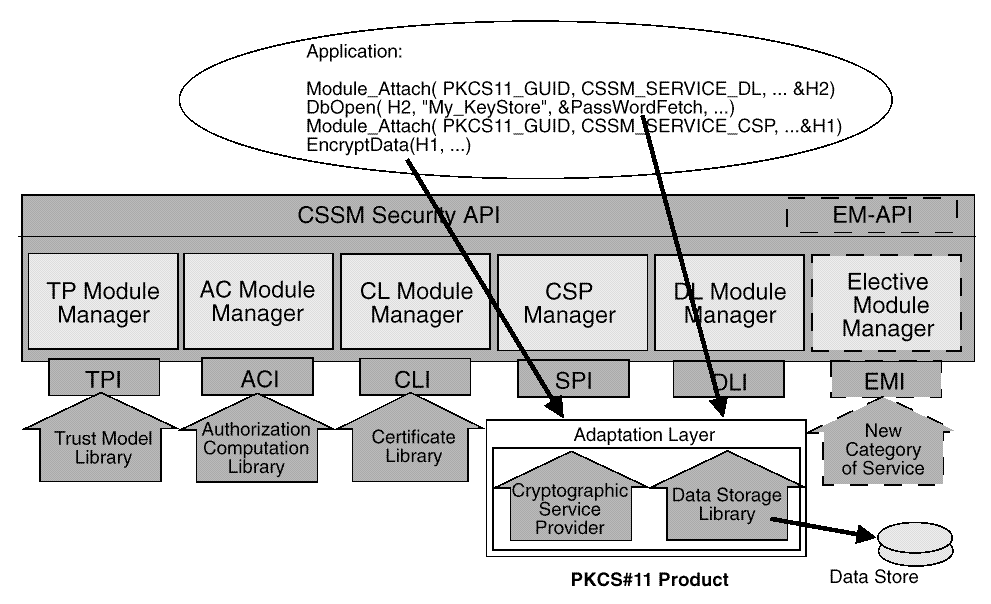
Multiple calls to attach are viewed as independent requests with respect to authorized exemptions and access control. The multi-service module can match-up the caller handles if a shared execution state is required.
When an add-in module is installed on a CSSM system, the module registers its name, GUID, and capability descriptions by adding records to relations in the Module Directory Services (MDS). MDS makes this information available for application queries. A multi-service module will register capabilities for each of the service categories supported by the module.
A multi-service module is not required to implement all of the functions in any functional category. The CSSM dispatching mechanism invokes only to those interfaces registered with the CSSM.
| Contents | Next section | Index |