| Data Type | Type Name | Example Type Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 16-bit Integer | BSA_Int16 | typedef short BSA_Int16; |
| 32-bit Integer | BSA_Int32 | typedef int BSA_Int32; |
| 64-bit Integer | BSA_Int64 | typedef struct { |
| BSA_Int32 left; | ||
| BSA_Int32 right; | ||
| } BSA_Int64; | ||
| /* or a single simple type if the target * platform supports a simple type that * yields a 64 bit quantity */ | ||
| 16-bit Unsigned Integer | BSA_UInt16 | typedef unsigned short BSA_UInt16; |
| 32-bit Unsigned Integer | BSA_UInt32 | typedef unsigned int BSA_UInt32; |
| 64-bit Unsigned Integer | BSA_UInt 64 | typedef struct { |
| BSA_UInt32 left; | ||
| BSA_UInt32 right; | ||
| } BSA_UInt64; | ||
| /* or a single simple type if the target * platform supports a simple type that * yields a 64 bit quantity */ | ||
| Shared Memory Buffer reference | BSA_ShareId | <operating system dependent> |
The 3rd column in the table above is not mandatory. The type definitions must be true to the what the type name specifies.
For 64 bit architectures, and architectures that support 64 bit quantities as a simple type, the BSA_UInt64 type may not be a structure.
-
-
typedef enum {
BSA_CopyType_ANY = 1,
BSA_CopyType_ARCHIVE = 2,
BSA_CopyType_BACKUP = 3
} BSA_CopyType;
The meaning of the enumeration values is as follows:
| Constant | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ANY | 1 | Used for matching any copy type (for example, "backup" or "archive" in the copy type field of structures for selecting query results). |
| ARCHIVE | 2 | Specifies that the copy type should be "archive". |
| BACKUP | 3 | Specifies that the copy type should be "backup". |
-
-
typedef enum {
BSA_ObjectStatus_ANY = 1,
BSA_ObjectStatus_MOST_RECENT = 2,
BSA_ObjectStatus_NOT_MOST_RECENT = 3
} BSA_ObjectStatus;
The meaning of the enumeration values is as follows:
| Constant | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ANY | 1 | Provides a wild card function. Can only be used in queries. |
| MOST_RECENT | 2 | Indicates that this is the most recent backup copy of an object. |
| NOT_MOST_RECENT | 3 | Indicates that this is not the most recent backup copy, or that the object itself no longer exists. |
-
-
typedef enum {
BSA_ObjectType_ANY = 1,
BSA_ObjectType_FILE = 2,
BSA_ObjectType_DIRECTORY = 3,
BSA_ObjectType_OTHER = 4
} BSA_ObjectType;
The meaning of the enumeration values is as follows:
| Constant | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| ANY | 1 | Used for matching any object type (for example, "file" or directory") value in the object type field of structures for selecting query results. |
| FILE | 2 | Used by the application to indicate that the type of application object is a "file" or single object. |
| DIRECTORY | 3 | Used by the application to indicate that the type of application object is a "directory" or container of objects. |
| OTHER | 4 | Used by the application to indicate that the type of application object is neither a "file" nor a "directory". |
-
-
typedef enum {
BSA_Vote_COMMIT = 1,
BSA_Vote_ABORT = 2
} BSA_Vote;
The meaning of the enumeration values is as follows:
| Constant | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| COMMIT | 1 | The transaction is to be committed. |
| ABORT | 2 | The transaction is to be aborted. |
| Constant | Value | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| [BSA_ANY] | 1 | General-purpose enumeration wild-card value |
| [BSA_MAX_APPOBJECT_OWNER] | 64 | Max end-user object owner length |
| [BSA_MAX_BSAOBJECT_OWNER] | 64 | Max BSA object owner length |
| [BSA_MAX_DESCRIPTION] | 100 | Description field |
| [BSA_MAX_OBJECTSPACENAME] | 1024 | Max ObjectSpace name length |
| [BSA_MAX_OBJECTINFO | 256 | Max object info size |
| [BSA_MAX_PATHNAME] | 1024 | Max path name length |
| [BSA_MAX_RESOURCETYPE] | 31 | Max resource mgr name length |
| [BSA_MAX_TOKEN_SIZE] | 64 | Max size of a security token |
-
-
typedef struct {
BSA_UInt16 issue;
BSA_UInt16 version;
BSA_UInt16 level;
} BSA_ApiVersion;
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
For implementations of the XBSA Preliminary Specification (Document Number P424), the values of the BSA_ApiVersion structure were implementation-dependent. For implementations of the XBSA Technical Standard (this document - C425), the values should be 1,1,X:
| Published Document | Issue | Version | Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preliminary Specification (P424) | * | * | * |
| Technical Standard (C425) | 1 | 1 | X |
* = implementation-dependent
-
-
typedef struct {
BSA_UInt32 bufferLen;
BSA_UInt32 numBytes;
BSA_UInt32 headerBytes;
BSA_ShareId shareId;
BSA_UInt32 shareOffset;
void *bufferPtr
} BSA_DataBlock32;
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bufferLen | Length of the allocated buffer |
| numBytes | Actual number of bytes read from or written to the buffer, or the minimum number of bytes needed |
| headerBytes | Number of bytes used at start of buffer for header information (offset to data portion of buffer) |
| shareId | Value used to identify a shared memory block. |
| shareOffset | Specifies the offset of the buffer in the shared memory block. |
| bufferPtr | Pointer to the buffer |
The values assigned to the various structure fields would always
obey the following relationships:
-
-
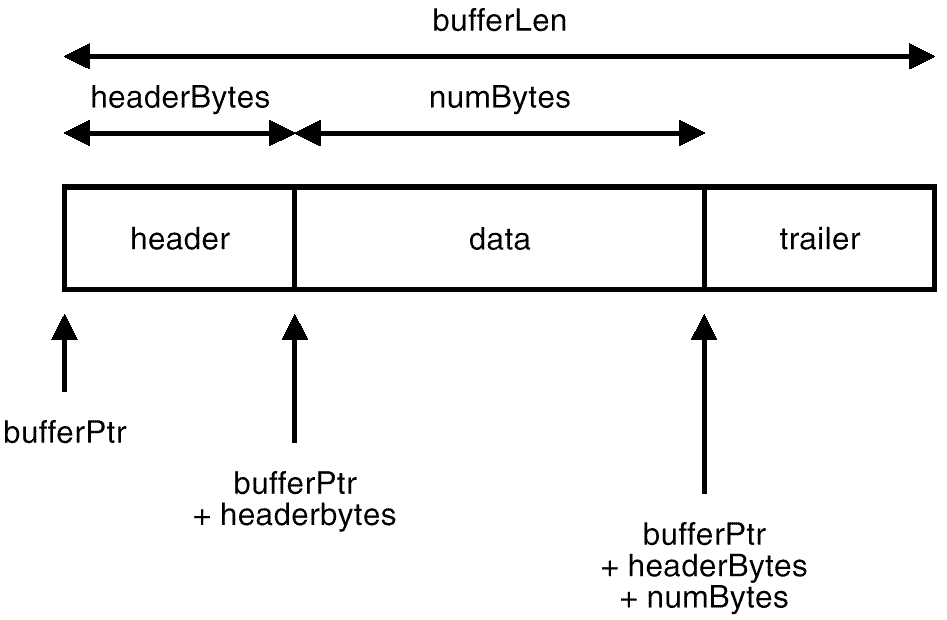
bufferLen >= headerBytes + numBytes
trailerBytes == (bufferLen - numBytes - headerBytes)
The layout of the buffer is as follows:

The header and trailer portions of the buffer are reserved for the use of the Backup Service, and should not be modified by the XBSA Application. The XBSA Application should only write to the data portion of the buffer, which is the only portion used for transferring application data.
The sizes for the header and trailer portions of the buffer that are required
by the Backup Service are obtained by calling
-
-
#include <time.h>
typedef struct {
BSA_UInt32 rsv1;
BSA_ObjectOwner objectOwner;
BSA_ObjectName objectName;
struct tm createTime;
BSA_CopyType copyType;
BSA_UInt64 copyId;
BSA_UInt64 restoreOrder;
char rsv2[31];
char rsv3[31];
BSA_UInt64 estimatedSize;
char resourceType[BSA_MAX_RESOURCETYPE];
BSA_ObjectType objectType;
BSA_ObjectStatus objectStatus;
char rsv4[31];
char objectDescription[MAX_RC_OBJECTDESCRIPTION];
unsigned char objectInfo[BSA_MAX_OBJECTINFO];
} BSA_ObjectDescriptor;
Some of the fields in this structure are supplied by the XBSA Application (Direction = in), and some by the Backup Service (Direction = out). Some fields are optional.
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
| Field Name | Definition | Supplied By | Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| rsv1 | reserved field | - | - |
| objectOwner | Owner of the object | client | optional |
| objectName | Object name | client | mandatory |
| createTime | Create time | service | mandatory |
| copyType | Copy type: archive or backup | client | mandatory |
| copyId | Unique object identifier | service | mandatory |
| restoreOrder | Provides hints to the XBSA Application that allow it to optimize the order of object retrieval requests | service | optional |
| rsv2 | reserved field | - | - |
| rsv3 | reserved field | - | - |
| estimatedSize | Estimated object size in bytes, may be up to (2^64 - 1) bits | client | mandatory |
| resourceType | for example, UNIX file system | client | mandatory |
| objectType | for example, file, directory, database | client | mandatory |
| objectStatus | Most recent / Not most recent | service | mandatory |
| rsv4 | reserved field | - | - |
| objectDescription | Descriptive label for the object | client | optional |
| objectInfo | Application-specific information | client | optional |
All values in a BSA_ObjectDescriptor must be valid before the BSA_ObjectDescriptor as a whole is valid. For enumerations valid values exclude the enumeration "ANY". For strings valid values are null-terminated.
The optional string value is the empty string. The optional restoreOrder value is zero. The optional objectInfo value is all zeros (that is, a zero-filled field).
The mandatory objectName must have a non-empty string in the pathName field. The mandatory createTime must be a valid time in UTC. The mandatory copyId must be non-zero. The mandatory resourceType must have a non-empty string value.
-
-
typedef struct {
char objectSpaceName[BSA_MAX_OBJECTSPACENAME];
char pathName[BSA_MAX_PATHNAME];
} BSA_ObjectName;
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectSpaceName | Highest-level name qualifier |
| pathName | Object name within objectspace |
An objectSpaceName is an optionally defined, fixed-length character string. It identifies a logical space, called an Object space, in which the object belongs. For example, an Object space may be used to identify a storage volume (for example, a disk partition, or a floppy disk), or a database in the XBSA Application's domain.
The concept of an Object space is used to provide a primary grouping of XBSA Objects, which may be used for object search by a user and/or for object management by the Backup Service. Additional groupings are provided by Filespec and by object attributes. Examples of an objectSpaceName are C: Drive and VolumeLabel=XYZ.
A pathName is a hierarchical character string that identifies an XBSA Object within an ObjectSpace.
An example of a pathName for the backup copy of a UNIX file may be its original path name and file name, for example, /documents/opengroup/backup.proposal.
The value of the delimiter used to
separate name components can be obtained by calling
-
-
typedef struct {
char bsa_ObjectOwner[BSA_MAX_BSAOBJECT_OWNER];
char app_ObjectOwner[BSA_MAX_APPOBJECT_OWNER];
} BSA_ObjectOwner;
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bsa_ObjectOwner | this is the name that the Backup Service authenticates |
| app_ObjectOwner | this is the name defined by the application |
The bsa_ObjectOwner identifies an XBSA Application (for example, an XBSA Application associated with a UNIX file system located at a certain node).
An app_ObjectOwner is an optional name, such as an actual end-user name, provided by the respective XBSA Application, so that the Backup Service can provide assistance to support application-specific access control by optimizing access for the given app_ObjectOwner.
The app_ObjectOwner may have multiple components defined in the application, such as a group name and a user id. In general, it is a hierarchical character string. An app_ObjectOwner is not registered with the Backup Service. Its registration and authentication is the XBSA Application's responsibility. Examples of a typical app_ObjectOwner are Smith, AccountingDept.Clerk1 and * (unspecified).
-
-
#include <time.h>;
typedef struct {
BSA_ObjectOwner objectOwner;
BSA_ObjectName objectName;
struct tm rsv1;
struct tm rsv2;
struct tm rsv3;
struct tm rsv4;
BSA_CopyType copyType;
char rsv5[31];
char rsv6[31];
char rsv7[31];
BSA_ObjectType objectType;
BSA_ObjectStatus objectStatus;
char rsv8[100];
} BSA_QueryDescriptor;
The usage of the structure fields is defined as follows:
| Field Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| objectOwner | Owner of the object |
| objectName | Object name |
| rsv1 | reserved field |
| rsv2 | reserved field |
| rsv3 | reserved field |
| rsv4 | reserved field |
| copyType | Copy type: archive or backup |
| rsv5 | reserved field |
| rsv6 | reserved field |
| rsv7 | reserved field |
| objectType | for example, file, directory, database |
| objectStatus | Most recent / Not most recent |
| rsv8 | reserved field |
-
-
typedef char BSA_SecurityToken[BSA_MAX_TOKEN_SIZE];
| Contents | Next section | Index |