
These APIs are implemented by the CSSM, not by add-in modules.
Applications can use this descriptive information to assist in selecting the appropriate CSSM instance.
Every CSSM instance must specify its unique identification GUID. Specification of the interface GUID and the version numbers is optional, but believed to be of value as an augmentation to the distinguished name for an executable instance of CSSM. Using these three pieces of information can determine interoperability and compatibility with an instance of CSSM.
Applications use the CSSM_GetInfo interface to obtain this identification information for any instance of CSSM that has been installed on a local system. Once an instance has been selected, the application must load that instance using CSSM_Load. Following the dynamic load operation, the application must perform all required initialization steps before using other CSSM services. Initialization includes invoking CSSM_Init and the optional exchange of application credentials for purposes of authentication between CSSM and the application.
System administration utilities use CSSM install and uninstall functions to maintain add-in modules on a local system.
The CSSM registry records information about each installed add-in module and elective module manager for the local system. The registry is CSSM's critical information base. CSSM must support the following services and features with respect to the CSSM registry:
The registry entries are queried by applications, add-in modules, and components of CSSM.
Applications select the particular security services they will use by selectively attaching add-in modules. These modules are provided by independent vendors. Each has an assigned, Globally Unique ID (GUID), and a set of descriptive attributes to assist applications in selecting appropriate modules for their use. A module can implement a range of services across the CSSM APIs (such as, cryptographic functions and data storage functions) or a module can restrict its services to a single CSSM category of service (such as, certificate library services only). Modules that span service categories are called Multi-Service modules.
Applications use a module's GUID to specify the module to be attached. The attach function returns a handle representing a unique pairing between the caller and the attached module. This handle must be provided as in input parameter when requesting services from the attached module. CSSM uses the handle to match the caller with the appropriate service module.
The calling application uses the handle to obtain any and all types of
services implemented by the attached module.

Multiple calls to attach are viewed as independent requests. Each attach request returns separate, independent handles that do not share execution state.
Before attaching a service module, an application can query the CSSM registry to obtain information on:
Applications use this information to select a module for use. A multi-service module has multiple capability descriptions associated with it, at least one per functional area supported by the module. Some areas (such as CSP and TP) may have multiple independent capability descriptions for a single functional area. There is one CSSM registry entry for a multi-service module. That entry records all service types for the module. CSSM returns all information about a module's capabilities when queried by the application. Each set of capabilities includes a type identifier to distinguish CSPinfo from Clinfo, and so on.
Applications can query about CSSM itself. Different versions of CSSM and add-in modules will exist. CSSM provides several functions to assist applications in selecting a version that meets the application's needs. One function returns version information about the running CSSM. Another function verifies whether the application's expected CSSM version is compatible with the currently-running CSSM version. The general function to query add-in module information also returns the module's version information.
At module attach time, CSSM requires successful certificate-based trust verification for:
All verifications performed to enforce CSSM-defined policy are based on CSSM-selected public root keys as points of trust.
When CSSM performs a verification check on any component in the CSSM environment, the verification process has three aspects:
These steps are implemented by CSSM' s Integrity Services. Integrity Services are packaged as a static library called the Embedded Integrity Services Library (EISL). CDSA defines a bilateral authentication procedure by which CSSM and a component interacting with CSSM authenticate each other to achieve a mutual trust.
As part of bilateral authentication, CSSM calls EISL to verify and load a module or a module manager. If EISL returns a failure condition, then the module or the module manager has not been linked and loaded. CSSM must detect this failure and must return the value CSSM_ATTACH_ERROR to the caller of the CSSM_ModuleAttach operation.
EISL services support unilateral authentication, identity verification, and object code integrity checks. EISL facilities are documented in the CSSM Embedded Integrity Services Library API Spec.
Module-defined policies are enforced by one of the following authentication checks:
The module specifies its policy by selecting one of these authentication checks. Options one and two use CSSM to enforce the module-defined policy during attach processing. Option three is carried out independently by the add-in module, using EISL services. The add-in module requests CSSM enforcement by setting MODULE_FLAGS corresponding to options one and two in the MODULE_INFO structure. When option two is selected, the MODULE_INFO structure should also contain a set of module-specific, public root keys corresponding to the module's points of trust.
The MODULE_INFO structure is presented to CSSM during module installation in two forms:
The policy is securely stored in the signed credentials. These credentials are authenticated by CSSM each time the module is attached. CSSM uses the signed policy description as the authoritative representation of the policy. The MODULE_INFO structure is also stored in the CSSM registry allowing applications to read the policy description by calling CSSM_GetModuleInfo.
Add-in modules can independently authenticate applications based on module-defined points of trust. The application must incorporate a verifiable certificate in its credentials. To authenticate the application directly, the add-in module:
An application's verifiable credentials must be created during
application manufacturing. The application vendor must obtain a
manufacturing/signing certificate from all service module vendors and
CSSM vendors who will provide it with privileged status. The
application vendor uses the manufacturing certificates to create the
certificate chains shown in
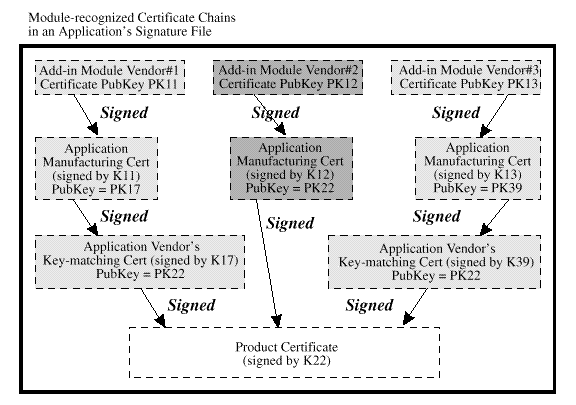
Three certificate chains representing the application's module-specific credentials for three distinct modules or module vendors
Application-defined policies are enforced by one of the following authentication checks:
The application specifies its policy by selecting one of these authentication checks. Options one and two use CSSM to enforce the application-defined policy during attach processing. Option one is part of the umbrella integrity policy defined and enforced by CSSM. This check is always performed by CSSM. Options two and three are checks performed in addition to the CSSM check. Option three is carried out independently by the application, using EISL services. The application requests CSSM enforcement by setting APP_SERVICE_FLAGS corresponding to option two in the APP_SERVICE_INFO structure. The APP_SERVICE_INFO structure should also contain a set of application-specific, public root keys corresponding to the application's points of trust.
The APP_SERVICE_INFO structure must be flattened and stored as an attribute value in the application's signed credentials. These credentials are used during module attach and provide verifiable information to CSSM for application-directed authentication of the attached add-in module.
Alternatively, applications can independently authenticate selected add-in service modules based on application-defined points of trust. This authentication procedure is in addition to procedures automatically performed by CSSM based on CSSM-defined roots of trust. By performing a second authentication, an application vendor or an application installer can preclude the use of non-authorized add-in modules. The policy defining which add-in modules an application is authorized to use is specified and maintained outside of the CSSM.
The add-in service module must incorporate a verifiable certificate in its credentials. The application must locate the module's credential files and verify them directly by invoking EISL facilities. A module's credentials can be located using file system path information published in the module's CSSM registry entry. (CSSM registry information can be retrieved using the CSSM_GetModuleInfo function.) Verification using EISL facilities must be based on application-defined roots of trust.
An application defines its roots of trust for authenticating add-in modules by one of two methods:
In either case, the application defines a root of trust that can be
used to verify the add-in module. The add-in module incorporates a
verifiable certificate in its credentials and the application can use
CSSM's EISL facilities to authenticate the add-in module based on the
application's (adopted or issued) root of trust. The add-in module's
credentials will appear as shown in
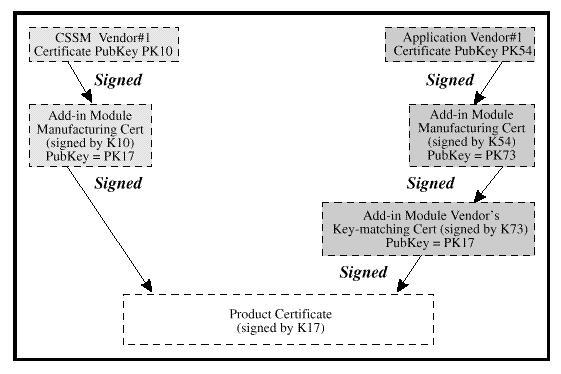
Add-in module credentials including a certificate chain recognized by an application
To authenticate the add-in module using EISL, the application proceeds as follows:
It is important to note that the application-defined roots of trust for authenticating add-in service modules are independent of the module-defined roots of trust for authenticating applications.
A service module's verifiable credentials must be created during
module manufacturing. The module vendor must obtain a
manufacturing/signing certificate from all application vendors
who wish to enforce exclusive use of the service module by their
application. The module vendor uses the manufacturing
certificates to create the certificate chains shown in
Exemptions can be granted per application thread, if threads are supported in the operating environment. Exemption privileges can not be inherited by spawned processes or spawned threads. Each process or thread must present credentials and obtain its own exemption status.
The CSSM_RequestCssmExemption function is used to request exemptions. Applications can invoke this function at any time after invoking the CSSM_Init function. This allows applications to change exemption status as appropriate during execution. Authentication and implied authorization are checked by CSSM at each request.
A bit mask represents the set of requested exemptions.
New elective module managers can define and implement additional built-in checks. Exemption categories, with corresponding bit mask values, should be defined by the elective module manager. This allows authorized applications to be exempt from these additional built-in checks.
typedef uint32 CSSM_BOOL;
#define CSSM_TRUE 1
#define CSSM_FALSE 0
typedef enum cssm_return {
CSSM_OK = 0,
CSSM_FAIL = -1
} CSSM_RETURN
#define CSSM_MODULE_STRING_SIZE 64
typedef char CSSM_STRING [CSSM_MODULE_STRING_SIZE + 4];
typedef struct cssm_data{
uint32 Length; /* in bytes */
uint8 *Data;
} CSSM_DATA, *CSSM_DATA_PTR
typedef struct cssm_guid{
uint32 Data1;
uint16 Data2;
uint16 Data3;
uint8 Data4[8];
} CSSM_GUID, *CSSM_GUID_PTR
typedef struct cssm_version {
uint32 Major;
uint32 Minor;
} CSSM_VERSION, *CSSM_VERSION_PTR
typedef struct cssm_subservice_uid {
CSSM_GUID Guid;
CSSM_VERSION Version;
uint32 SubserviceId;
uint32 SubserviceFlags;
} CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID, *CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID_PTR;
typedef uint32 CSSM_HANDLE, *CSSM_HANDLE_PTR
typedef uint32 CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE
typedef struct cssm_list_item{
CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID SubserviceUid;
char *Name;
} CSSM_LIST_ITEM, *CSSM_LIST_ITEM_PTR
typedef struct cssm_list{
uint32 NumberItems;
CSSM_LIST_ITEM_PTR Items;
} CSSM_LIST, *CSSM_LIST_PTR
typedef struct cssm_cssminfo {
CSSM_VERSION Version;
CSSM_STRING Description; /* Description of CSSM */
CSSM_STRING Vendor; /* Vendor of CSSM */
CSSM_BOOL ThreadSafe;
CSSM_STRING Location;
CSSM_GUID GUID CssmGUID;
CSSM_GUID InterfaceGUID; /* opt GUID defining supported
interface */
}CSSM_CSSMINFO, *CSSM_CSSMINFO_PTR
typedef uint32 CSSM_EVENT_TYPE, *CSSM_EVENT_TYPE_PTR;
#define CSSM_EVENT_ATTACH (0)
/* application has requested an attach operation */
#define CSSM_EVENT_DETACH (1)
/* application has requested an detach operation */
#define CSSM_EVENT_INFOATTACH (2)
/* application has requested module info for dynamic module
capabilities */
#define CSSM_EVENT_INFODETACH (3)
/* CSSM has completed obtaining dynamic module capabilities */
#define CSSM_EVENT_CREATE_CONTEXT (4)
/* application has performed a create context operation */
#define CSSM_EVENT_DELETE_CONTEXT (5)
/* application has performed a delete context operation */
typedef uint32 CSSM_SERVICE_MASK;
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CSSM 0x1
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CSP 0x2
#define CSSM_SERVICE_DL 0x4
#define CSSM_SERVICE_CL 0x8
#define CSSM_SERVICE_TP 0x10
#define CSSM_SERVICE_LAST CSSM_SERVICE_TP
typedef CSSM_SERVICE_MASK CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE
typedef uint32 CSSM_SERVICE_FLAGS
#define CSSM_SERVICE_ISWRAPPEDPRODUCT 0x1
/* On = Contains one or more embedded products
Off = Contains no embedded products */
typedef struct cssm_serviceinfo {
CSSM_STRING Description; /* Service description */
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE Type; /* Service type */
CSSM_SERVICE_FLAGS Flags; /* Service flags */
uint32 NumberOfSubServices; /* Number of sub services in
SubService List */
union cssm_subservice_list { /* List of sub services */
void *SubServiceList;
CSSM_CSPSUBSERVICE_PTR CspSubServiceList;
CSSM_DLSUBSERVICE_PTR DlSubServiceList;
CSSM_CLSUBSERVICE_PTR ClSubServiceList;
CSSM_TPSUBSERVICE_PTR TpSubServiceList;
} SubserviceList;
void *Reserved;
} CSSM_SERVICE_INFO, *CSSM_SERVICE_INFO_PTR;
typedef uint32 CSSM_MODULE_FLAGS;
#define CSSM_MODULE_THREADSAFE 0x1 /* Module is threadsafe */
#define CSSM_MODULE_EXPORTABLE 0x2 /* Module can be exported
outside the USA */
#define CSSM_MODULE_CALLER_AUTHENTOCSSM 0x04
/* CSSM authenticates the caller based on CSSM-known points
of trust */
#define CSSM_MODULE_CALLER_AUTHENTOMODULE 0x08
/* CSSM authenticates the caller based on module-supplied
points of trust */
typedef struct cssm_moduleinfo {
CSSM_VERSION Version; /* Module version */
CSSM_VERSION CompatibleCSSMVersion; /* CSSM version the
module is written for*/
CSSM_GUID_PTR InterfaceGUID; /* opt GUID defining supported
interface */
CSSM_STRING Description; /* Module description */
CSSM_STRING Vendor; /* Vendor name */
CSSM_MODULE_FLAGS Flags; /* Flags to describe and control
module use */
CSSM_KEY_PTR AppAuthenRootKeys; /* Module-specific keys to
authenticate apps */
uint32 NumberOfAppAuthenRootKeys; /* Number of module-
specific root keys */
CSSM_SERVICE_MASK ServiceMask; /* Bit mask of supported
services */
uint32 NumberOfServices; /* Number of services in ServiceList */
CSSM_SERVICE_INFO_PTR ServiceList; /* A list of service
info structures */
void *Reserved;
} CSSM_MODULE_INFO, *CSSM_MODULE_INFO_PTR;
typedef enum cssm_info_level {
CSSM_INFO_LEVEL_MODULE = 0,
/* values from CSSM_SERVICE_INFO struct */
CSSM_INFO_LEVEL_SUBSERVICE = 1,
/* values from CSSM_SERVICE_INFO and XXsubservice struct */
CSSM_INFO_LEVEL_STATIC_ATTR = 2,
/* values from CSSM_SERVICE_INFO and XXsubservice and
all static-valued attributes of a subservice */
CSSM_INFO_LEVEL_ALL_ATTR = 3,
/* values from CSSM_SERVICE_INFO and XXsubservice and
all attributes, static and dynamic, of a subservice */
} CSSM_INFO_LEVEL;
typedef enum cssm_net_address_type {
CSSM_ADDR_NONE = 0,
CSSM_ADDR_CUSTOM = 1,
CSSM_ADDR_URL = 2, /* char* */
CSSM_ADDR_SOCKADDR = 3,
CSSM_ADDR_NAME = 4 /* char* - qualified by access method */
} CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_TYPE;
typedef struct cssm_net_address {
CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_TYPE AddressType;
CSSM_DATA Address;
} CSSM_NET_ADDRESS, *CSSM_NET_ADDRESS_PTR;
typedef enum cssm_net_protocol {
CSSM_NET_PROTO_NONE = 0, /* local */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_CUSTOM = 1, /* proprietary implementation */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_UNSPECIFIED = 2, /* implementation default */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAP = 3, /* light weight directory access
protocol */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAPS = 4, /* ldap/ssl where SSL initiates
the connection */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_LDAPNS = 5, /* ldap where ldap negotiates an
SSL session */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_X500DAP = 6, /* x.500 Directory access
protocol */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_FTPDAP = 7, /* file transfer protocol for
cert/crl fetch */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_FTPDAPS = 8, /* ftp/ssl where SSL initiates
the connection */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_NDS = 9, /* Novell directory services */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_OCSP = 10, /* online certificate status
protocol */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_PKIX3 = 11, /* the cert request protocol
in PKIX3 */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_PKIX3S = 12, /* The ssl/tls derivative
of PKIX3 */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_PKCS_HTTP = 13, /* PKCS client <=> CA protocol
over HTTP */
CSSM_NET_PROTO_PKCS_HTTPS = 14, /* PKCS client <=> CA protocol
over HTTPS */
} CSSM_NET_PROTOCOL;
typedef uint32 CSSM_APP_SERVICE_FLAGS
#define CSSM_APP_SERVICE_AUTHENTOAPP 0x1
/* CSSM authenticates the service module based on
application-supplied points of trust */
typedef struct cssm_app_keys {
CSSM_KEY_PTR ModuleAuthenRootKeys,
/* Application-specified keys to authen service modules*/
uint32 NumberOfModuleAuthenRootKeys,
/* Number of application-specified root keys */
} CSSM_APP_KEYS, *CSSM_APP_KEYS_PTR;
typedef struct cssm_app_service_info {
CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID_PTR ModuleList; /* List of module
service ID structs */
uint32 NumberOfModules; /* Number of modules to
authenticate */
CSSM_APP_SERVICE_FLAGS Flags;
/* Flags selecting CSSM or app-specified roots of trust */
CSSM_APP_KEYS_PTR *Keys,
/* Application-specified keys to authenticate modules */
void *Reserved;
} CSSM_APP_SERVICE_INFO, *CSSM_APP_SERVICE_INFO_PTR;
typedef uint32 CSSM_EXEMPTION_MASK
#define CSSM_EXEMPT_NONE 0x00000001
#define CSSM_EXEMPT_MULTI_ENCRYPT_CHECK 0x00000002
#define CSSM_EXEMPT_ALL 0xFFFFFFFF
typedef enum cssm_user_authentication_mechanism {
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_NONE = 0,
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_CUSTOM = 1,
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_PASSWORD = 2,
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_USERID_AND_PASSWORD = 3,
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_CERTIFICATE_AND_PASSPHRASE = 4,
CSSM_AUTHENTICATION_LOGIN_AND_WRAP = 5,
} CSSM_USER_AUTHENTICATION_MECHANISM;
typedef CSSM_DATA_PTR (CSSMAPI *CSSM_CALLBACK) (void *allocRef, uint32 ID);
typedef struct cssm_crypto_data {
CSSM_DATA_PTR Param;
CSSM_CALLBACK Callback;
uint32 ID;
}CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA, *CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA_PTR
typedef struct cssm_user_authentication {
CSSM_DATA_PTR Credential; /* a cert, a shared secret, other */
CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA_PTR MoreAuthenticationData;
} CSSM_USER_AUTHENTICATION, *CSSM_USER_AUTHENTICATION_PTR;
typedef CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CSSM_NOTIFY_CALLBACK)
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle,
uint32 Application,
uint32 Reason,
void* Param);
| Reason | Description |
|---|---|
| CSSM_NOTIFY_SURRENDER | The add-in module is temporarily surrendering control of the process |
| CSSM_NOTIFY_COMPLETE | An asynchronous operation has completed |
| CSSM_NOTIFY_DEVICE_REMOVED | A device, such as a token or storage device, has been removed |
| CSSM_NOTIFY_DEVICE_INSERTED | A device, such as a token or storage device, has been inserted |
typedef struct cssm_memory_funcs {
void * (*malloc_func) (uint32 Size, void *AllocRef);
void (*free_func) (void *MemPtr, void *AllocRef);
void * (*realloc_func) (void *MemPtr, uint32 Size, void *AllocRef);
void * (*calloc_func) (uint32 Num, uint32 Size, void *AllocRef);
void *AllocRef;
} CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS, *CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR;
typedef CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS;
typedef CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS *CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR;
See
| Contents | Next section | Index |