The use of names in The Open Group DCE often involves more than one directory service.
For example, CDS interacts with either GDS or DNS to find names outside the
local cell.
Implementations may support additional national character sets to be used in names and attribute values. However, implementations that provide for support of additional character sets may lose interoperability to other implementations that conform to this specification.

The default schema of GDS contains only naming attributes that specify character sets of type Printable string or T.61 graphical character set.
| Country Name | Code | Country Name | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFGHANISTAN | AF | ALBANIA | AL |
| ALGERIA | DZ | AMERICAN SAMOA | AS |
| ANDORRA | AD | ANGOLA | AO |
| ANGUILLA | AI | ANTARCTICA | AQ |
| ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA | AG | ||
| ARGENTINA | AR | ARUBA | AW |
| AUSTRALIA | AU | AUSTRIA | AT |
| BAHAMAS | BS | BAHRAIN | BH |
| BANGLADESH | BD | BARBADOS | BB |
| BELGIUM | BE | BELIZE | BZ |
| BENIN | BJ | BERMUDA | BM |
| BHUTAN | BT | BOLIVIA | BO |
| BOTSWANA | BW | BOUVET ISLAND | BV |
| BRAZIL | BR | BRITISH INDIAN OCEAN | IO |
| TERRITORY | |||
| BRUNEI DARUSSALAM | BN | BULGARIA | BG |
| BURKINA FASO | BF | BURMA | BU |
| BURUNDI | BI | BYELORUSSIAN SSR | BY |
| CAMEROON | CM | CANADA | CA |
| CAPE VERDE | CV | CAYMAN ISLANDS | KY |
| Country Name | Code | Country Name | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC | CF | CHAD | TD |
| CHILE | CL | CHINA | CN |
| CHRISTMAS ISLAND | CX | COCOS (KEELING) | |
| ISLANDS | CC | ||
| COLOMBIA | CO | COMOROS | KM |
| CONGO | CG | COOK ISLANDS | CK |
| COSTA RICA | CR | COTE D'IVOIRE | CI |
| CUBA | CU | CYPRUS | CY |
| CZECHOSLOVAKIA | CS | DENMARK | DK |
| DJIBOUTI | DJ | DOMINICA | DM |
| DOMINICAN REPUBLIC | DO | EAST TIMOR* | TP |
| ECUADOR | EC | EGYPT | EG |
| EL SALVADOR | SV | EQUATORIAL GUINEA | GQ |
| ETHIOPIA | ET | FALKLAND ISLANDS | FK |
| (MALVINAS) | |||
| FAROE ISLANDS | FO | FIJI | FJ |
| FINLAND | FI | FRANCE | FR |
| FRENCH GUIANA | GF | FRENCH POLYNESIA | PF |
| FRENCH SOUTHERN | TF | GABON | GA |
| TERRITORIES | |||
| GAMBIA | GM | GERMAN DEMOCRATIC | DD |
| REPUBLIC | |||
| GERMANY, FEDERAL | DE | GHANA | GH |
| REPUBLIC OF | |||
| GIBRALTAR | GI | GREECE | GR |
| GREENLAND | GL | GRENADA | GD |
| GUADELOUPE | GP | GUAM | GU |
| GUATEMALA | GT | GUINEA | GN |
| GUINEA-BISSAU | GW | GUYANA | GY |
| HAITI | HT | HEARD AND MC | HM |
| DONALD ISLANDS | |||
| HONDURAS | HN | HONG KONG | HK |
| HUNGARY | HU | ICELAND | IS |
| INDIA | IN | INDONESIA | ID |
| IRAN (ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF) | IR | IRAQ | IQ |
| IRELAND | IE | ISRAEL | IL |
| ITALY | IT | JAMAICA | JM |
| JAPAN | JP | JORDAN | JO |
| KAMPUCHEA, DEMOCRATIC | KH | KENYA | KE |
| KIRIBATI | KI | KOREA, DEMOCRATIC | KP |
| PEOPLE'S REPUBLIC OF | |||
| KOREA, REPUBLIC OF | KR | KUWAIT | KW |
| LAO PEOPLE'S DEMOCRATIC | LA | LEBANON | LB |
| REPUBLIC | |||
| LESOTHO | LS | LIBERIA | LR |
| LIBYAN ARAB JAMAHIRIYA | LY | LIECHTENSTEIN | LI |
| LUXEMBOURG | LU | MACAU | MO |
| MADAGASCAR | MG | MALAWI | MW |
| MALAYSIA | MY | MALDIVES | MV |
| Country Name | Code | Country Name | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| MALI | ML | MALTA | MT |
| MARSHALL ISLANDS | MH | MARTINIQUE | MQ |
| MAURITANIA | MR | MAURITIUS | MU |
| MEXICO | MX | MICRONESIA | FM |
| MONACO | MC | MONGOLIA | MN |
| MONTSERRAT | MS | MOROCCO | MA |
| MOZAMBIQUE | MZ | NAMIBIA | NA |
| NAURU | NR | NEPAL | NP |
| NETHERLANDS | NL | NETHERLANDS ANTILLES | AN |
| NEUTRAL ZONE | NT | NEW CALEDONIA | NC |
| NEW ZEALAND | NZ | NICARAGUA | NI |
| NIGER | NE | NIGERIA | NG |
| NIUE | NU | NORFOLK ISLAND | NF |
| NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS | MP | NORWAY | NO |
| OMAN | OM | PAKISTAN | PK |
| PALAU | PW | PANAMA | PA |
| PAPUA NEW GUINEA | PG | PARAGUAY | PY |
| PERU | PE | PHILIPPINES | PH |
| PITCAIRN | PN | POLAND | PL |
| PORTUGAL | PT | PUERTO RICO | PR |
| QATAR | QA | REUNION | RE |
| ROMANIA | RO | RWANDA | RW |
| ST. HELENA | SH | SAINT KITTS AND NEVIS | KN |
| SAINT LUCIA | LC | ST. PIERRE AND MIQUELON | PM |
| SAINT VINCENT AND THE | VC | SAMOA | WS |
| GRENADINES | |||
| SAN MARINO | SM | SAO TOME AND PRINCIPE | ST |
| SAUDI ARABIA | SA | SENEGAL | SN |
| SEYCHELLES | SC | SIERRA LEONE | SL |
| SINGAPORE | SG | SOLOMON ISLANDS | SB |
| SOMALIA | SO | SOUTH AFRICA | ZA |
| SPAIN | ES | SRI LANKA | LK |
| SUDAN | SD | SURINAME | SR |
| SVALBARD AND JAN | SJ | ||
| MAYEN ISLANDS | |||
| SWAZILAND | SZ | SWEDEN | SE |
| SWITZERLAND | CH | SYRIAN ARAB REPUBLIC | SY |
| TAIWAN, PROVINCE | TW | TANZANIA, UNITED | TZ |
| OF CHINA | REPUBLIC OF | ||
| THAILAND | TH | TOGO | TG |
| TOKELAU | TK | TONGA | TO |
| TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO | TT | TUNISIA | TN |
| TURKEY | TR | TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS | TC |
| TUVALU | TV | UGANDA | UG |
| UKRAINIAN SSR | UA | UNITED ARAB | AE |
| EMIRATES | |||
| UNITED KINGDOM | GB | UNITED STATES | US |
| Country Name | Code | Country Name | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| UNITED STATES MINOR | UM | URUGUAY | UY |
| OUTLYING ISLANDS | |||
| USSR | SU | VANUATU | VU |
| VATICAN CITY STATE | VA | VENEZUELA | VE |
| VIET NAM | VN | VIRGIN ISLANDS (BRITISH) | VG |
| VIRGIN ISLANDS (U.S.) | VI | WALLIS AND FUTUNA | WF |
| ISLANDS | |||
| WESTERN SAHARA* | EH | YEMEN | YE |
| YEMEN, DEMOCRATIC | YD | YUGOSLAVIA | YU |
| ZAIRE | ZR | ZAMBIA | ZM |
| ZIMBABWE | ZW |
The optional use of additional character repertoires is permitted and provided for, according to the CCITT T.61 specification. However, neither the composition and allocation of these character sets nor the specific conformance requirements are specified here.
Some T.61 alphabetical characters have a two-byte representation. For example, a lower-case letter a with acute accent is represented by 0xc2 (code for acute accent) followed by 0x61 (code for lower-case a).
Only certain combinations of diacritical characters and basic letters
are valid. They are shown in
| Name | Repr. | Code | Valid Basic Letters Following |
|---|---|---|---|
| grave accent | ` | 0xc1 | a, A, e, E, i, I, o, O, u, U |
| acute accent | ´ | 0xc2 | a,A,c,C,e,E,g,i,I,l,L,n,N,o,O,r,R, |
| s,S,u,U,y,Y,z,Z | |||
| circumflex | ^ | 0xc3 | a,A,c,C,e,E,g,G,h,H,i,I,j,J,o,O,s,S, |
| accent | u,U,w,W,y,Y | ||
| tilde | ~ | 0xc4 | a,A,i,I,n,N,o,O,u,U |
| macron | [??] | 0xc5 | a,A,e,E,i,I,o,O,u,U |
| breve | [??] | 0xc6 | a, A, g, G, u, U |
| dot above | [??] | 0xc7 | c,C,e,E,g,G,I,z,Z |
| umlaut | [??] | 0xc8 | a,A,e,E,i,I,o,O,u,U,y,Y |
| ring | ° | 0xca | a,A,u,U |
| cedilla | [??] | 0xcb | c,C,G,k,K,l,L,n,N,r,R,s,S,t,T |
| double accent | " | 0xcd | o, O, u, U |
| ogonek | [??] | 0xce | a, A, e, E, i, I, u, U |
| caron | [??] | 0xcf | c,C,d,D,e,E,l,L,n,N,r,R,s,S,t,T,z,Z |
The non-spacing underline (code 0xcc) must be followed by a Latin alphabetical character; that is, a basic letter (a-z or A-Z), or a valid diacritical combination.
Bold characters cannot be reverse mapped.
All characters that stand alone must be followed by a space.
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | A | B | C | D | E | F | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | SP | 0 | P | ` | p | NBSP | ° | À | Ð | à | ||
| 1 | ! | 1 | A | Q | a | q | [??] | ± | [??] | Ñ | [??] | ñ |
| 2 | " | 2 | B | R | b | r | ¢ | 2 | Â | Ò | â | ò |
| 3 | # | 3 | C | S | c | s | £ | 3 | Ã | [??] | ã | [??] |
| 4 | $ | 4 | D | T | d | t | [??] | Ä | Ô | ä | ô | |
| 5 | % | 5 | E | U | e | u | [??] | [??] | Å | Õ | å | õ |
| 6 | & | 6 | F | V | f | v | [??] | [??] | Æ | Ö | æ | ö |
| 7 | ' | 7 | G | W | g | w | § | * | Ç | code × | ç | [??] |
| 8 | ( | 8 | H | X | h | x | [??] | [??] | È | Ø | è | ø |
| 9 | ) | 9 | I | Y | i | y | © | 1 | [??] | Ù | [??] | ù |
| A | * | : | J | Z | j | z | [??] | [??] | Ê | [??] | ê | [??] |
| B | + | ; | K | [ | k | { | << | >> | Ë | Û | ë | û |
| C | , | < | L | \ | l | | | [??] | [??] | Ì | Ü | ì | ü |
| D | - | = | M | ] | m | } | SHY | ½ | [??] | '-.1m"-.15m'´'.15m'Y | [??] | 'y´' |
| E | . | > | N | ^ | n | ~ | ® | [??] | Î | Þ | î | þ |
| F | / | ? | O | [??] | o | DEL | - | [??] | Ï | ß | ï | [??] |
| Name | Repr. | Code | Valid Basic Letters Following |
|---|---|---|---|
| grave accent | ` | 0xc1 | |
| acute accent | ´ | 0xc2 | c,C,g,l,L,n,N,r,R,s,S,z,Z |
| circumflex | ^ | 0xc3 | c,C,g,G,h,H,j,J,s,S,w,W,y,Y |
| accent | |||
| tilde | ~ | 0xc4 | i,I,u,U |
| macron | [??] | 0xc5 | a,A,e,E,i,I,o,O,u,U |
| breve | [??] | 0xc6 | a,A,g,G,u,U |
| dot above | [??] | 0xc7 | c,C,e,E,g,G,I,z,Z |
| umlaut | [??] | 0xc8 | Y |
| ring | ° | 0xca | u,U |
| cedilla | [??] | 0xcb | G,k,K,l,L,n,N,r,R,s,S,t,T |
| double accent | " | 0xcd | o,O,u,U |
| ogonek | [??] | 0xce | a,A,e,E,i,I,u,U |
| caron | [??] | 0xcf | c,C,d,D,e,E,l,L,n.N,r,R,s,S,t,T,z,Z |
The following characters cannot be converted from ISO 8859-1 syntax to T.61 syntax; GDS generates an error when it attempts to perform the conversion:
Certain characters have special meaning to the directory services; these
are known as metacharacters.
| Directory | ||
|---|---|---|
| Service | Character | Meaning |
| CDS | / | Separates components of a name (atomic names). |
| * | When used in the rightmost atomic name of a name, acts as a wildcard, matching zero or more characters. | |
| ? | When used in the rightmost atomic name of a name, acts as a wildcard, matching exactly one character. | |
| \ | Used where necessary in front of a / (slash), an * (asterisk) or a ? (question mark) to escape the character (indicates that the following character is not a metacharacter). | |
| GDS | / | Separates Relative Distinguished Names (RDNs). |
| , | Separates multiple attribute type/value pairs (attribute value assertions) within an RDN. | |
| = | Separates an attribute type and value in an attribute value assertion. | |
| \ | Used in front of a / (slash), a , (comma) or an = (equal sign) to escape the character (indicates that the following character is not a metacharacter). | |
| DNS | . | Separates elements of a name. |
Some metacharacters are not permitted as normal characters within a name. For example, a \ (backslash) cannot be used as anything but an escape character in GDS.
| Characteristic | CDS | GDS | DNS |
|---|---|---|---|
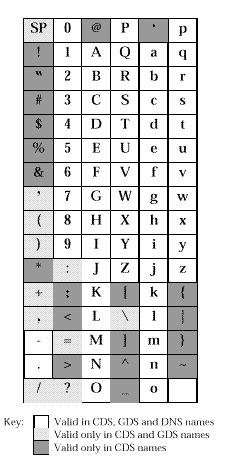
| Character Set | a to z, A to Z, 0 to 9 plus space and special characters shown in Figure A-1 | a to z, A to Z, 0 to 9 plus . : , ' + - = () ? / and space | a to z, A to Z, 0 to 9 plus . - |
| Metacharacters | / * ? \ | / , = \ | . |
| Restrictions | Atomic names cannot contain a / (slash).
The first atomic name following the global cell name (or /.: prefix) cannot contain an = (equal sign). For enumeration operations, a \ (backslash) must be used to escape any * (asterisk) or ? (question mark) character in the rightmost atomic name. Otherwise (if not escaped in the rightmost atomic name), the character is interpreted as a wildcard. | Relative distinguished names cannot begin or end
with a / (slash).
Attribute types must begin with an alphabetic character, can contain only alphanumerics, and cannot contain spaces. An alternative method of specifying attribute types is by object identifier, a sequence of digits separated by . (dots). A \ (backslash) must be used to escape a / (slash), a , (comma), and an = (equal sign) when using them as anything other than metacharacters. Multiple consecutive unescaped instances of / (slashes), , (commas), = (equal signs) and \ (back-slashes) are not allowed. Each attribute value assertion contains exactly one unescaped = (equal sign). | The first character must be alphabetic.
The first and last characters cannot be a . (dot) or a - (dash). Cell names in DNS must contain at least one . (dot); they must be more than one level deep. |
| Characteristic | CDS | GDS | DNS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case-Matching Rules | Case exact | Attribute types are matched case insensitive. The case-matching rule for an attribute value can be case exact or case insensitive, depending on the rule defined for its type at the DSA. | Case insensitive | |
| Internal Representation | Case exact | Depends on the case-matching rule defined at DSA. If the rule says case insensitive, alphabetic characters are converted to all lower-case characters. Spaces are removed regardless of the case-matching rule. | Alphabetic characters are converted to all lower-case characters. | |
| Ordering of Name Elements | Big endian (left to right from root to lower-level names). | Big endian (left to right from root to lower-level names). | Little endian (right to left from root to lower-level names). |
| Maximum Size | |
|---|---|
| Name Type | (octets) |
| CDS atomic name (character string between two slashes) | 254 |
| CDS full name (including global or local prefix, cell name and slashes separating atomic names) | 1023 |
| CDS attribute name | 31 |
| CDS class name | 31 |
| GDS distinguished name | 1023 |
| DNS relative name (character string between two dots) | 64 |
| DNS fully qualified name (sum of all relative names) | 255 |
[??] Some characters or strings that appear in the printed document are not easily representable using HTML.
Please note that the html version of this specification may contain formatting aberrations. The definitive version is available as an electronic publication on CD-ROM from The Open Group.
| Contents | Next section | Index |