The use of digital certificates is the foundation on which the CDSA is designed. The CDSA assumes the concept of digital certificates in its broadest sense. Applications use the credential for:
The applications interpret and manipulate the contents of certificates to achieve these ends, based on the real-world trust model they chose as their model for trust and security. The primary purpose of a Trust Policy (TP) module is to answer the question, "Is this certificate trusted for this action?" The CSSM Trust Policy API determines the generic operations that should be defined for certificate-based trust in every application domain. The specific semantics of each operation is defined by the:
The trust model is expressed as an executable policy that is used by all applications that subscribe to that policy and the trust model it represents. As an infrastructure, CSSM is policy-neutral with respect to application-domain policies; it does not incorporate any single policy. For example, the verification procedure for a credit card certificate should be defined and implemented by the credit company issuing the certificate. Employee access to a lab housing a critical project should be defined by the company whose intellectual property is at risk. Rather than defining policies, CSSM provides the infrastructure for installing and managing policy- specific modules. This ensures complete extensibility of certificate-based trust on every platform hosting CSSM.
Policies define the credentials required for authorization to perform an action on another object. Certificates are the basic credentials representing a trust relationship among a set of two or more parties. When an organization issues certificates it defines its issuing procedure in a Certification Practice Statement (CPS). The statement identifies existing policies with which it is consistent. The statement can also be the source of new policy definitions if the action and target object domains are not covered by an existing, published policy. An application domain can recognize multiple policies. A given policy can be recognized by multiple application domains.
Evaluation of trust depends on relationships among certificates. The trust domain can define accepted sources of trust, called anchors. Anchors can be mandated by fiat or can be computed by some other means. In contrast to the sources of trust, certificate revocation lists represent sources of distrust. Trust policies may consult these lists during the verification process
Different trust policies define different actions that an application may request. Some of these actions are common to every trust policy, and are operations on objects all trust models use. The objects believed to be common to all trust models are certificates and certificate revocation records. The basic operations on these objects are sign, verify, and revoke.
Based on this analysis, CSSM defines two categories of API calls that should be implemented by TP modules. The first category allows the TP module to validate operations relevant within an application domain (such as requesting authorization to make a $200 charge on a credit card certificate, and requesting access to the locked project lab). The second category supports all of the currently provided operations supporting the life cycle of certificates and certificate revocation lists.
Application developers and trust domain authorities benefit from the ability to define and implement policy-based modules. Application developers are freed from the burden of implementing a policy description and certifying that their implementation conforms. Instead, the application needs only to build in a list of the authorities and certificate issuers it uses.
Domain authorities also benefit from an infrastructure that supports add-in Trust Policy modules. Authorities are ensured that applications using their module(s) adhere to the policies of the domain. Also, dynamic download of trust modules (possibly from remote systems) ensures timely and accurate propagation of policy changes. Individual functions within the module may combine local and remote processing. This flexibility allows the module developer to implement policies based on the ability to communicate with a remote authority system. This also allows the policy implementation to be decomposed in any convenient distributed manner.
Implementing a Trust Policy module may or may not be tightly coupled with one or more Certificate Library modules or one or more Data Storage Library modules. The trust policy embodies the semantics of the domain. The certificate library and the data storage library embody the syntax of a certificate format and operations on that format. A trust policy can be completely independent of certificate format, or it may be defined to operate with one or a small number of certificate formats. A trust policy implementation may invoke a certificate library module or data storage library modules to facilitate making policy based manipulations.
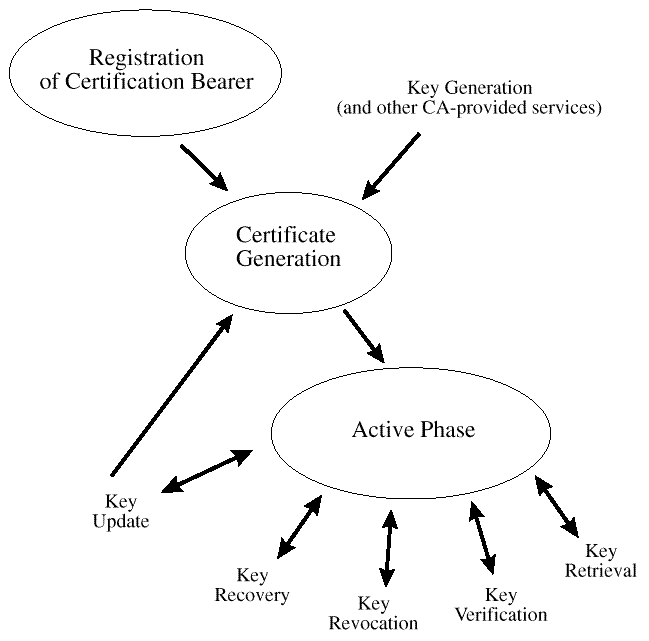
The certificate life cycle is presented in
After registration, keying material is generated and certificates are created. Once the private key material and public key certificate are issued to a user and backed up if appropriate, the active phase of the certificate management life cycle begins.
The active phase includes:

typedef struct cssm_spi_tp_funcs {
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *SubmitCredRequest)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType,
const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *ReferenceIdentifier);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *RetrieveCredResult)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_BOOL *ConfirmationRequired,
CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET_PTR *RetrieveOutput);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *ConfirmCredResult)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *ReceiveConfirmation)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses,
sint32 *ElapsedTime);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertReclaimKey)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
uint32 CertIndex,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertReclaimAbort)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *FormRequest)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *FormSubmit)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
const CSSM_DATA *Form,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority,
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertGroupVerify)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertCreateTemplate)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertGetAllTemplateFields)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertSign)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CrlVerify)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CrlCreateTemplate)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertRevoke)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CrlSign)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *ApplyCrlToDb)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertGroupConstruct)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const void *ConstructParams,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertGroupPrune)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *CertGroupToTupleGroup)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *TupleGroupToCertGroup)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates);
CSSM_RETURN (CSSMAPI *PassThrough)
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams);
} CSSM_SPI_TP_FUNCS, *CSSM_SPI_TP_FUNCS_PTR;
All trust policy service provider modules can return the following common error codes from any trust policy service function. These error codes are not repeated in individual function definitions.
TP_SubmitCredRequest
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_SubmitCredRequest (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority, CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType, const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput, const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext, sint32 *EstimatedTime, CSSM_DATA_PTR *ReferenceIdentifier)
If the caller is successfully authenticated, then this function submits a request to the Authority identified by PreferredAuthority. The authority service can be local or remote. If the Authority is not specified, then the TP module can assume a default authority based on the RequestType and the CallerAuthContext. RequestType indicates the type of Authority request and RequestInput specifies the input parameters needed by the authority to perform the request.The request is submitted to the authority only if the TP module can successfully authenticate the caller. The CallerAuthContext presents the caller's credentials and a list of one or more policies under which the caller should be authenticated. Caller credentials can be presented in several forms:
- Memory-resident credential values, directly referenced by the structure
- Data bases containing credentials
- Callback functions that can be invoked to obtain credentials from an active entity
The local service provider must select and forward the credentials required by the Authority. The caller must provide all necessary credentials through the CallerAuthContext parameter.
If the caller can not be authenticated by the local service provider, the function fails and the request is not submitted to the selected authority.
This function returns a ReferenceIdentifier and an EstimatedTime (specified in seconds). ReferenceIdentifier is an ID for the submitted request. EstimatedTime defines the expected time to process the request. This time may be substantial when the request requires offline authentication procedures by the Authority process. In contrast, the estimated time can be zero, meaning the result can be obtained immediately using
TP_RetrieveCredResult() . After the specified time has elapsed, the caller must use the functionTP_RetrieveCredResult() , with the reference identifier, to obtain the result of the request.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to perform this function.
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Certificate Service Authority to submit the request to.
- RequestType (input)
The identifier of the type of request to submit.
- RequestInput (input)
A pointer to the input parameters to be submitted to the authority who will perform the requested service.
- CallerAuthContext (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials. The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific data. The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module and recorded in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials can be required. If the local service provider module does not require credentials from a caller, then the Credentials field of this verification context structure can be NULL. The structure optionally contains additional credentials that can be used to support the authentication process. Authentication credentials required by the authority should be included in the RequestInputi. The local service provider module can forward this credential information to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
- EstimatedTime (output)
The number of estimated seconds before the service results are ready to be retrieved. A (default) value of zero indicates that the results can be retrieved immediately via the correspondingTP_RetrieveCredResult() function call. When the local service provider module or the authority cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
- ReferenceIdentifier (output)
A reference identifier, which uniquely identifies this specific request. The handle persists across application executions and becomes undefined when all local processing of the request has completed. Local processing is completed in one of two ways:
- For certificate services that do not require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is invalidated when the corresponding
TP_RetrieveCredResult() function completes (by returning valid results or by failure, which blocks returned results)
- For certificate services that require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is invalidated by successfully invoking the function
TP_ConfirmCredResult() .
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_SubmitCredRequest()
TP_ConfirmCredResult
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ConfirmCredResult (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier, const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials, const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses, const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority)
This function submits a vector of acknowledgements to a Certificate Authority for a set of requests and corresponding results identified by ReferenceIdentifier. The caller must execute the call sequenceTP_SubmitCredRequest() andTP_RetrieveCredResult() to submit a set of requests and to retrieve the results of those requests. Some Certificate Authority services accessed through the request and retrieve functions require confirmation. The functionTP_RetrieveCredResult() returns a value indicating whether the caller must invokeTP_ConfirmCredResult() to successfully complete the service.The Responses vector accepts or rejects each result independently. If the caller rejects a returned result, the action taken by the authority depends on the requested type of service.
The ReferenceIdentifier also identifies the authority process state associated with the function pair
TP_SubmitCredRequest() andTP_RetrieveCredResult() . The PreferredAuthority information can be used to further identify the authority to receive the acknowledgement. After successful execution of this function, the value of the ReferenceIdentifier is undefined and should not be used in subsequent operations in the current module attach session.This function fails if ReferenceIdentifier is invalid or the Authority process can not be located.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to perform this function.
- ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies execution of the call sequenceTP_SubmitCredRequest() andTP_RetrieveCredResult() to submit a set of requests and to retrieve the results of those requests.
- CallerAuthCredentials (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials. The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific data. The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials can be required. If the local service provider module does not require credentials from a caller, then the Credentials field of this verification context structure can be NULL. The structure optionally contains additional credentials that can be used to support the authentication process. Authentication credentials required by the authority should be included in the RequestInput. The local TP module can forward information from the CallerAuthCredentials to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
- Responses (input)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the caller's acceptance or rejection of results. The vector contains one acknowledgement per result returned byTP_RetrieveCredResult() .
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Authority to receive the acknowledgements. The structure can include:
- An identity certificate for the authority
- The location of the authority
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_SubmitCredRequest()
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
TP_ReceiveConfirmation()
TP_ReceiveConfirmation
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ReceiveConfirmation (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier, CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses, sint32 *ElapsedTime)
A certificate authority uses this function to poll for confirmation from a requester who has been served by the authority. A requester sends a confirmation to the authority by successfully invoking the functionTP_ConfirmCredResult() .The ReferenceIdentifier uniquely identifies the service request and corresponding results for which confirmation is expected. This reference identifier need not be identical to the reference identifier used by the requester, but a one-to-one mapping between the two name spaces must be well-defined.
Responses is an ordered vector of acknowledgements indicating, for each returned result, whether the result was accepted or rejected by the original requester for whom the service was performed. If a result is rejected by the receiver, then the authority process must undo the service if a reverse operation is possible and available.
If a fatal error occurs, this function returns an error code, indicating that the function call can never be completed. If confirmation has not been received, the function return value is CSSM_OK and the ElapsedTime is returned to the caller of this function. The time represents elapsed seconds since the service results were produced by the authority process. Note that there can be a difference between the time the authority process produces the results and the time the results are actually received by the requester. Elapsed time is relative and should increase with consecutive calls using the same ReferenceIdentifier. If the TP module has no knowledge of the elapsed time, the value CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN must be returned. If the service requester has confirmed receipt of the service results, this function returns CSSM_OK and ElapsedTime is CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
This function can be invoked repeatedly until the confirmation is received or until the caller decides the acknowledgement may be lost and chooses to undo the results of the original service request.
This function fails if the ReferenceIdentifier is invalid or does not match any requested service for which confirmation is expected.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to perform this function.
- ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies a set of service requests and the results created in response to those requests.
- Responses (output)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the caller's acceptance or rejection of results. The vector contains one acknowledgement per result created by the certificate authority.
- ElapsedTime (output)
- If the confirmation has not been received, this output value is the number of seconds elapsed since the certificate authority created the results or CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN. If the confirmation has been received, this output value is CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
A CSSM return value combined with elapsed time to indicate one of three results:
Complete Function Function Return RetrieveOutput EstimatedTime Result Value Confirmation Received CSSM_OK CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE Confirmation not received, but expected in the future CSSM_OK CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN or <elapsed seconds> Fatal Error, Confirmation is not expected (!CSSM_OK) NA For a return value of (!CSSM_OK) the return value is an error code.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_ConfirmCredResult()
TP_CertReclaimKey
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimKey (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup, uint32 CertIndex, CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry)
This function recovers the private key associated with a certificate and securely stores that key in the specified cryptographic service provider. The key and its associated certificate are among a set of certificates and private keys reclaimed from a certificate authority.The particular private key to be recovered to the local system is identified by its associated certificate. The certificate is identified by its CertIndex position within the CertGroup.
The reclamation process associates the private key with the public key contained in the certificate, securely stores the private key in the specified cryptographic service provider, and associates the new Credentials with the restored private key.
When all required private keys have been reclaimed, the key cache can be discarded using the function
TP_CertReclaimAbort() . The caller must free the CertGroup when it is no longer needed.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider module used to perform this operation.
- CertGroup (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a reference to a group of certificates and the number of certificates contained in that group. The certificate group contains all certificates that are candidates for reclamation.
- CertIndex (input)
An index value that identifies the certificate whose associated private key is to be recovered and stored in the local CSP. This index value I references the I-th certificate in CertGroup.
- KeyCacheHandle (input)
A reference handle that uniquely identifies the cache of protected private keys associated with the reclaimed certificates contained in CertGroup. The structure of the cache is opaque to the caller.
- CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the CSP module where the private key is to be stored. Optionally, the CA service provider can use this CSP to perform additional cryptographic operations or may use another default CSP for that purpose.
- CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively. If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key, then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_RetrieveCredResult()
TP_Cert_ReclaimAbort()
TP_CertReclaimAbort
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimAbort (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle)
This function terminates the iterative process of reclaiming certificates and recovering their associated private keys from a protected key cache. This function must be called even if all private keys are recovered from the cache. This function destroys all intermediate state and secret information used during the reclamation process. At completion of this function, the cache handle is invalid.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider module used to perform this function.
- KeyCacheHandle (input)
An opaque handle that identifies the cache of protected private keys reclaimed from a certificate authority for potentially recovery on the local system.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertReclaimKey()
TP_FormRequest
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormRequest (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority, CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType, CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm)
This function returns a blank form of type FormType from an Authority. If the PreferredAuthority list is NULL, the CA module can use a default authority name and location based on FormType. The CA module must incorporate knowledge of the interface protocol for communicating with the authority.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority module used to perform this function.
- PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate that identifies the Authority process, or a network address directly or indirectly identifying the location of the authority. If the input is NULL, the module can assume a default authority location. If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated and the operation fails.
- FormType (input)
Indicates the type of form being requested.
- BlankForm (output)
A CSSM_DATA structure containing the requested form. The caller must have knowledge of the structure of the form based on `FormType.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_FormSubmit()
TP_FormSubmit
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormSubmit (CSSM_TP_Handle TPHandle, CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType, const CSSM_DATA *Form, const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority, const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority, CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials)
The completed Form is submitted to a ClearanceAuthority, who is acting on behalf of a RepresentedAuthority. Typically the submitted form is requesting an authorization credential required as input to future service requests to the RepresentedAuthority.If the form is honored by the ClearanceAuthority, then a set of one or more Credentials is returned to the requester. These credential can be used as the input credential in future service requests submitted to the RepresentedAuthority.
- TPHandle (input)
A handle for the service provider module that will perform the operation.
- FormType (input)
Indicates the type of form being submitted.
- Form (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the completed form to be submitted to the ClearanceAuthority.
- ClearanceAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate that identifies the clearance authority process, or a network address directly or indirectly identifying the location of the authority. If the input is NULL, the service provider module can assume a default authority based on the FormType and contents of Form. If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated and the operation fails.
- RepresentedAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate that identifies the authority represented by the ClearanceAuthority. If the input is NULL, the service provider module can assume a default authority based on the FormType and contents of Form. If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated and the operation fails.
- Credentials (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing one or more credentials issued in response to the contents of the Form. If the output is NULL, either no credentials were returned or an error occurred.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_FormRequest()
TP_CertGroupVerify
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupVerify (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult)
This function determines whether the certificate is trusted. The actions performed by this function differ based on the trust policy domain. The factors include practices, procedures and policies defined by the certificate issuer.Typically certificate verification involves the verification of multiple certificates. The first certificate in the group is the target of the verification process. The other certificates in the group are used in the verification process to connect the target certificate with one or more anchors of trust. The supporting certificates can be contained in the provided certificate group or can be stored in the data stores specified in the VerifyContext DBList. This allows the trust policy module to construct a certificate group and perform verification in one operation. The data stores specified by DBList can also contain certificate revocation lists used in the verification process. It is also possible to provide a data store of anchor certificates. Typically the points of Trust are few in number and are embedded in the caller or in the TPM during software manufacturing or at runtime
The caller can select to be notified incrementally as each certificate is verified. The CallbackWithVerifiedCert parameter (in the VerifyContext) can specify a caller function to be invoked at the end of each certificate verification, returning the verified certificate for use by the caller.
Anchor certificates are a list of implicitly trusted certificates. These include root certificates, cross certified certificates, and locally defined sources of trust. These certificates form the basis to determine trust in the subject certificate.
A policy identifier can specify an additional set of conditions that must be satisfied by the subject certificate in order to meet the trust criteria. The name space for policy identifiers is defined by the application domains to which the policy applies. This is outside of CSSM. A list of policy identifiers can be specified and the stopping condition for evaluating that set of conditions.
The evaluation and verification process can produce a list of evidence. The evidence can be selected values from the certificates examined in the verification process, entire certificates from the process or other pertinent information that forms an audit trail of the verification process. This evidence is returned to the caller after all steps in the verification process have been completed.
If verification succeeds, the trust policy module may carry out the action on the specified data or may return approval for the action requiring the caller to perform the action. The caller must consult TP module documentation outside of this specification to determine all module-specific side effects of this operation.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that can be used to manipulate the subject certificate and anchor certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider module used to perform this function. If no cryptographic service provider handle is specified, the TP module allocates a suitable CSP.
- CertGroupToBeVerified (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be verified. The first certificate in the group is the primary target certificate for verification. Use of the subsequent certificates during the verification process is specific to the trust domain.
- VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values in the context are optional except Action. The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- VerifyContextResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertCreateTemplate
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertCreateTemplate (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, uint32 NumberOfFields, const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields, CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
This function allocates and initializes memory for an encoded certificate template output in CertTemplate->Data. The template values are specified by the input OID/value pairs contained in CertFields. The initialization process includes encoding all certificate field values according to the certificate type and certificate template encoding supported by the trust policy library module.The memory for CertTemplate->Data is allocated by the service provider using the calling application's memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library module used to perform this function.
- NumberOfFields (input)
The number of certificate field values specified in the CertFields.
- CertFields (input)
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs that identify the field values to initialize a new certificate.
- CertTemplate (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure that will contain the unsigned certificate template as a result of this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields()
TP_CertSign()
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate, uint32 *NumberOfFields, CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
This function returns all field values from CertTemplate. CertTemplate is an unsigned certificate template in the format supported by the TP. Fields are returned as a set of OID-value pairs. The OID identifies the TP certificate template field and the data format of the value extracted from that field. The Trust Policy module defines and uses a preferred data format for returning field values from this function. Memory for the CertFields output is allocated by the service provider using the calling application's memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CertTemplate (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the packed, Encoded certificate template.
- NumberOfFields (output)
The length of the output array of fields.
- CertFields (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures which contains the OIDs and values of the fields of the input certificate template.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertCreateTemplate()
TP_CertSign()
TP_CertSign
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertSign (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle, const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult, CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
The TP module decides whether the signer certificate is trusted to sign the CertTemplateToBeSigned. The signer certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established, this operation signs the entire certificate. The caller must provide a credential that permits the caller to use the private key for this signing operation. The credential can be provided in the cryptographic context CCHandle. If CCHandle is NULL, the credentials in the SignerVerifyContext specify the credential value.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context for signing the certificate. This context also identifies the cryptographic service provider to be used to perform the signing operation. If this handle is not provided by the caller, the trust policy module can assume a default signing algorithm and a default CSP. If the trust policy module does not assume defaults or the default CSP is not available on the local system, an error occurs.
- CertTemplateToBeSigned (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a certificte template to be signed. The CRL type and encoding are included in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the signer for this operation. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the signer. Use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
- SignerVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- SignerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- SignedCert (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the signed certificate. The SignedCert->Data is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlSign()
TP_CertGroupVerify()
TP_CreateCertTemplate()
TP_CrlVerify
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlVerify (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult)
This function verifies the integrity of the certificate revocation list and determines whether it is trusted. Some of the checks that may be performed include: verifying the signatures on the signer's certificate group, establishing the authorization of the signer to issue CRLs, verification of the signature on the CRL, verifying validity period of the CRL and the date the CRL was issued, and so on.The caller can specify additional points of trust represented by anchor certificates in the VerifyContext. The trust policy module can use these additional points of trust in the verification process.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that can be used to manipulate the certificates to be verified. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service Provider to be used to verify signatures on the signer's certificate and on the CRL. The TP module is responsible for creating the cryptographic context structure required to perform the verification operation. If no CSP is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CSP to perform the operations.
- CrlToBeVerified (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a signed certificate revocation list to be verified. The CRL type and encoded are included in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the signer of the certificate revocation list. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the CRL signer . Use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
- VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- VerifyContextResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing a signed certificate revocation list to be verified. The CRL type and encoded are included in this structure.
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlVerify()
TP_CrlCreateTemplate
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlCreateTemplate (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, uint32 NumberOfFields, const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields, CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
This function creates an unsigned, memory-resident CRL template. Fields in the CRL are initialized based on with the descriptive data specified by the OID/value input pairs in CrlFields and the local domain policy of the TP. The specified OID/value pairs can initialize all or a subset of the general attribute fields in the new CRL, though the module developer may specify a set of fields that must be or cannot be set using this operation. The NewCrlTemplate output is an unsigned CRL template in the format supported by the TP.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID/value pairs specified in the CrlFields input parameter.
- CrlFields (input)
Any array of field OID/value pairs containing the values to initialize the CRL attribute fields
- NewCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the new CRL. The NewCrl->Data is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_TPCL_CrlSignWithKey()
TP_CrlSignWithCert()
TP_CertRevoke
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRevoke (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult, CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason, CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
The TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can revoke the subject certificate group. The revoker certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established, the TP revokes the subject certificate by adding it to the certificate revocation list.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider module used to perform this function.
- OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing an existing certificate revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list is created or the operation fails.
- CertGroupToBeRevoked (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be revoked by this operation.
- RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the revoker. The use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
- RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in verifying certificates and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional elements in the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module vendor release documents. This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
- RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- Reason (input/optional)
The reason for revoking the subject certificate.
- NewCrlTemplate (outputl)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the updated certificate revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error has occurred.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert()
TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult, CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
The TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can remove the subject certificate group from the CRL template. The revoker certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established, the TP removes the certificates from the CRL template.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in cryptographic service provider module used to perform this function.
- OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing an existing certificate revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list is created or the operation fails.
- CertGroupToBeRemoved (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be removed from the the CRL template.
- RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the revoker. The use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
- RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in verifying certificates and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional elements in the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module vendor release documents. This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
- RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- NewCrlTemplate (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the updated certificate revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error has occurred.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert()
TP_CrlSign
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlSign (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle, const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeSigned, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult, CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl)
The TP module decides whether the signer certificate is trusted to sign the entire certificate revocation list. The signer certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established, this operation signs the entire certificate revocation list. Individual records within the certificate revocation list were signed when they were added to the list. The caller must provide a credential that permits the caller to use the private key for this signing operation. The credential can be provided in the cryptographic context CCHandle. If CCHandle is NULL, the credentials in the SignerVerifyContext specify the credential value.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context for signing the CRL. This context also identifies the cryptographic service provider to be used to perform the signing operation. If this handle is not provided by the caller, the trust policy module can assume a default signing algorithm and a default CSP. If the trust policy module does not assume defaults or the default CSP is not available on the local system an error occurs.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the signer for this operation. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the signer. Use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
- SignerVerifyContext (input/output)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- SignerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
- SignedCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing the signed CRL. The SignedCrl->Data is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlSign()
TP_ApplyCrlToDb
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ApplyCrlToDb (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup, const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext, CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult)
This function first determines whether the memory-resident CRL is trusted. The CRL is authenticated, its signer is verified, and its authority to update the data sources is determined. If trust is established, this function updates persistent storage to reflect entries in the certificate revocation list. This results in designating persistent certificates as revoked.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module that can be used to manipulate the CRL as it is applied to the data store and to manipulate the certificates effected by the CRL, if required. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required. If optional, the caller will set this value to 0.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service Provider to be used to verify signatures on the CRL determining whether to trust the CRL and apply it to the data store. The TP module is responsible for creating the cryptographic context structures required to perform the verification operation. If no CSP is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CSP to perform these operations. If optional, the caller will set this value to 0.
- CrlToBeApplied (input)
A pointer to a structure containing the encoded certificate revocation list to be applied to the data store. The CRL type and encoding are included in this structure.
- SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially or fully represent the signer of the certificate revocation list. The first certificate in the group is the target certificate representing the signer. Use of subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
- ApplyCrlVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information, and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
- ApplyCrlVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing a information generated during the verification process. The information can include:
- Evidence
- (output/optional)
- NumberOfEvidences
- (output/optional)
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstItem()
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextItem()
CSSM_DL_CertRevoke()
TP_CertGroupConstruct
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupConstruct (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle, const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList, const void *ConstructParams, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag, CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
This function builds a collection of certificates that together make up a meaningful credential for a given trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust domain, a certificate group is a chain of certificates from an end entity to a top level certification authority. The constructed certificate group format (such as ordering) is implementation specific. However, the subject or end-entity is always the first certificate in the group.A partially constructed certificate group is specified in CertGroupFrag. The first certificate is interpreted to be the subject or end-entity certificate. Subsequent certificates in the CertGroupFrag structure may be used during the construction of a certificate group in conjunction with certificates found in the data stores specified in DBList. The trust policy defines the certificates that will be included in the resulting set.
The output set is a sequence of certificates ordered by the relationship among them. The result set can be augmented by adding semantically-related certificates obtained by searching the certificate data stores specified in DBList. The data stores are searched in order of appearance in DBList. If the TP supports a hierarchical model of certificates, the function output is an uninterrupted, ordered chain of certificates based on the first certificate as the leaf of the certificate chain. If the certificate is multiply-signed, then the ordered chain will follow the first signing certificate. The function should also detect cross-certificate pairs and should include both certificates without duplicating either certificate.
Extraneous certificates in the CertGroupFrag fragment or contained in the DBList data stores are ignored. The certificate group returned by this function can be used as input to the function
TP_CertGroupVerify() .The constructed certificate group can be consistent locally or globally. Consistency can be limited to the local system if locally-defined points of trust are inserted into the group.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CSPHandle (input/optional)
A handle specifying the Cryptographic Service Provider to be used to verify certificates as the certificate group is constructed. If the a CSP handle is not specified, the trust policy module can assume a default CSP. If the module cannot assume a default, or the default CSP is not available on the local system, an error occurs.
- DBList(input)
A list of certificate databases containing certificates that may be used to construct the trust structure of the subject certificate group.
- ConstructParams (input/optional)
A pointer to data that can be used by the add-in trust policy module in constructing the CertGroup.Thesemanticsofthisparameteraredefinedby the trust policy and the credential model supported by that policy. The input parameter can consist of a set of values, each guiding some aspect of the construction process. Parameter values can:
- Limit the certificates that are added to the constructed set.
- Identify other sources of certificates for inclusion in the constructed set.
- CertGroupFrag (input)
The first certificate in the group represents the target certificate for which a group of semantically related certificates will be assembled. Subsequent intermediate certificates can be supplied by the caller. They need not be in any particular order.
- CertGroup (output)
A pointer to a complete certificate group based on the original subset of certificates and the certificate data stores. The CSSM_CERTGROUP and its sub-structures are allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertGroupPrune()
TP_CertVerify()
TP_CertGroupPrune
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupPrune (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup, CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup)
This function removes any locally issued anchor certificates from a constructed certificate group. The resulting certificate group can be exported to external entities.
- TPHandle input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- DBList (input)
A list of certificate databases containing certificates that contain anchor certificates restricted to have local scope. These certificates are candidates for removal from the subject certificate group.
- OrderedCertGroup (input)
A group of semantically related certificates (for example, the result ofTP_CertGroupConstruct() ).
- PrunedCertGroup (output)
A pointer to a certificate group containing those certificates which are verifiable credentials outside of the local system. The CSSM_CERTGROUP and its sub-structures are allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
TP_CertGroupConstruct()
TP_CertVerify()
TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup, CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup)
This function creates a set of authorization tuples based on a set of input certificates. The certificates must be of the type managed by the Trust Policy module. The trust policy module may require that the input certificates be successfully verified before being translated to tuples. It is assumed that the certificates carry authorizations. The trust policy service provider interprets the certificate authorization fields and generates one or more tuples corresponding to those authorizations. The certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy module.The resulting tuples can be input to an authorization evaluation function, such as
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute() , which determines whether a particular action is authorized under a basic set of authorization assumptions.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library module that can be used to scan the certificate fields for values. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module.
- CertGroup (input)
A group of certificates in the native certificate format supported by the Trust Policy module. The certificates carry authorizations for one or more certificate subjects.
- TupleGroup (output)
A pointer to a sub-structure containing references to one or more tuples resulting from the translation process. Storage for the structure and the tuples is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup()
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute()
TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup, CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates)
This function creates a set of certificate templates based on a set of input tuples. The tuples describe a set of authorizations for one or more subjects. The trust policy service provider maps these authorizations to appropriate template values for one or more certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy module. The resulting certificate templates can be input to a certificate creation function, such asCSSM_CL_CertSign() . The signed certificates created by these functions should carry the authorizations described in the input tuples.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library module that can be used to assist in the creation of field values. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
- TupleGroup (input)
A pointer to a group of CSSM_TUPLE describing authorizations for one or more subjects.
- CertTemplates (output)
A pointer to a structure containing references to one or more certificate templates resulting from the translation process. Storage for the structure and certificate templates is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup()
CSSM_AC_AuthCompute()
TP_PassThrough
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_PassThrough (CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle, CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle, CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle, const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList, uint32 PassThroughId, const void *InputParams, void **OutputParams)
This function allows clients to call Trust Policy module-specific operations that have been exported. Such operations may include queries or services specific to the domain represented by the TP module.
- TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy module used to perform this function.
- CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate library module used to perform this function.
- CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of the cryptographic operation. If the module-specific operation does not perform any cryptographic operations, a cryptographic context is not required
- DBList (input/optional)
A list of certificate databases containing certificates that may be used by the pass through operation.
- PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by the TP module to indicate the exported function to perform.
- InputParams (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner by the TP module.
- OutputParams (output/optional)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing the output data. The service provider allocates the memory for the structure and sub-structures. The application must free the memory for the structure and sub-structures.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
See the corresponding function call definition in Part 2 of this document.
| Contents | Next section | Index |