Previous section.
Common Security: CDSA and CSSM
Copyright © 1997 The Open Group
Goals and General Approach
The basic goal is to enhance CDSA with transparent support for
system-wide, policy-based control of security services in a flexible
and extensible manner. This means CSSM cannot hard-wire policy-specific
mechanisms into the framework.
Even in the case of stable, long term policies, policy definition,
interpretation, and enforcement can require complex procedures. In
response, new mechanisms are continually under development to address
these complex policy requirements.
Goals
The goals for an enhanced CDSA include:
-
Support for a broad range of system-wide policies on the use of security
services-different organizations will define distinctly different policies.
-
Support for a broad range of mechanisms to evaluate and enforce
system-wide policies-complex policy definitions can require more
complex evaluation mechanisms to determine compliance. New mechanisms
are continually under development and CSSM must be able to incorporate
these new mechanisms.
-
Create an interoperable business market for competing products for
policy compliance mechanisms-if a sufficient number of new
mechanisms are designed, a product market could emerge for these
products. CSSM must be able to incorporate those products.
-
Support changing policies-even stable, long term policy definitions
evolve over time and are subject to reinterpretation.
Requirements
These CDSA goals generate requirements for enhanced CSSM mechanisms to
perform the following services:
-
Verify that each security service request is authorized according to
the system-wide policy (this can include dependencies among CSSM add-in
module service providers).
-
Verify the correct (permitted) operation of a security service
module (if required).
-
Ensure that it is reasonably difficult to remove or alter the CSSM
policy evaluation and enforcement mechanisms.
-
Ensure that it is reasonably difficult to modify or delete the
system-wide policy definition.
-
Delay binding the system-wide policy to the runtime environment.
-
Override/change an active policy.
-
Support multiple, concurrently-active policies.
-
Support a hierarchical or weighted relationship among
concurrently-active policies.
-
Provide plug-able policy mechanisms.
-
Use a trusted component to determine trusted policy compliance.
Specifying a System-Wide Policy
Policies are stated as a set of restrictions on the use of security
services. The restrictions are defined in terms of the attributes of
the service being restricted. The primary attribute categories for
security services are as follows:
-
Service Representation-what is being restricted with respect to the
service, its implementation, technical knowledge about it, or technical
assistance with it
-
Restriction Type-does the restriction apply to individual use of the
service or to general availability
-
Service User-is the service being requested by a special application
(for example, system software performing authentication to make the
platform more secure)
-
Service Features-is the service generally available, but selected
features of the service are restricted
-
Service Strength-is the service weak or strong (for example, is the
cryptographic cipher 56-bits or less; is the certificate management
service capable of Certification Authority operations).
Corporations distinguish service representations in product licensing
and the United States government has detailed definitions of the
representation of cryptography. In a broad definition, an
implementation is hardware or software that provides the security
operation. Technical knowledge is the schematics or source code for the
implementation, and technical assistance is the personal assistance
given to another so that person can create an implementation. These do
not constitute legal definitions but serve as a
guideline to understanding these differences.
Various government entities may consider a cryptographic framework,
such as CSSM, to be an implementation of cryptographic services. This
may make CSSM subject to the same restrictions as a general purpose
cryptographic library. CSSM is best described as "crypto with a hole";
software that provides a common, programmable interface for
cryptographic operations where cryptography is added at a later time.
While CSSM does not actually implement cryptographic operations, the
enhanced CSSM mechanisms for system-wide policy control of security
services may facilitate in complying with these government-defined
policies.
Policies governing the use of security services can be defined in terms
of any combination of the five aspects listed earlier. Every
installation can run distinct system-wide policies. Clearly the
CSSM-provided policy compliance mechanism(s) must be flexible,
configurable, and relatively trustworthy.
Assumptions and Architectural Approach
The enhanced CDSA design assumes:
-
Existence of a manufacturing infrastructure for components of CDSA
(including elective module managers, add-in security service modules,
layered application services, and applications)
-
Add-in modules can declare the security services they can and will
provide under specified conditions
-
CSSM can evaluate and enforce policies without defining policies
-
Complex policies require more complex mechanisms of evaluation and
enforcement
Three policy enforcement mechanisms consistent with CDSA are shown in
Enhanced Common Data Security Architecture
.
These mechanisms include:
-
Authentication checks on attaching add-in service modules and elective
module managers
-
Screened access to security service modules based on a system-wide
policy (if specified)
-
Use of existing CSSM extensibility mechanisms to add complex policy
checks or services that enable the caller to be compliant with the
policy
CSSM is uniquely positioned architecturally to provide these services, as it:
-
Dynamically attaches add-in security service modules upon application
request
-
Manages the dispatching of application function calls for security
services to appropriate add-in modules
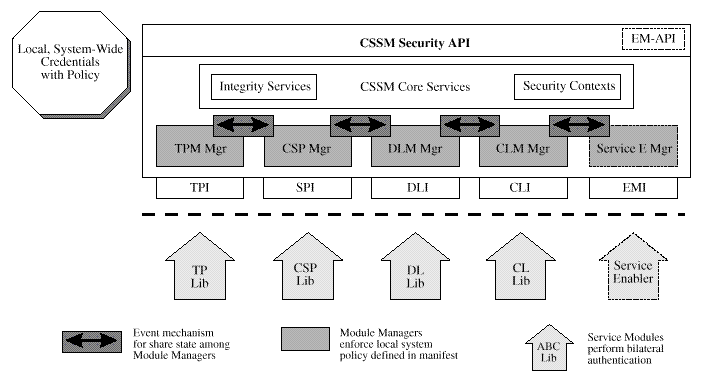 Figure: Enhanced Common Data Security Architecture
Figure: Enhanced Common Data Security Architecture
Why not acquire a nicely bound hard copy?
Click here to return to the publication details or order a copy
of this publication.
You should also read the
legal notice explaining the terms and conditions relating to
the CDSA documentation.

