Previous section.
Universal Measurement Architecture Guide
Copyright © 1997 The Open Group
Overview of UMA Architecture
The UMA reference model defines four layers and two interfaces as shown in
UMA Reference Model
.
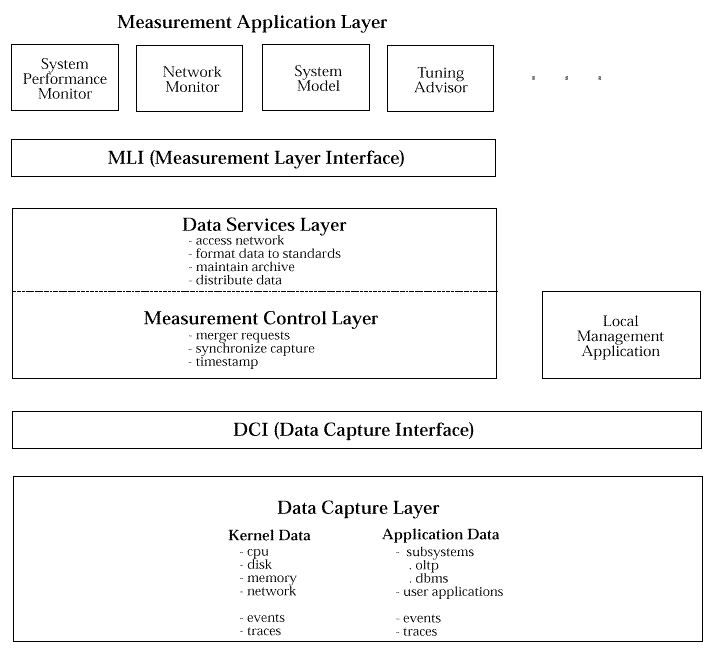
Figure: UMA Reference Model
In this Chapter,
these layers and interfaces are briefly described from the bottom up, that is,
starting from the Data Capture Layer.
Data Capture Layer
The Data Capture Layer is responsible for collecting raw data. Its architecture together
with the Data Capture Interface (DCI) allow data from multiple sources
to be obtained by
a single consumer above the DCI, and this in turn improves the synchronisation of the data
collection.
Data Capture Interface
The Data Capture Interface is the interface between the Measurement Control Layer and
the Data Capture Layer. It provides the means for dynamically extending data collection
to new providers such as databases without affecting existing programs.
Measurement Control Layer
The Measurement Control Layer schedules and synchronises data collection through the
Data Capture Interface.
Data Services Layer
The Data Services Layer accepts measurement requests from Measurement Application
Programs (MAPs) through the Measurement Layer Interface, and distributes data to the
destination requested by the MAP. A destination may include, the MAP itself, a
private
file or the UMA Data Storage (UMADS), which will be described later.
A feature of UMA is that the interface between the Data Services Layer and the Measurement Control
Layer is not formally specified. These two layers, though functionally distinct, and which
constitute a logical service layer for the MLI, may be combined in some implementations.
Local Measurement Application
Where the facilities provided by the Measurement Control Layer and
the Data Services Layer are not required, Local Measurement Applications
can be provided which use the DCI directly. Such an application could
also function as an agent for distributing performance data outside the
scope of the UMA.
Measurement Layer Interface
The Measurement Layer Interface (MLI) is the interface between the Measurement
Application Layer and the Data Services Layer. It provides the medium for all
interactions between a MAP and UMA, thus isolating the application for the
implementation details of the rest of UMA.
The Measurement Layer Interface allows transparent communication across networks,
therefore a MAP running on one system can request and examine data from another
system. Together with the Data Services Layer, it provides an infrastructure for the
distribution of data over large numbers of heterogeneous sites and multiple platforms.
Measurement Application Layer
The Measurement Application Layer consists of the various Measurement Application
Programs (MAPs) that provide services for technical support of management goals.
These MAPs may consist of performance monitors, capacity planning tools, tuning
advisors, and so on.
Why not acquire a nicely bound hard copy?
Click here to return to the publication details or order a copy
of this publication.

