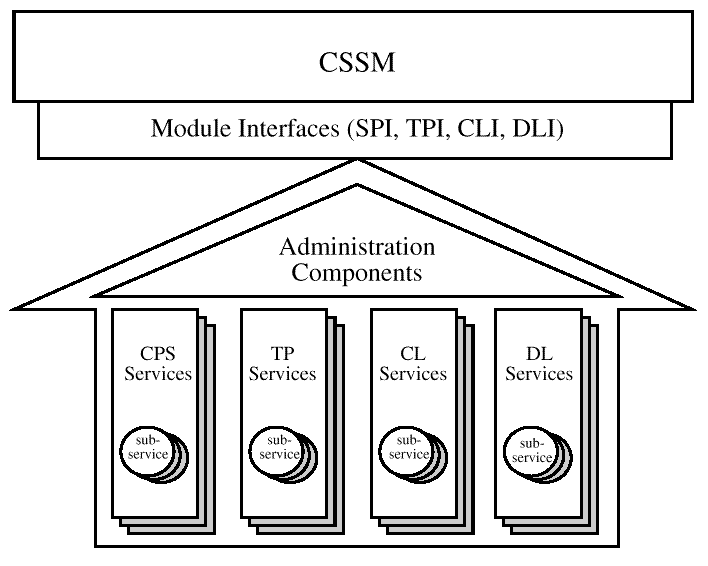

A CDSA add-in module is a dynamically-linkable library, composed of functions that implement some or all of the CSSM Module Interfaces. Add-in module functionality is partitioned into two areas:
Add-in modules provide one or more categories of security services to applications. The service categories are Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) services, Key Recovery Service Provider (KRSP) services, Trust Policy (TP) services, Certificate Library (CL) services, and Data Storage Library (DL) services. Each security service contains one or more implementation instances, called sub-services. For a CSP service providing access to hardware tokens, a sub-service would represent a slot. For a DL service provider, a sub-service would represent a type of persistent storage. These sub-services each support the module interface for their respective service categories. This documentation-part describes the module interface functions in the KRSP service category. More information about CSP services can be found in the CSSM Cryptographic Service Provider Interface Specification. More information about DL services can be found in the CSSM Data Storage Library Interface Specification. More information about TP services can be found in the CSSM Trust Policy Interface Specification. More information about CL services can be found in the CSSM Certificate Library Interface Specification.
Each module, regardless of the security services it offers, has the same set of administrative responsibilities. Every module must expose functions which allow CSSM to indicate events such as module attach and detach. In addition, as part of the attach operation, every module must be able to verify its own integrity, verify the integrity of CSSM, and register with CSSM. Detailed information about add-in module structure, administration, and interfaces can be found in the CSSM Add-in Module Structure and Administration Specification.
There can also be hybrid schemes that use escrow mechanisms in addition to encapsulation mechanisms.
An orthogonal way to classify key recovery mechanisms is based on the nature of the key:
Both types can be escrowed or encapsulated. Since escrow schemes involve the actual archival of keys, they typically deal with long-term keys, in order to avoid the proliferation problem that arises when trying to archive the myriad ephemeral keys. Key encapsulation techniques, on the other hand, usually operate on the ephemeral keys.
For a large class of key recovery (escrow as well as encapsulation) schemes, there are a set of key recovery fields that accompany an enciphered message or file. These key recovery fields may be used by the appropriate authorized parties to recover the decryption key and or the plaintext. Typically, the key recovery fields comprise information regarding the key escrow or recovery agent(s) that can perform the recovery operation; they also contain other pieces of information to enable recovery.
In a key escrow scheme for long-term private keys, the "escrowed" keys are used to recover the ephemeral data confidentiality keys. In such a scheme, the key recovery fields may comprise the identity of the escrow agent(s), identifying information for the escrowed key, and the bulk encryption key wrapped in the recipient's public key (which is part of an escrowed key pair); thus the key recovery fields include the key exchange block in this case. In a key escrow scheme where bulk encryption keys are archived, the key recovery fields may comprise information to identify the escrow agent(s), and the escrowed key for that enciphered message.
In a typical key encapsulation scheme for ephemeral bulk encryption keys, the key recovery fields are distinct from the key exchange block, (if any.) The key recovery fields identify the recovery agent(s), and contain the bulk encryption key encapsulated using the public keys of the recovery agent(s).
The key recovery fields are generated by the party performing the data encryption, and associated with the enciphered data. To ensure the integrity of the key recovery fields, and its association with the encrypted data, it may be required for processing by the party performing the data decryption. The processing mechanism ensures that successful data decryption cannot occur unless the integrity of the key recovery fields are maintained at the receiving end. In schemes where the key recovery fields contain the key exchange block, decryption cannot occur at the receiving end unless the key recovery fields are processed to obtain the decryption key; thus the integrity of the key recovery fields are automatically verified. In schemes where the key recovery fields are separate from the key exchange block, additional processing must be done to ensure that decryption of the ciphertext occurs only after the integrity of the key recovery fields are verified.
In both cases, since it is a not meaningful to archive key recovery fields without archiving the associated ciphertext, the lifetimes of key recovery fields should never be greater than the lifetime of the associated ciphertext.
It is important to note that the lifetime of key recovery fields should
never be greater than the lifetime of the associated ciphertext. This
is somewhat obvious, since recovery of the key is only meaningful if
the key can be used to recover the plaintext from the ciphertext.
Hence, when archived-ciphertext products are key recovery enabled, the
key recovery fields are typically archived as long as the ciphertext.
Similarly, when transient-ciphertext products are key
recovery enabled,
the key recovery fields are associated with the ciphertext for the
duration of its lifetime. It is not meaningful to archive key recovery
fields without archiving the associated ciphertext.
Key recovery policies come in two flavors: key recovery enablement policies and key recovery inter-operability policies. Key recovery enablement policies specify the exact cryptographic protocol suites (algorithms, modes, key lengths and so on) and perhaps usage scenarios, where key recovery enablement is mandated. Furthermore, these policies may also define the number of bits of the cryptographic key that may be left out of the key recovery enablement operation; this is typically referred to as the workfactor. Key recovery inter-operability policies specify to what degree a key-recovery-enabled cryptographic product is allowed to interoperate with other cryptographic products.
Enterprise key recovery allows enterprises to enforce stricter monitoring of the use of cryptography, and the recovery of enciphered data when the need arises. The user in this scenario is the enterprise employee. Enterprise key recovery is based on a mandatory key recovery policy; however, this policy is set (typically through administrative means) by the organization or enterprise at the time of installation of a recovery-enabled cryptographic product. The enterprise key recovery policy should not be modifiable or by-passable by the individual using the cryptographic product. Enterprise key recovery mechanisms may use special, enterprise-authorized escrow or recovery agents.
In the law enforcement scenario, key recovery is mandated by the jurisdictional law enforcement authorities in the interest of national security and law enforcement. The user in this scenario is the private citizen in the jurisdiction where the product is being used. For a specific cryptographic product, the key recovery policies for multiple jurisdictions may apply simultaneously. The policies (if any) of the jurisdiction(s) of manufacture of the product, as well as the jurisdiction of installation and use, need to be applied to the product such that the most restrictive combination of the multiple policies is used. Thus, law enforcement key recovery is based on mandatory key recovery policies; these policies are logically bound to the cryptographic product at the time the product is shipped. There may be some mechanism for vendor-controlled updates of such law enforcement key recovery policies in existing products; however, organizations and end users of the product are not able to modify this policy at their discretion. The escrow or recovery agents used for this scenario of key recovery need to be strictly controlled in most cases, to ensure that these agents meet the eligibility criteria for the relevant political jurisdiction where the product is being used.
Individual key recovery is user-discretionary in nature, and is performed for the purpose of recovery of enciphered data by the owner of the data, if the cryptographic keys are lost or corrupted. The user in this scenario is the traditional "end-user" of the software product. Since this is a non-mandatory key recovery scenario, it is not based on any policy that is enforced by the cryptographic product; rather, the product may allow the user to specify when individual key recovery enablement is to be performed. There are few restrictions on the use of specific escrow or recovery agents.
Key recovery enabled cryptographic products must be designed so that the key recovery enablement operation is mandatory and noncircumventable in the law enforcement and enterprise scenarios, and discretionary for the individual scenario. The escrow and recovery agent(s) that are used for law enforcement and enterprise scenarios must be tightly controlled so that the agents are validated to belong to a set of authorized or approved agents. In the law enforcement and enterprise scenarios, the key recovery process typically needs to be performed without the knowledge and cooperation of the parties involved in the cryptographic association.
The components of the key recovery fields also varies somewhat between the three scenarios. In the law enforcement scenario, the key recovery fields must contain identification information for the escrow or recovery agent(s); whereas for the enterprise and individual scenarios, the agent identification information is not so critical, since this information may be available from the context of the recovery enablement operation. For the individual scenario, there needs to be a strong user authentication component in the key recovery fields, to allow the owner of the key recovery fields to authenticate themselves to the agents; however, for the enterprise and law enforcement scenarios, the authorization credentials checked by the agents may be in the form of legal documents, or enterprise-authorization documents for key recovery, that may not be tied to any authentication component in the key recovery fields. For the law enforcement and enterprise scenarios, the key recovery fields may contain recovery information for both the generator and receiver of the enciphered data; in the individual scenario, only the information of the generator of the enciphered data is typically included (at the discretion of the generating party.)
CSSM acts as a broker between applications requesting security services and dynamically loadable security service modules. The CSSM application programming interface (CSSM-API) defines the interface for accessing security services. The CSSM service provider interface (CSSM-SPI) defines the interface for service providers who develop plug-able security service products.
CSSM is extensible in that it also provides dynamic loading of module managers that provide elective categories of security services. Key recovery is an important security service for applications and institutions that choose to use it. CSSM accommodates key recovery as an elective category of security service.
A complete architectural description of CDSA and CSSM is contained in the Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) Specification.
| Contents | Next section | Index |