Previous section.
Common Security: CDSA and CSSM
Copyright © 1997 The Open Group
Key Recovery Service Provider Interface
Overview
A CDSA add-in module is a dynamically-linkable library, composed of
functions that implement some or all of the CSSM Module Interfaces.
Add-in module functionality is partitioned into two areas:
-
The provision of security services to applications
-
Module administration
Add-in modules provide one or more categories of security services to
applications. The service categories are Cryptographic Service
Provider (CSP) services, Trust Policy (TP) services, Certificate
Library (CL) services, and Data Storage Library (DL) services. Each
security service contains one or more implementation instances, called
sub-services. For a CSP service providing access to hardware tokens, a
sub-service would represent a slot. For a CL service provider, a
sub-service would represent a specific certificate format. These
sub-services each support the module interface for their respective
service categories. This documentation-part describes the module
interface functions in the KR service category.
Each module, regardless of the security services it offers, has the
same set of administrative responsibilities. Every module must expose
functions which allow CSSM to indicate events such as module attach and
detach. In addition, as part of the attach operation, every module
must be able to verify its own integrity, verify the integrity of CSSM,
and register with CSSM. Detailed information about add-in module
structure, administration, and interfaces can be found in the CSSM Add-in Module Structure and Administration Specification.
Key Recovery Phases
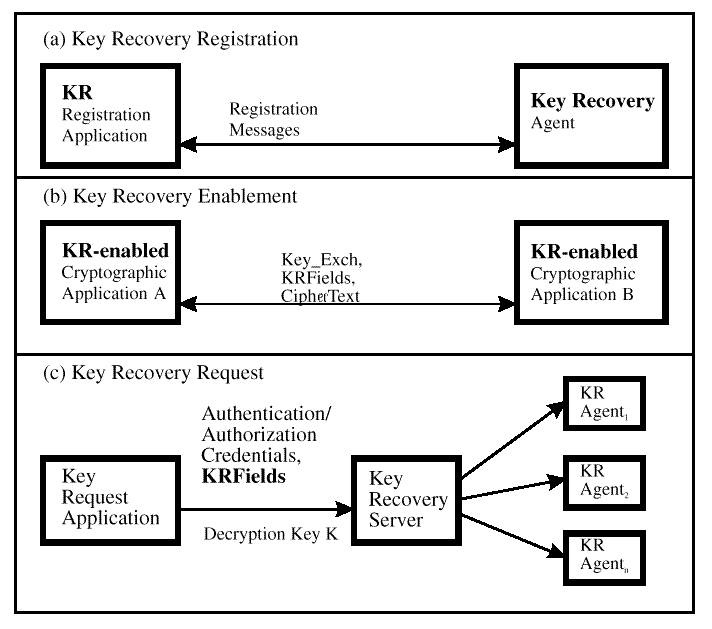 Figure: Key Recovery Phases
Figure: Key Recovery Phases
The process of cryptographic key recovery involves three major phases.
First, there is an optional key recovery registration phase where
the parties that desire key recovery perform some initialization
operations with the escrow or recovery agents; these operations include
obtaining a user public key certificate (for an escrowed key pair)
from an escrow agent, or obtaining a public key certificate from a
recovery agent . Next, parties that are involved in cryptographic
associations have to perform operations to enable key recovery (such as
the generation of key recovery fields, and so on)-this is typically
called the key recovery enablement phase. Finally, authorized
parties that desire to recover the data keys, do so with the help of a
recovery server and one or more escrow agents or recovery
agents-this is the key recovery request phase.
Key Recovery Phases
illustrates the three phases of key recovery. In
Key Recovery Phases
(a),
a key recovery client registers with a recovery agent prior to engaging
in cryptographic communication. In
Key Recovery Phases
(b),
two key-recovery-enabled cryptographic applications are communicating
using a key encapsulation mechanism; the key recovery fields are passed
along with the ciphertext and key exchange block, to enable subsequent
key recovery. The key recovery request phase is illustrated in
Key Recovery Phases
(c),
where the key recovery fields are provided as input to the key recovery
server along with the authorization credentials of the client
requesting service. The key recovery server interacts with one or more
local or remote key recovery agents to reconstruct the secret key that
can be used to decrypt the ciphertext.
It is envisioned that governments or organizations will operate their
own recovery server hosts independently, and that key recovery servers
may support a single or multiple key recovery mechanisms. There are a
number of important issues specific to the implementation and operation
of the key recovery servers, such as vulnerability and liability. The
focus of this documentation-part is a framework based approach to
implementing the key recovery operations pertinent to end parties that
use encryption for data confidentiality. The issues with respect to the
key recovery server and agents will not be discussed further here.
Key Recovery Registration Operations
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RegistrationRequest()
Performs a recovery registration request operation. A callback may be
supplied to allow the registration operation to query for additional
input information, if necessary. The result of the registration request
operation is a reference handle that may be used to invoke the
KRSP_RegistrationRetrieve function.
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RegistrationRetrieve()
Completes a recovery registration operation. The result of the
registration operation is returned in the form of a key recovery
profile.
Key Recovery Enablement Operations
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_GenerateRecoveryFields()
Accepts as input the key recovery context handle, the session based
recovery parameters and the cryptographic context handle, and several
other parameters of relevance to the KRSP, and outputs a buffer of the
appropriate mechanism-specific key recovery fields in a format defined
and interpreted by the specific KRSP involved. It returns a
cryptographic context handle, which now be used for the encryption APIs
in the cryptographic framework.
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_ProcessRecoveryFields()
Accepts as input the key recovery context handle, the cryptographic
context handle, several other parameters of relevance to a KRSP, and
the unparsed buffer of key recovery fields. It returns with a
cryptographic context handle which can then be used for the decryption
APIs in the cryptographic framework.
Key Recovery Request Operations
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRequest()
Performs a recovery request operation for one or more recoverable
keys. A callback may be supplied to allow the recovery request
operation to query for additional input information, if necessary. The
result of the recovery request operation is a results handle that may
be used to obtain each recovered key and its associated meta
information using the KRSP_GetRecoveredObject function.
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRetrieve()
Completes a recovery request operation for one or more recoverable
keys. The result of the recovery operation is a results handle that
may be used to obtain each recovered key and its meta information using
the KRSP_GetRecoveredObject function.
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_GetRecoveredObject()
Retrieves a single recovered key and its associated meta information.
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_RecoveryRequestAbort()
Terminates a recovery request operation and releases any state
information associated with it
Privileged Context Functions
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_PassPrivFunc()
Returns a private CSSM callback function that the service provider can
use to exempt itself from recursive screening by its own key recovery
policy.
Extensibility Functions
- CSSM_RETURN CSSMKRSPI KRSP_PassThrough()
Accepts as input an operation ID and an arbitrary set of input
parameters. The operation ID may specify any type of operation the KR
wishes to export. Such operations may include queries or services
specific to the key recovery mechanism implemented by the KR module.
Data Structures
CSSM_KR_HANDLE
This data structure represents the key recovery module handle. The
handle value is a unique pairing between a key recovery module and an
application that has attached that module. KR handles can be returned
to an application as a result of the CSSM_ModuleAttach function.
typedef uint32 CSSM_KRSP_HANDLE
/* Key Recovery Service Provider Handle */
CSSM_KR_NAME
This data structure contains a typed name. The namespace type specifies
what kind of name is contained in the third parameter.
typedef struct cssm_kr_name {
uint8 type; /* namespace type */
uint8 length; /* name string length */
char *name; /* name string */
} CSSM_KR_NAME
Definition
- type
The type of the key recovery name space.
- length
The length of the name (in bytes).
- name
The name represented in a string.
CSSM_KR_PROFILE
This data structure encapsulates the key recovery profile for a given
user and a given key recovery mechanism.
typedef struct cssm_kr_profile {
CSSM_KR_NAME UserName; /* name of the user */
CSSM_DATA_PTR UserCertificate /* public key certificate of
the user */
uint8 LE_KRANum; /* number of KRA cert chains in the
following list */
CSSM_CERT_LIST_PTR LE_KRACertChainList; /* list of Law
enforcement KRA certificate chains*/
uint8 ENT_KRANum; /* number of KRA cert chains in the
following list */
CSSM_CERT_LIST_PTR ENT_KRACertChainList; /* list of
Enterprise KRA certificate chains*/
CSSM_DATA_PTR ENTAuthenticationInfo; /* authentication
information for enterprise key recovery */
uint8 INDIV_KRANum; /* number of KRA cert chains in the
following list */
CSSM_CERT_LIST_PTR INDIV_KRACertChainList; /* list of
Individual KRA certificate chains*/
CSSM_DATA_PTR INDIVAuthenticationInfo; /* authentication
information for individual key recovery */
uint32 KRFlags; /* flag values to be interpreted by KRSP */
CSSM_DATA_PTR Extensions; /* reserved for extensions
specific to KRSPs */
} CSSM_KR_PROFILE, *CSSM_KR_PROFILE_PTR;
Definition
- UserName
The user's name.
- UserCertificate
The user's certificate chain, used for identity and
authentication when performing policy evaluation.
- LE_KRANum
The number of LE Key Recovery agents in the following list.
- LE_KRACertChainList
A list of certificates chains one per Key Recovery Agent
authorized for LE key recovery.
- ENT_KRANum
The number of ENT Key Recovery agents in the following list.
- ENT_KRACertChainList
A list of certificates chains one per Key Recovery Agent
authorized for ENT key recovery.
- ENTAuthenticationInfo
Authentication information to be used for ENT key recovery.
- INDIV_KRANum
The number of INDIV Key Recovery agents in the following list.
- INDIV_KRACertChainList
A list of certificates chains one per Key Recovery Agent
authorized for INDIV key recovery.
- INDIVAuthenticationInfo
Authentication information to be used for INDIV key recovery.
- KRFlags
A bit mask specifying the user's selected service options specific to the
selected key recovery service module.
- Extensions
Reserved for future use.
CSSM_CERT_LIST
This data structure encapsulates a generic list of items.
typedef struct cssm_cert_list {
uint32 NumberCerts;
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertList;
} CSSM_CERT_LIST, *CSSM_CERT_LIST_PTR;
Definition
- NumberCerts
Count of the number of certs in the list.
- CertList
Pointer to a list of certificate items.
CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE Extensions
The key recovery context creation operations return key recovery
context handles that are represented as cryptographic context handles.
In order to use to the CSSM_CONTEXT data structure to implement key
recovery contexts, the CSSM_CONTEXT will be used to hold new types of
attributes, as shown below:
typedef struct cssm_context_attribute {
uint32 AttributeType;
uint32 AttributeLength;
union cssm_context_attribute_value {
char *String;
uint32 Uint32;
CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA_PTR Crypto;
CSSM_KEY_PTR Key;
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data;
CSSM_DATE_PTR Date;
CSSM_RANGE_PTR Range;
CSSM_KR_PROFILE_PTR KRProfile;
} Attribute;
} CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, *CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE_PTR;
All but the last member of the union above are part of the core CSSM
API Specification. The descriptions of these basic fields and members
are in the CSSM Application Programming Interface. The KRProfile member of the union
has been added specifically to support key recovery contexts, and is
described below.
Definition
- KRProfile
A pointer to the key recovery profile structure that defines the user
parameters with respect to the key recovery process.
CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_TYPE Additions
Several new attribute types were defined to support the key recovery
context attributes. The following definitions are added to the
enumerated type CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_TYPE:
CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_KRPROFILE_LOCAL = CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_LAST+1,
/* local entity profile */
CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_KRPROFILE_REMOTE = CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_LAST+2,
/* remote entity profile */
CSSM_KRSUBSERVICE
Two structures are used to contain all of the static information that
describes a key recovery add-in module: the krinfo structure and the
krsubservice structure. This descriptive information is securely stored
in the CSSM registry when the KR module is installed with CSSM. A key
recovery module may implement multiple types of services and organize
them as sub-services. For example, a KR module supporting two an
encapsulation mechanism and an escrow mechanism may organize its
implementation as two subservices.
The descriptive information stored in these structures can be queried
using the function CSSM_GetModuleInfo() and specifying the key
recovery module GUID.
typedef struct cssm_krsubservice {
uint32 SubServiceId;
char *Description; /* Description of this sub service */
CSSM_CALLER_AUTHENTICATION_MECHANISM AuthenticationMechanism;
} CSSM_KRSUBSERVICE, *CSSM_KRSUBSERVICE_PTR;
Definition
- SubServiceId
A unique, identifying number for the sub-service described in this
structure.
- Description
A string containing a descriptive name or title for this
sub-service.
- AuthenticationMechanism
An enumerated value defining the credential format accepted by the KR
module. When an authentication credential is required by a KR function,
the presented credentials must be of the required format.
CSSM_KRINFO
Two structures are used to contain all of the static information that
describes a key recovery add-in module: the krinfo structure and the
krsubservice structure. This descriptive information is securely stored
in the CSSM registry when the KR module is installed with CSSM. A key
recovery module may implement multiple types of services and organize
them as sub-services. For example, a KR module supporting two an
encapsulation mechanism and an escrow mechanism may organize its
implementation as two subservices.
The descriptive information stored in these structures can be queried
using the function CSSM_GetModuleInfo() and specifying the key
recovery module GUID.
typedef struct cssm_krinfo {
CSSM_VERSION Version; /* major and minor version number */
char *Description; /* Detailed description of this KR */
char *Vendor; /* KRSP Vendor name */
char *Jurisdiction; /* Home jurisdiction of the
KRSP installation */
uint32 NumberSubService;
CSSM_KRSUBSERVICE_PTR SubService;
} CSSM_KRINFO, *CSSM_KRINFO_PTR;
Definition
- Version
The major and minor version number of the add-in module.
- Description
A character string containing a general description of this key
recovery module.
- Vendor
A character string containing the name of the vendor who implemented and
manufactured this key recovery module.
- Jurisdiction
A character string describing the geographical region where the key
recovery module is installed.
- NumberOfSubServices
The number of sub-services implemented by this key recovery
module. Every KR module implements at least one sub-service.
- Subservices
A pointer to an array of sub-service structures. Each structure
contains detailed information about that sub-service.
CSSM_PRIV_FUNC_PTR
The callback function provided by the CSSM to allow a cryptographic
context to be made privileged with respect to key recovery policy
override operations.
typedef CSSM_RETURN (*CSSM_PRIV_FUNC_PTR)
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE hContext,
CSSM_BOOL Priv);
Definition
- hContext
The context whose privilege state is to be modified.
- Priv
Flag value denoting whether the privilege should be acquired (Priv = TRUE)
or dropped (Priv = FALSE)
Key Recovery Registration Operations
The manpages for
Key Recovery Registration Operations
can be found at the end of this chapter.
Key Recovery Enablement Operations
The manpages for
Key Recovery Enablement Operations
can be found at the end of this chapter.
Key Recovery Request Operations
The manpages for
Key Recovery Request Operations
can be found at the end of this chapter.
Privileged Context Operations
The manpages for
Privileged Context Operations
can be found at the end of this chapter.
Extensibility Functions
The KRSP_PassThrough function is provided to allow KRSP developers to
extend the key recovery functionality of the CSSM API. Because it is
only exposed to CSSM as a function pointer, its name internal to the
KRSP can be assigned at the discretion of the KRSP module developer.
However, its parameter list and return value must match what is shown
below. The error codes given in this section constitute the generic
error codes which may be used by all KRSPs to describe common error
conditions. KRSP developers may also define their own module-specific
error codes, as described in the CSSM Add-in Module Structure and Administration Specification.
The manpages for
Extensibility Functions
can be found at the end of this chapter.
Why not acquire a nicely bound hard copy?
Click here to return to the publication details or order a copy
of this publication.
You should also read the
legal notice explaining the terms and conditions relating to
the CDSA documentation.

