Previous section.
Authorization (AZN) API
Copyright © 2000 The Open Group
Authorization API Usage Model
System Structure
aznAPI System Structure
illustrates the structure of a system which uses the aznAPI.
-
-
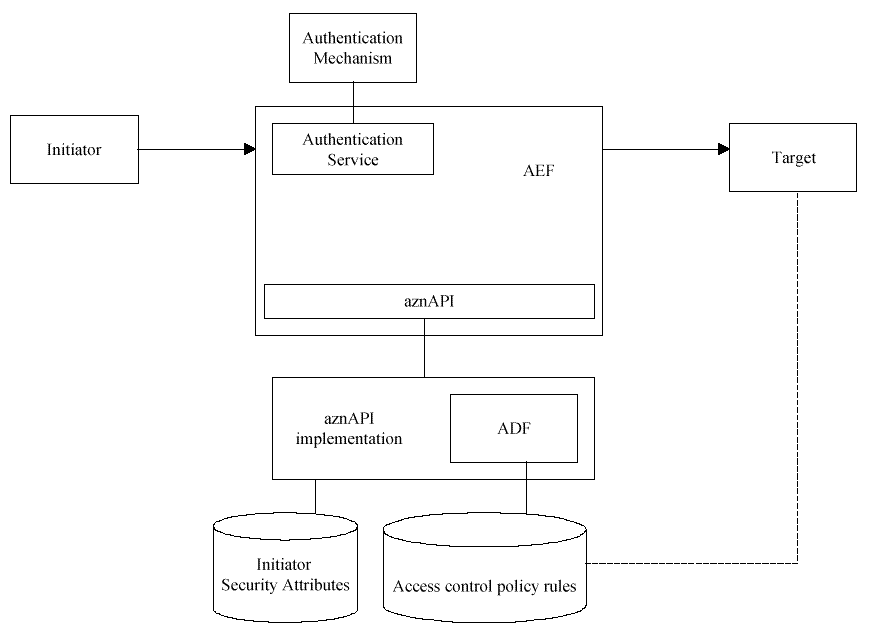
Figure: aznAPI System Structure
Resource requests in a system using
the aznAPI are mediated by Access Enforcement Functions (AEFs).
AEFs authenticate users (often using Authentication Services). They also
authorize requests by passing Access Control Information (ACI) to the
Authorization API (aznAPI). They fulfill authorized requests and
reject unauthorized requests.
The aznAPI translates ACI received from
AEFs into Access Control Decision Information (ADI). The aznAPI also
uses Access Decision Functions (ADFs) to make access decisions.
ADFs use ADI and Access Policy Rules to decide whether an initiator's
request to perform an operation on a target should be permitted or
denied.
Supported Functions
aznAPI Functions
lists the
families of functions provided by the aznAPI and briefly describes what
each family of functions does.
| Interface Family Name Prefix
| Interface Family Supported Functions
|
|---|
| azn_initialize, azn_shutdown
| Initialize aznAPI implementation
Clean up aznAPI implementation in preparation for shutdown
|
| azn_creds
| Create, delete, modify, and combine credentials chains
Get information from credentials chains
Build PAC based on credentials chain
|
| azn_id
| Build credentials chain based on authenticated identity produced by an authentication service
|
| azn_decision
| Make an access decision
|
| azn_entitlement
| Get access control policy information
|
| azn_pac
| Build credentials chain based on PAC produced by an authorization service
|
| azn_error
| Retrieve error information from status values returned by aznAPI functions
|
| azn_authority
| Discover authentication, authorization, and credentials, label, and pac mechanisms supported by aznAPI implementation
|
| azn_attrlist
| Create and delete attribute/value pair list
Write parameter data into attribute/value pair list
Read parameter data from attribute/value pair list
|
| azn_release
| Release data allocated by aznAPI implementation
|
Table: aznAPI Functions
State Machine
aznAPI State Machine Summary
summarizes the state machine of application (typically an AEF) which
calls the aznAPI. AEFs should call aznAPI functions in the sequence
indicated in
aznAPI State Machine Summary.
Note that the state machine in
aznAPI State Machine Summary
is only a summary overview and does not enumerate all the states the
caller of an aznAPI implementation can take on. Note also that, since
AEFs call authentication service functions through APIs other than
aznAPI, not every state transition in
aznAPI State Machine Summary
is caused by an aznAPI function call.
aznAPI State Machine Transitions
indicates the aznAPI function calls or other AEF operations
which cause transitions from one state to another.
-
-
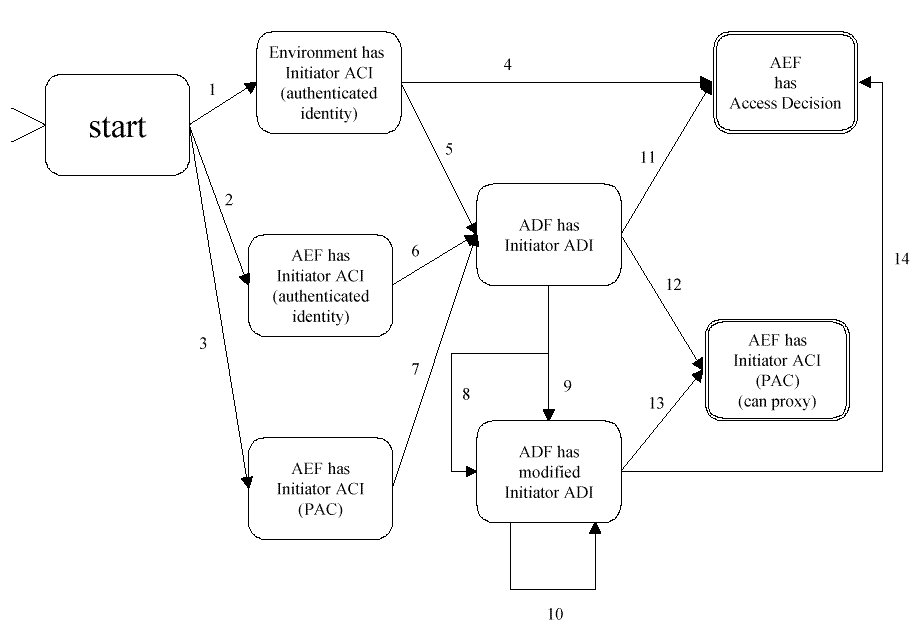
Figure: aznAPI State Machine Summary
| Transition
| Operation Causing Transition
|
|---|
| 1
| AEF gets request whose initiator has been authenticated by authentication service
|
| 2
| AEF gets request; AEF authenticates initiator
|
| 3
| AEF gets request whose initiator is described by a PAC produced by an aznAPI implementation
|
| 4
| AEF calls azn_decision_access_allowed() to authorize request (credentials chain is built implicitly by authorization service using authentication service's identity obtained from environment)
|
| 5
| AEF calls azn_id_get_creds() with null ID (authorization service uses authentication service's identity obtained from environment)
|
| 6
| AEF calls azn_id_get_creds() with ID AEF generated when it authenticated initiator
|
| 7
| AEF calls azn_pac_get_creds()
|
| 8
| AEF calls azn_creds_combine() to add its credentials chain to that of the initiator
|
| 9
| AEF calls azn_creds_modify() to change the attributes of the credentials chain
|
| 10
| AEF calls azn_creds_modify() to change the attributes of the credentials chain
|
| 11
| AEF calls azn_decision_access_allowed()
|
| 12
| AEF calls azn_creds_get_pac()
|
| 13
| AEF calls azn_creds_get_pac()
|
| 14
| AEF calls azn_decision_access_allowed()
|
Table: aznAPI State Machine Transitions
The state machine in
aznAPI State Machine Summary
is divided into three phases:
-
Credential Establishment
During this phase, represented by the leftmost
column of states after the start state, the AEF uses the aznAPI to
establish credentials chain which the authorization service will use as
the basis for later operations.
-
Credential Modification
During this
phase, represented by the second column to the right of the start
state, the AEF modifies the initiator's credentials chain, either by
changing the attributes contained in it or by combining its own
credentials chain with the initiator's.
-
Credential Use
During this
phase, represented by the rightmost column, the AEF uses the
credentials chain, either to make authorization decisions or to create
PACs which it can pass to other AEFs.
Functions Not Included in State Diagram
aznAPI State Machine Summary
Some functions of the aznAPI have
been omitted from the summary state diagram shown in
aznAPI State Machine Summary
for purposes of simplicity. The omitted functions include:
-
Housekeeping
These include
initialization
and
shutdown
of the aznAPI. Initializaion must be done
before any other aznAPI function is used. Shutdown should be done after
the last call to an aznAPI function and before the AEF exits.
-
Memory Management
These functions include creation and deletion of credentials chain and
attribute list data structures. These data structures must be created
before they can be used. Note especially that the calls which build
credentials chains (.Fn azn_id_get_creds
and
azn_pac_get_creds())
assume
that memory for the credentials chain has already been allocated via a
call to
azn_creds_create().
Memory for credentials chain and attribute
data structures is not released by the authorization service; AEFs must
release the memory by using the
azn_release
calls or
azn_credential_delete().
-
Error Information Retrieval
These calls
should be used after an error status has been returned by a call to
another aznAPI function.
-
Credential Information Retrieval
These calls
can be used any time after establishment of a credentials chain.
-
Entitlement
These calls can be used any time after establishment of a
credentials chain.
Trust Model
Each component of a secure
system needs to know which other components can be trusted, and what
they can be trusted to do. This section describes the trust
relationships among the components of a system which uses the aznAPI.
Relationship between Authentication and Authorization
The aznAPI
separates authentication from authorization, as illustrated in
Relationship between Authentication and Authorization.
-
-
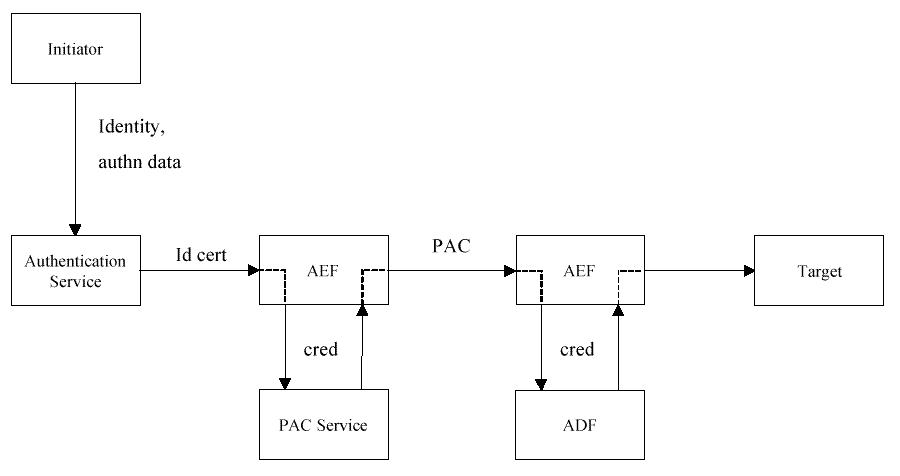
Figure: Relationship between Authentication and Authorization
The initiator may use an authentication service to create an "Identity"
which is received by an AEF along with the initiator's request to
access a target.
The AEF calls the aznAPI to transform the initiator's
identity into a credentials chain, which can be used to make access
control decisions.
The AEF may, if it needs to pass the initiator's
request on to another AEF for fulfillment, call the aznAPI to transform
the credentials chain into a PAC, which represents the authorization
service's view of the initiator (rather than the authentication
service's view, which was represented by the Identity).
Another AEF
receiving this PAC is able to transform it into a credentials
chain, which can be used to make access control decisions.
In a system using the aznAPI, therefore:
-
Authentication data is always represented by an Identity.
-
Initiator ACI, which is
authorization data about the initiator, is always represented inside
the authorization service as a credentials chain.
-
Initiator ACI, which is authorization data about the initiator, is always
represented outside the authorization service as a PAC.
It is
therefore always possible to distinguish authentication data and
authorization data, and the authorization service never uses one
type of data where another is required. In particular, the
authorization service never uses authentication data to make an
access decision.
It is up to AEFs to make trust decisions about
authentication data; an aznAPI implementation does not make trust or
authenticity judgments about the identities passed to it by AEFs.
TCB Boundary
Trust Relationships in an aznAPI System
indicates that the AEF, the aznAPI, the
ADF, the PAC Service, the authentication service, and any
authentication mechanisms used by the authentication service, are all
inside the trusted computing base (TCB) of the system and thus need to
be protected against unauthorized modification.
-
-
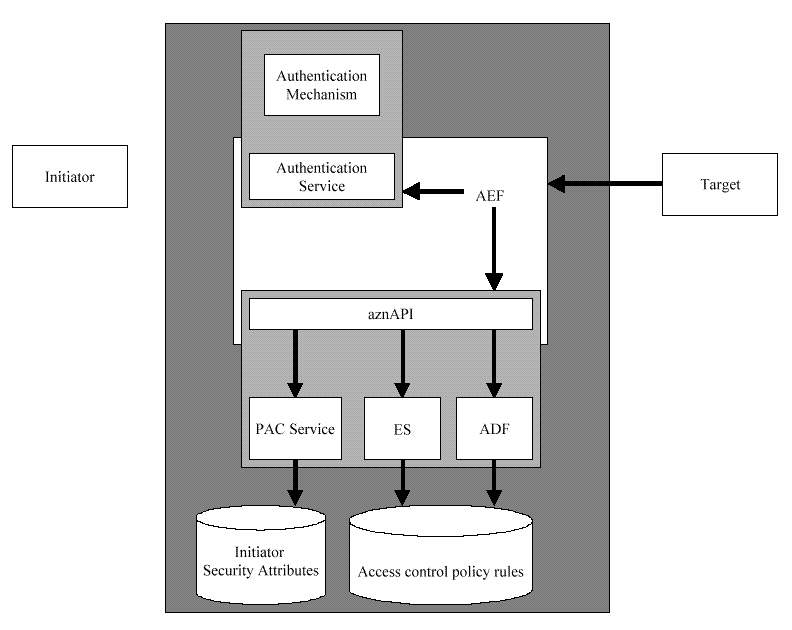
Figure: Trust Relationships in an aznAPI System
The components of the system have the following trust relationships:
-
The owner of a
target resource trusts the AEF, and implicitly the authentication and
authorization services (everything inside the outer dark gray box) to
prevent unauthorized initiators from accessing the target.
-
The
authentication service trusts its authentication mechanisms to function
correctly and provide a correct identity for the initiator.
-
The AEF
trusts the authentication service, and implicitly its authentication
mechanisms, to provide a correct, authenticated identity for the
initiator.
-
The aznAPI trusts the AEF to provide correct ACI.
-
The AEF
trusts the aznAPI, and implicitly the authorization service, to make
and return correct access decisions and to return correct PACs,
entitlements, and credentials chain privilege attributes.
-
The aznAPI
trusts its implementation (and the underlying initiator security
attribute repository) to translate initiator identities into
credentials chains correctly.
-
The aznAPI trusts the PAC service to
generate PACs from credentials chains correctly, and to return
credentials chains' privilege attributes correctly.
-
The aznAPI
implementation and the PAC service trust the security attribute
repository to contain correct information.
-
The aznAPI trusts the
authorization service's ADF (and the underlying access control policy
repository) to make correct access decisions.
-
The aznAPI trusts the
authorization service's entitlement service, or ES, and the underlying
access control policy repository, to return entitlements correctly.
-
The ADF and the ES trust the access control policy repository to
contain correct information.
Why not acquire a nicely bound hard copy?
Click here to return to the publication details or order a copy
of this publication.




